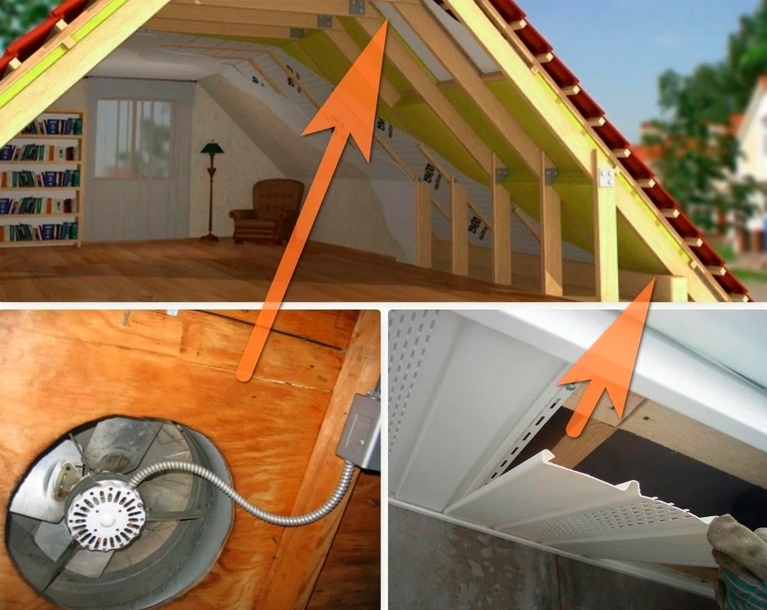
A split system is essential for a well-maintained home. Agree, there is simply no other means to withstand the heat of summer and the coolness of several weeks of the off-season. However, splits are prohibited on many city facades. So why not set up an air conditioner unit in the attic where you can't see it?
We will investigate the conditions for placing the outer part of the split system in the attic or technical room of an apartment building. And we will also consider the factors that reasonably prevent this method of installing a two-unit climate control complex.
The content of the article:
- Possibility of positioning the unit in the technical room
-
Features of installation in the attic
- What is the danger of a multi-meter height difference between blocks?
- How to reduce the risk of water hammer when there is a large difference in block levels?
- The problem of heat emission of the compressor block
- How to avoid overheating of a split unit on the technical floor?
- Optimal split with block placement in the attic
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Possibility of positioning the unit in the technical room
Non-residential premises of an apartment building, which are not part of any apartment, belong to all apartment owners of this high-rise building at the same time. This is approved by the Housing Code in the first part of Article 36.
This means that any attic, as well as technical room of an apartment building is in the common share ownership of the tenants.

From the point of view of the law, the attic is intended to accommodate communal and technical communications for household purposes, and therefore climatic equipment (i.e. air conditioners)
Article 161 of the Housing Code reflects the need to maintain favorable living conditions for all residents of a high-rise building. This premise, which is the common property of the apartment owners, must be kept in proper condition both in terms of sanitary and epidemiological welfare and fire safety.
According to the "Rules for the maintenance of housing stock" developed by Gosstroy No. 170 dated September 27, 2003, the managing organization (hereinafter referred to as UO) must ensure the temperature and humidity conditions of the attic (technical floor), excluding the formation of condensation on the enclosing structures buildings (p. 3.3.1).
Moreover, the temperature of a cold (unheated) technical room can only exceed the outside temperature by 4 ° C (p. 3.3.2).
Access to the attic is allowed only to employees of the MA and personnel of operating companies, whose equipment is located on the roof or in the attic (p. 3.3.5).
According to the above norms, they have not defined a direct prohibition on installing an element of a split air conditioner in the attic. If the MA does not provide valid objections and if 50% of the homeowners in the apartment building do not speak out against the placement of the compressor-evaporation unit (or units) in the technical floor, then such an installation will be legal.
Features of installation in the attic
Most household climatic appliances are designed for the location of the outdoor unit at a short distance from the room evaporator and literally on the street, i.e. in a "street" atmosphere. And when installing an external unit of a split-system air conditioner in the attic, you will need to take into account a number of mandatory technical nuances.
What is the danger of a multi-meter height difference between blocks?
Among the significant characteristics of each split system (in the data sheet), the maximum height and length of the freon line is given. The minimum parameters start from 5 (height) and 15 (length) meters. Longer and more distant vertical pipe line than indicated in the passport split systems, the compressor simply does not pump.
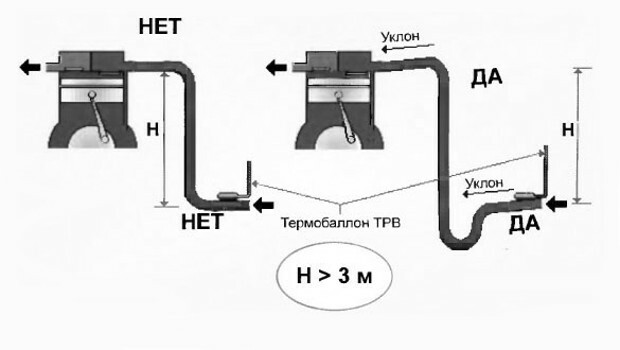
The absence of an oil-collecting loop and a downward slope will inevitably cause jamming of the air conditioning compressor due to water hammer
So, is it possible to install an outdoor unit of an air conditioner in the attic if there are more than 3 "vertical" meters between it and the indoor unit? You need to calculate the total length.
The length ratio of the copper pipes connecting the split modules vertically and horizontally is approximately 1: 3.
Those. with a horizontal distance from the indoor unit to the "street" one, for example, equal to 4 m, the vertical section of the highway will remain less than 3.5 m. Note that this is the maximum height that the compressor can handle, which means that it will have to work under a consistently high load and wear.
Another problem is the location of the split compressor module above the evaporator block at an elevation more than 3 m there is a lack of oil in the "street" block - it accumulates in the pipes near the room module.
And since room temperatures are usually higher than in the area where the compressor unit is located, the vapors refrigerant condenses in the "compressor" sector of the freon line after stopping air conditioner. Oil at the bottom, refrigerant vapors at the top of the line - ideal conditions are formed for a water hammer at the next start of the split system.
How to reduce the risk of water hammer when there is a large difference in block levels?
To avoid the formation of an oil plug in the lower section of the refrigerant line, an oil lifting loop must be installed on the ascending (suction) pipe. It is U-shaped and no more than eight pipe diameters in length.
For a ¼ ”pipe, for example, the maximum length of the oil lifting loop should not exceed 50 mm. The loop is created at the bottom of the riser.

It will not be correct to bend the copper tube under the loop, but to solder the finished loop into the pipeline. This will preserve the uniformity of the cross-section of the pipe line along its entire length.
If the vertical section of copper pipes has a length of more than 7.5 m, then the gas mixture of the refrigerant at a speed of 5 m / s (normal speed in the air conditioning system) will not be able to keep the oil film on the walls highways.
The force of gravity will "pull" the oil down, filling the oil-collecting loop entirely and again threatening a water hammer when the split system is turned on. Then you should mount two loops at a distance of 3 meters from each other (one at the bottom, the other higher along the suction pipe).
Note that the intermediate oil-lifting loop on the freon line, led to the attic or technical floor from the apartment through ventilation duct, will significantly overlap its cross-section and will prevent a full-fledged hood. If pipes are pulled into the attic through the regular ventilation channel from two split systems, then air exchange in the apartment may stop altogether.

It is highly discouraged to pull a vertical pipeline between the split-system blocks to a height of more than 25 m, even with a powerful compressor capable of "working" with a pipeline of such length. Refrigerant pressure loss in the line will be too high
In addition to installing the oil-collecting loop, all horizontal sections of the pipes must be set with an inclination in the direction of the refrigerant movement. Those. the slope on the pipe leading to the compressor block should be directed towards this module, and on the outlet pipe - directed from it down to the evaporator.
The problem of heat emission of the compressor block
In fact, in the air cooling mode, the split system takes heat from the “indoor” unit, transfers it outside the apartment and throws it out through the “street” unit.
So that the work on cooling the room takes place at the intensity set by the user (set temperature mode), the air mass in the sector of dumping excess heat must correspond to certain parameters.
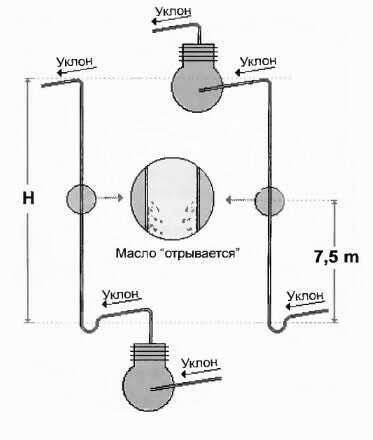
The location of the oil collector loops every 3-4 meters will protect the air conditioning pipe line from gravitational oil drainage to its lowest point
The condenser built into the outdoor split-module will work normally if there is more than 17 cubic meters of air atmosphere per one kilowatt of its thermal power at the location of the device. For example, the condenser of the split-system "nine" with a heating power of 2.8 kW (indicated in the passport) needs at least 48 m3 air per hour to release heat.
Considering that the height of the technical room in an apartment building does not exceed 1.6 m (sometimes it is only 1.2 m), then one “street” block “nine” installed in the technical room will need 30 m2 area. If the attic is not higher than 1.2 m, then 40 m will be needed2 its area.
With an insufficiently effective air change in the attic, its atmosphere will warm up to more than 40OC, because of what compressor block will overheat. Then the overheating protection will work, which will turn off the split system and will not allow it to be turned on until the module with the compressor has cooled.
Therefore, in the hot summer, and with several split-system modules actively working on the technical floor, their protection will work hourly. As a result, maintaining an acceptable microclimate in residential premises will be a rather difficult task.
How to avoid overheating of a split unit on the technical floor?
Attic vents and dormers are designed for natural air exchange. Air enters the technical floor from the living quarters from below, through ventilation openings and gaps at the eaves of the roof structure.
Slot vents and technical ventilation openings are not capable of providing sufficient changeable air mass in the attic with several actively operating compressor blocks of air conditioners.

It works on the principle of suction of additional air volume due to the reduced pressure in the internal mixing chamber.
Here it is required forced air supply, however, equipping the technical floor with electromechanical ventilation units is not always effective and unambiguously expensive. There is a better solution - equipping the attic with a low pressure ejector that can speed up the ventilation process many times without consuming electricity.
For example, the EI-1 ejector of the Tula enterprise "Promventilyatsiya-Servis" provides a turnover of 1000 cubic meters of air per hour.
Those. Such an ejector is effective for ventilation of a technical floor with 15-17 external blocks of split-systems "nines" simultaneously operating for cooling. Note that the ejector structure is quite long - the EI-1 type has a length of 2.75 m.
Optimal split with block placement in the attic
Several living quarters of the apartment will need conditioned air for both cooling and heating. However, equip it with several two-unit air conditioners with the removal of external modules into the attic the room will be difficult, even if the apartment is on the top floor (i.e. located under the attic directly).
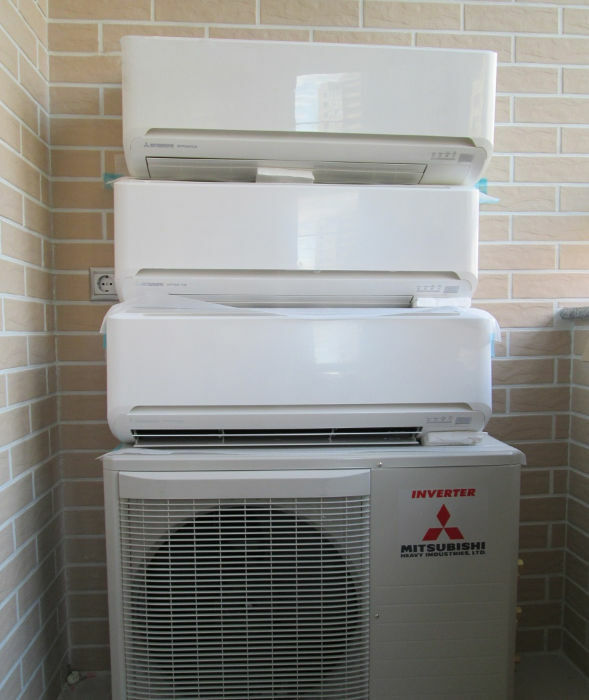

Since paired pipes go from its compressor module to each "indoor" unit separately, the capacity of the outdoor unit must be known to be high. It is important!
It's simple: the paired pipelines of several split systems will completely block the exhaust duct. To prevent this from happening, you will have to drill the ceiling plate for each pair of pipes or prepare one common hole.
Perhaps an effective option would be to equip living quarters with an air conditioning unit with one external and several indoor units - multisplit system. Although you still have to pull several independent freon lines vertically upwards, it will still be easier to cool a single compressor module.
You will need a sufficiently powerful multisplit of a well-known brand, capable of working with a large height difference between modules and pump a pipeline more than 50 meters long (taking into account the vertical: horizontal ratio as 1:3).
Given the low intensity of natural ventilation of the technical floor, it is better to use a compressor split unit with a centrifugal fan, which cools the compressor more efficiently than an axial ventilation installation.
To bring a "street" split-module to the attic with pipes in the ventilation from the apartments located on the penultimate the level of a high-rise building or lower - this should not be done, since air exchange in living quarters is definitely will get worse.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
How to fix the problem with overheating of the air conditioner in the technical floor:
How an oil lifting loop is built into the split system pipeline:
Among the technical tasks for the installation of a split air conditioner in the technical floor, the problem of condensate drainage is the simplest - the drain pipe is led out at a slope into the pipe of the drain pipe. As for the peculiarities of the operation of the "attic" compressor block, it will be difficult to flush it, since the traditional pressure washer is not applicable here.
Perhaps a better option would be to place a split-system street module on the roof of the building. This will allow avoiding difficulties both with overheating of the air conditioner due to insufficient air exchange, and with its periodic cleaning.
Do you want to share your personal experience in the arrangement of an external split unit in the attic? Do you have useful information on the topic of the article? Please write your comments in the sector below for feedback, post a photo on the topic of the article, ask questions.


