The interesting thing is progress. Previously, everything worked on steam, later it was time for internal combustion engines, but now? Today everyone is striving to switch to electrical energy. Even cars, no, no, will get an electric motor. What can I say about various gadgets.
No matter what modern electronic equipment we take, whether it is an echo sounder or a music player, a radio-controlled toy or radio player - all this requires a source for its operation nutrition. Of course, many of these devices can be connected to the network, but most of them run on batteries.
If you disassemble this battery, then there will be an anode and a cathode inside - these are electrodes, one of which is positively charged, and the other negatively. They are located inside a container, which is filled with electrolyte, and all this is in a metal case.
When the contacts are closed, the electrons begin to "run" from the electrode to the electrode - from this "running around" an electric current appears. After some time, the amount of active substance at the anode will decrease, and the number of electrons will decrease. And the electrolyte begins to conduct electricity worse. This is how the battery goes down.
What batteries are there
The content of the article
-
What batteries are there
- Battery shape
- Chemical reaction
- How to determine which batteries can be charged
- Why you can't charge a regular battery
- How to properly charge the battery
Having a common purpose, batteries differ not only in form, but also in the chemical reaction, the flow of which ensures the occurrence of an electric current inside.
Battery shape
We are all accustomed to "finger" (with the designation AA) and "little finger" (with the designation AAA). They are made in the form of a cylinder and are used in most electronic equipment.
Batteries marked C and D, presented in the form of a "barrel", are somewhat larger than the former, due to which they have a greater capacity. As a rule, they are used in flashlights, portable tape recorders and other types of devices.
No less widespread are batteries of a rectangular shape "krone".
Small disc (CR) batteries are most commonly used in miniature devices such as watches, toys, etc.
Cylinder-shaped batteries have a voltage of 1.6 volts. "Krona" is more powerful and produces 9 volts.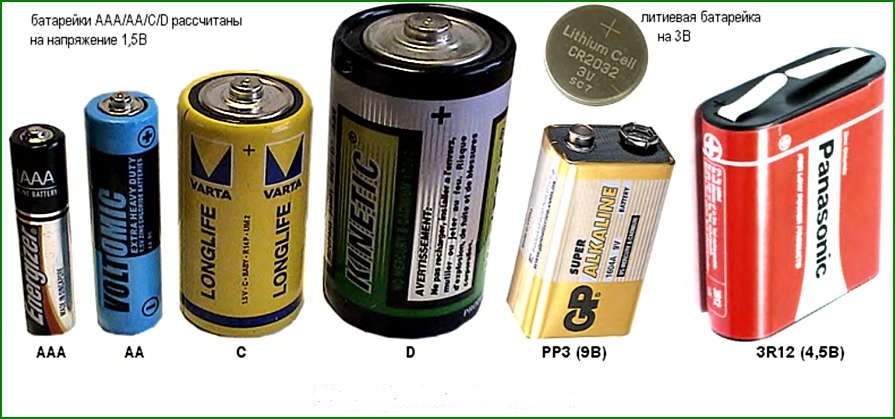
Chemical reaction
The lowest power of all are salt batteries. They have a short shelf life, no more than three years.
More powerful elements are alkaline. We are accustomed to their import name - "alkaline". They can be stored for up to five years.
The most powerful of all are the lithium batteries. They retain their working capacity for up to seven years.
How to determine which batteries can be charged
It is possible to recharge only batteries of the rechargeable type, which have a special marking. Any other batteries, whatever type they are, cannot be charged.
If you ignore the safety instructions, the following can happen:
- if you're lucky, nothing happens;
- the battery can boil and fail;
- it may overheat, which can lead to a fire or explosion;
- can short-circuit the electrical wiring.
Based on the materials used, batteries are divided into types:
- nickel metal hydride;
- nickel-cadmium;
- nickel-zinc;
- lithium-ion;
- lithium polymer.
Attention! Nickel-cadmium-based batteries have the ability to remember the amount of charge, which is why it is recommended to first discharge them to zero, and only then charge to one hundred percent. Nickel-metal hydride also have this effect, but they have it is minimal.
The size of the batteries does not stand out from other batteries. Therefore, it is difficult to distinguish them from ordinary ones. The only thing that is not among them is the button cell batteries, except for a small series, which is intended for use in hearing aids.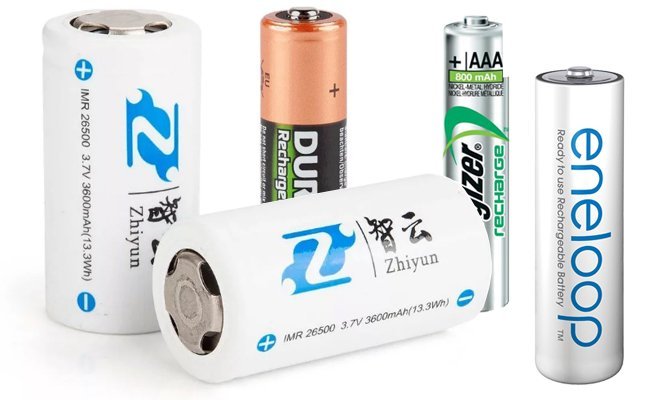
Why you can't charge a regular battery
All kinds of button-type batteries cannot be recharged, and it is better not to try to recharge others. If you see the inscription alkaline on the battery, then you shouldn't even try to charge it.
The device and principle of operation of batteries, which are intended to be used and discarded, are different from those of a rechargeable battery. The electrolyte supplies ions to the electrodes. And gradually their number becomes less and less. Therefore, the battery is discharged.
If you put a regular battery to charge, there will be no effect. It won't work again. For example, in conventional manganese and zinc batteries, the electrode is made of zinc. During work, it gradually dissolves.
Rechargeable batteries are capable of resetting the value of their electrolyte and electrodes during charging. Oxygen and hydrogen ions are generated in the charger and in the battery inside the electrolyte. And the reduction process starts, hydrogen works as a catalyst and converts the cathode into lead, and oxygen, in turn, forms lead dioxide from the anode.
How to properly charge the battery
Even such a simple matter as charging a battery requires compliance with certain safety measures:
- Before putting the battery on charge, you need to carefully read what the manufacturer recommends in the instructions supplied with the device.
- Rechargeable batteries, which are produced by modern industry, do not have the ability to remember the charge level, so there is no need to completely discharge them in order to recharge them later. The only exceptions are nickel-cadmium batteries.
- You need to use the charger at a certain temperature, if it is not more than five degrees and not lower than fifty - it is better to refrain from this.
- The charger must match the batteries. For them, it is not the charging speed that is important, but the quality. And the slower you charge, the better.
- Do not charge batteries for more than twenty-four hours. If during this time the charge is not replenished, then you can no longer try.
During charging, the battery gets very hot, do not be afraid - this is normal. But at the same time, the surface of the battery should not be hot. If these are the sensations that arise when you touch them, stop charging.