Financing the heating season makes up a significant part of the budget spent on housing maintenance. Knowing the price and average gas consumption for heating a house 150 m2, you can fairly accurately determine the cost of heating the premises. These calculations are easy to perform on your own without paying for the services of heating engineers.
You will learn all about the gas consumption standards and methods for calculating the consumption of blue fuel from the article we have presented. We will tell you about how much energy is required to compensate for the heat losses of the house during the heating season. Let us show you what formulas should be used in calculations.
The content of the article:
-
Heating country cottages
- Calculation of the amount of heat to be compensated
- Ways to minimize heat loss
-
Calculation of the required volume of gas
- Boiler selection rule
- Heat release formula
- Gas consumption calculation example
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Heating country cottages
When calculating the gas consumption that is required to heat a house, the most difficult task will be
calculation of heat loss, which must fully compensate for the heating system during operation.The complex of heat losses depends on the climate, the structural features of the building, the materials used and the parameters of the ventilation system.
Calculation of the amount of heat to be compensated
The heating system of any building must compensate for its heat loss Q (W) during the cold period. They happen for two reasons:
- heat exchange through the perimeter of the house;
- heat loss due to the ingress of cold air through the ventilation system.
Formally, heat loss through the wall and roof QTP can be calculated using the following formula:
QTP = S * dT / R,
where:
- S - surface area (m2);
- dT - temperature difference between indoor and outdoor air (° С);
- R - indicator of resistance to heat transfer of materials (m2 * ° С / W).
The latter indicator (which is also called the "coefficient of thermal resistance") can be taken from the tables attached to the building materials or products.
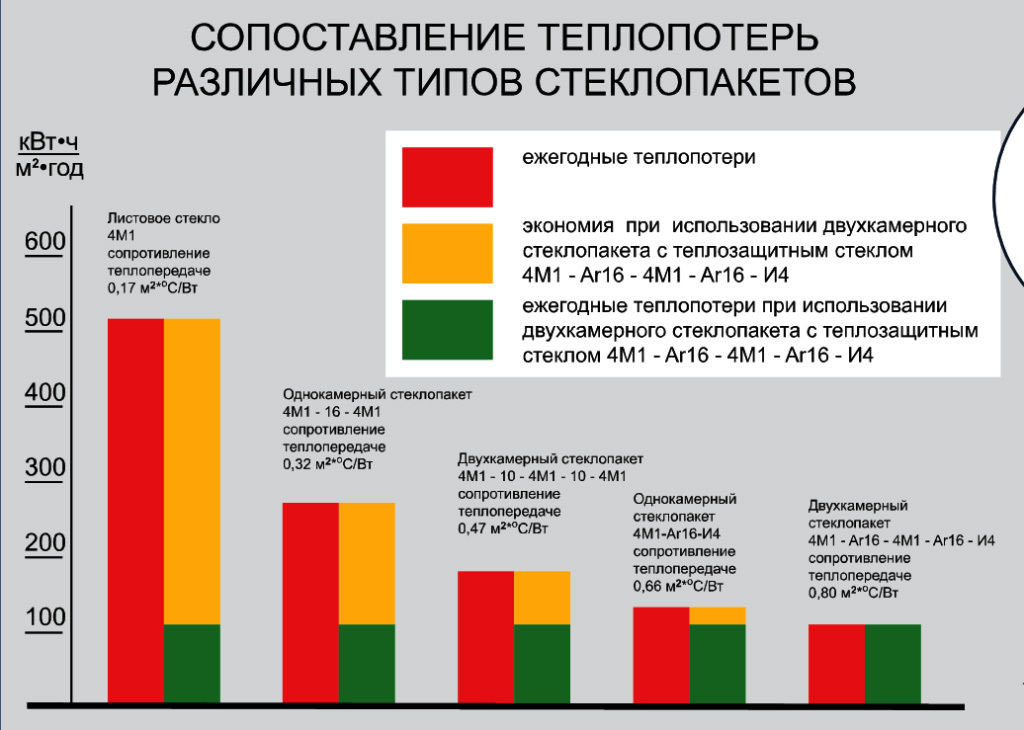
The rate of heat loss at home significantly depends on the type of double-glazed window. The high price of insulated windows will be justified due to fuel economy
Example. Let the outer wall of the room have an area of 12 m2, of which 2 m2 occupies the window.
Heat transfer resistance indicators are as follows:
- Aerated concrete blocks D400: R = 3.5.
- Double-glazed window unit with argon “4M1 - 16Ar - 4M1 - 16Ar - 4I”: R = 0.75.
In this case, at room temperature “+ 22 ° С”, and street temperature - “–30 ° С”, the heat loss of the outer wall of the room will be:
- QTP (wall) = 10 * (22 - (- 30)) / 3.5 = 149 W:
- QTP (window) = 2 * (22 - (- 30)) / 0.75 = 139 W:
- QTP = QTP (wall) + QTP (window) = 288 W.
This calculation gives the correct result, provided there is no uncontrolled air exchange (infiltration).
It can occur in the following cases:
- The presence of structural defects, such as a loose fit of window frames to the walls or delamination of the insulation material. They need to be eliminated.
- Aging of a building, resulting in chips, cracks or voids in the masonry. In this case, it is necessary to enter correction factors in the indicator of the resistance to heat transfer of materials.
In the same way, it is necessary to determine the heat loss through the roof if the object is located on the top floor. Through the floor, any significant loss of energy occurs only in the case of an unheated, vented basement, such as a garage. In the ground, the heat practically does not go away.
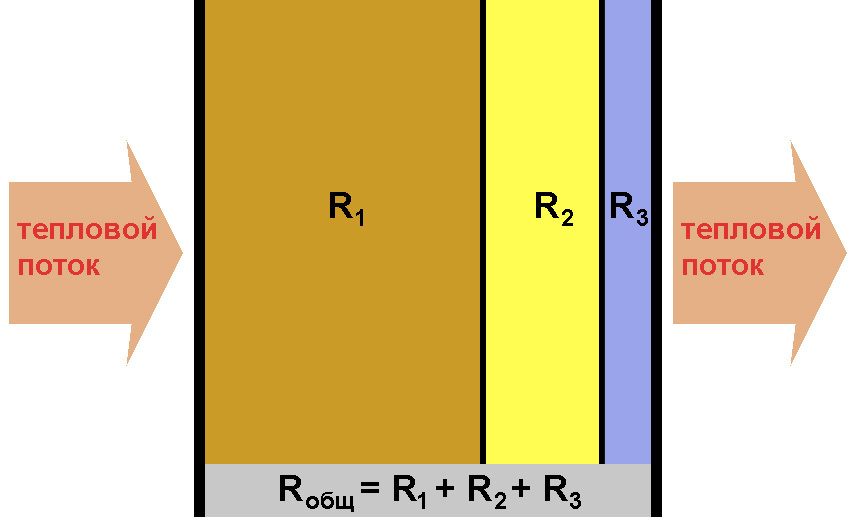
To calculate the resistance to heat transfer of multilayer materials, it is necessary to summarize the indicators of the individual layers. Usually, only the most non-conductive materials are taken for calculations.
Consider the second reason for heat loss - building ventilation. Energy consumption for heating the supply air (Qin) can be calculated using the formula:
Qin = L * q * c * dT, where:
- L - air consumption (m3 / h);
- q - air density (kg / m3);
- c - specific heat capacity of the incoming air (kJ / kg * ° С);
- dT - temperature difference between indoor and outdoor air (° С).
Specific heat capacity of air in the temperature range of interest to us [–50.. +30 ° С] is equal to 1.01 kJ / kg * ° С or in terms of the dimension we need: 0.28 W * h / kg * ° С. Air density depends on temperature and pressure, but for calculations, you can take a value of 1.3 kg / m3.
Example. For a room of 12 m2 with the same temperature difference as in the previous example, the heat loss due to the operation of ventilation will be:
Qin = (12 * 3) * 1.3 * 0.28 * (22 - (- 30)) = 681 W.
Designers take air flow in accordance with SNiP 41-01-2003 (in our example, 3 m3 / h at 1 m2 living room area), but this value can be significantly reduced by the owner of the building.
In total, the total heat loss of the model room is:
Q = QTP + Qin = 969 W.
To calculate heat loss per day, week or month, you need to know the average temperature for these periods.
From the above formulas it can be seen that the calculation of the volume of consumed gas both for a short period of time and and for the entire cold season, it is necessary to carry out taking into account the climate of the area where the heated an object. Therefore, it is possible to use well-proven standard solutions only for similar environmental conditions.
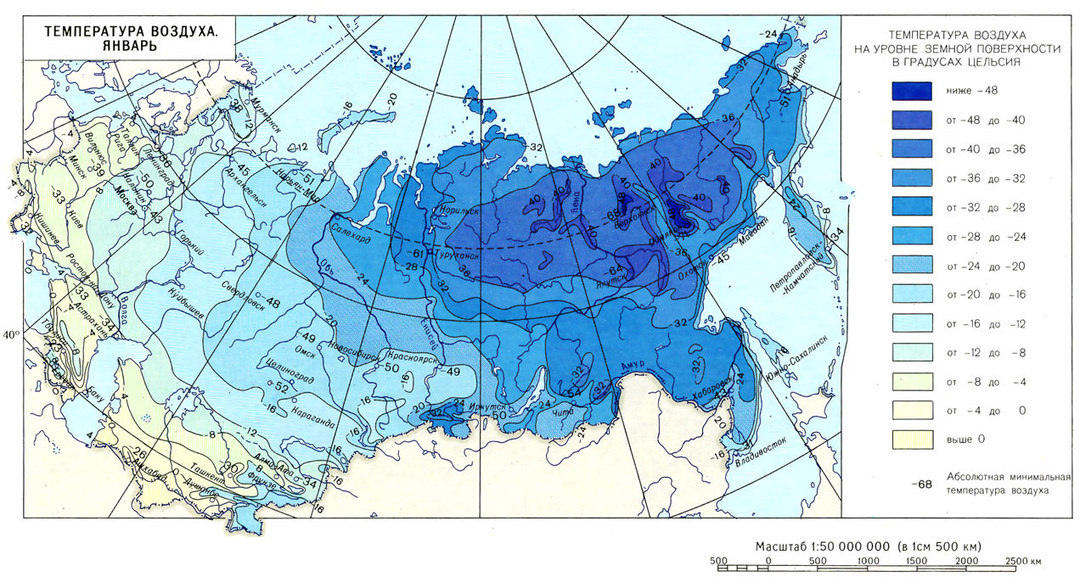
To determine similar climatic parameters, you can use maps of average monthly temperatures in winter. They can be easily found on the Internet.
With the complex geometry of the house and the variety of materials used in its construction and insulation, you can use the services of specialists to calculate the required amount of heat.
Ways to minimize heat loss
The cost of heating a house is a significant part of the cost of its maintenance. Therefore, it is reasonable to perform some types of work aimed at reducing heat loss by ceiling insulation, the walls of the house, floor insulation and related designs.
Application outside insulation schemes and from the inside of the house can significantly reduce this indicator. This is especially true for old buildings with heavy wear of walls and floors. The same expanded polystyrene plates allow not only to reduce or completely eliminate freezing, but also minimize air infiltration through the protected coating.
Also, significant savings can be achieved if summer areas of the house, such as verandas or the attic floor, are not connected to heating. In this case, there will be a significant reduction in the perimeter of the heated part of the house.

Using the attic floor only in the summer significantly saves the cost of heating the house in winter. However, in this case, the ceiling of the upper floor must be well insulated.
If you strictly follow the ventilation standards of the premises, which are prescribed in SNiP 41-01-2003, then the heat loss from air exchange will be higher than from freezing of the walls and roof of the building. These rules are binding on designers and any legal entity if the premises are used for the production or provision of services. However, the tenants of the house can, at their discretion, reduce the values indicated in the document.
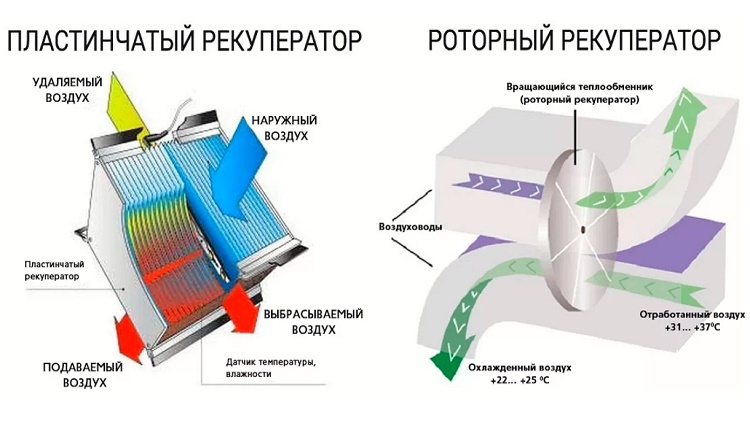
In addition, heat exchangers can be used to heat the cold air coming from the street, rather than appliances that consume electricity or gas. So an ordinary plate recuperator can save more than half of the energy, and a more complex device with a heat carrier - about 75%.
Calculation of the required volume of gas
The combustible gas must compensate for the heat loss. For this, in addition to the heat loss of the house, it is necessary to know the amount of energy released during combustion, which depends on the efficiency of the boiler and the calorific value of the mixture.
Boiler selection rule
The choice of the heater must be carried out taking into account the heat loss at home. It should be enough for the period when the annual minimum temperature is reached. In the passport of the floor or wall-mounted gas boiler this is the responsibility of the “rated thermal power” parameter, which is measured in kW for household appliances.
Since any structure has thermal inertia, then to calculate the required boiler power for the minimum temperature, the indicator of the coldest five-day period is usually taken. For a specific area, it can be found in the organizations involved in the collection and processing of meteorological information, or from Table 1. SNiP 23-01-99 (column No. 4).
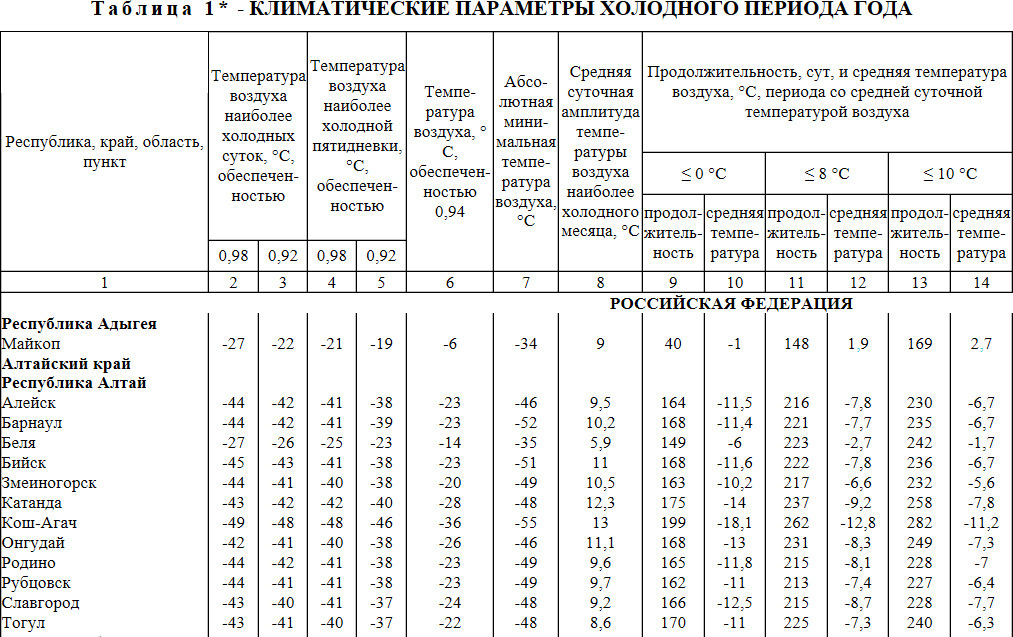
Fragment of table 1 from SNiP 23-01-99. With the help of it, you can obtain the necessary data on the climate of the area where the heated object is located.
If the boiler power exceeds the indicator sufficient for heating the room, then this does not lead to an increase in gas consumption. In this case, the equipment downtime will be longer.
Sometimes there is a reason to choose a boiler with a slightly lower capacity. Such devices can be significantly cheaper both in purchase and in operation. However, in this case, it is necessary to have a spare heat source (for example, a heater complete with a gas generator), which can be used in severe frosts.
The main indicator of the efficiency and economy of the boiler is the efficiency. For modern household equipment, it is in the range from 88 to 95%. The efficiency is registered in the device passport and is used when calculating gas consumption.
Heat release formula
To correctly calculate the consumption of natural or liquefied gas for heating a house with an area of about 150 m2 it is necessary to find out one more indicator - the calorific value (specific heat of combustion) of the supplied fuel. According to the "SI" system, it is measured in J / kg for liquefied gas or in J / m3 for natural.
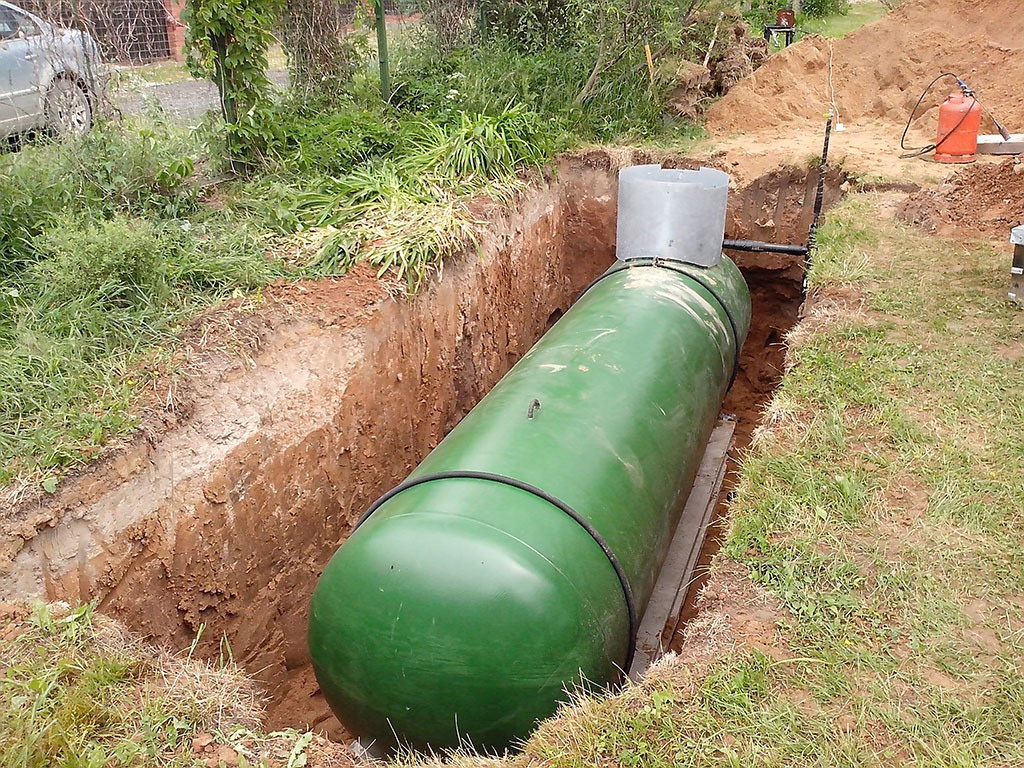

Gas holders (tanks for storing liquefied gas) are characterized in liters. To find out how much fuel will enter into it in kilograms, you can apply a ratio of 0.54 kg / 1 l
There are two values of this indicator - net calorific value (Hl) and higher (Hh). It depends on the moisture and temperature of the fuel. When calculating, take the indicator Hl - and you need to find out from the gas supplier.
If there is no such information, then the following values can be taken in the calculations:
- for natural gas Hl = 33.5 mJ / m3;
- for liquefied gas Hl = 45.2 mJ / kg.
Taking into account that 1 mJ = 278 W * h, we obtain the following calorific value:
- for natural gas Hl = 9.3 kW * h / m3;
- for liquefied gas Hl = 12.6 kW * h / kg.
The volume of gas consumed for a certain period of time V (m3 or kg) can be calculated using the following formula:
V = Q * E / (Hl * K), where:
- Q - heat loss of the building (kW);
- E - duration of the heating period (h);
- Hl - minimum calorific value of gas (kW * h / m3);
- K - boiler efficiency.
For liquefied gas, the dimension Hl is equal to kW * h / kg.
Gas consumption calculation example
For example, let's take a typical prefabricated timber frame two-story cottage. Region - Altai Territory, g. Barnaul.

The size of the cottage is 10 x 8.5 m. The slope of the gable roof is 30 °. This project is distinguished by a warm attic, a relatively large glazing area, the absence of a basement and protruding parts of the house.
Step 1. Let's calculate the main parameters of the house for calculating heat loss:
- Floor. In the absence of a ventilated basement, losses through the floor and foundation can be neglected.
- Window. Double-glazed window unit “4M1 - 16Ar - 4M1 - 16Ar - 4I”: Ro = 0.75. Glazing area So = 40 m2.
- Walls. The area of the longitudinal (side) wall is 10 * 3.5 = 35 m2. The area of the transverse (front) wall is 8.5 * 3.5 + 8.52 * tg(30) / 4 = 40 m2. Thus, the total area of the building perimeter is 150 m2, and taking into account the glazing, the desired value Ss = 150 - 40 = 110 m2.
- Walls. The main insulating materials are glued laminated timber, 200 mm thick (Rb = 1.27) and basalt insulation, 150 mm thick (Ru = 3.95). The total indicator of the resistance to heat transfer for the wall Rs = Rb + Ru = 5.22.
- Roof. Insulation completely repeats the shape of the roof. Roof area without overhangs Sk = 10 * 8.5 / cos (30) = 98 m2.
- Roof. The main thermal insulation materials are lining, 12.5 mm thick (Rv = 0.07) and basalt insulation, 200 mm thick (Ru = 5.27). The total indicator of the resistance to heat transfer for the roof Rk = Rv + Ru = 5.34.
- Ventilation. Let the air flow be calculated not by the area of the house, but taking into account the requirements to ensure a value of at least 30 m3 per person per hour. Since 4 people permanently live in the cottage, then L = 30 * 4 = 120 m3 / h
Step. 2. Let's calculate the required boiler power. If the equipment has already been purchased, then this step can be skipped.
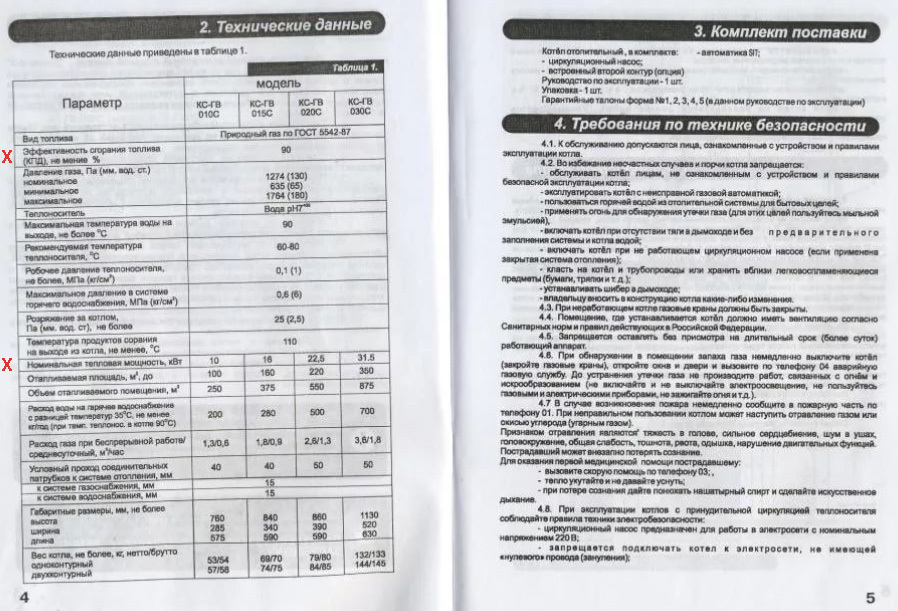
For our calculations, it is necessary to know only two indicators of a gas boiler: efficiency and rated power. They must be registered in the passport of the device.
The temperature of the coldest five-day period is “–41 ° C”. We will take the comfortable temperature as “+24 ° С”. Thus, the average temperature difference over this period will be dT = 65 ° C.
Let's calculate the heat loss:
- through windows: Qo = So * dT / Ro = 40 * 65 / 0.75 = 3467 W;
- through the walls: Qs = Ss * dT / Rs = 110 * 65 / 5.22 = 1370 W;
- through the roof: Qk = Sk * dT / Rk = 98 * 65 / 5.34 = 1199 W;
- due to ventilation: Qv = L * q * c * dT = 120 * 1.3 * 0.28 * 65 = 2839 W.
The total heat loss of the whole house during the cold five-day period will be:
Q = Qo + Qs + Qk + Qv = 3467 + 1370 + 1199 + 2839 = 8875 W.
Thus, for this model house, you can choose a gas boiler with a maximum heat output of 10-12 kW. If gas is also used to provide hot water supply, then you will have to take a more efficient device.
Step 3. Let's calculate the duration of the heating period and the average heat loss.
The cold season, when heating is needed, is understood as a season with average daily temperatures below 8-10 ° C. Therefore, for calculations, you can take either columns No. 11-12 or columns No. 13-14 of Table 1 SNiP 23-01-99.
This choice remains with the owners of the cottage. At the same time, there will be no significant difference in the annual fuel consumption. In our case, we will focus on the period with the temperature below “+10 ° С”. The duration of this period is 235 days or E = 5640 hours.

With centralized heating, the heating medium supply is switched on and off according to the established standards. One of the advantages of a private house is the launch of heating mode at the request of residents
The heat loss of the house for the average temperature for this period is calculated in the same way as in step 2, only the parameter dT = 24 - (- 6.7) = 30.7 ° C. After carrying out the calculations, we get Q = 4192 W.
Step 4. Let's calculate the volume of consumed gas.
Let the boiler efficiency K = 0.92. Then the volume of consumed gas (with averaged indicators of the minimum calorific value of the gas mixture) for the cold period of time will be:
- for natural gas: V = Q * E / (Hl * K) = 4192 * 5640 / (9300 * 0.92) = 2763 m3;
- for liquefied gas: V = Q * E / (Hl * K) = 4192 * 5640 / (12600 * 0.92) = 2040 kg.
Knowing gas prices, you can calculate the financial costs of heating.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Reducing gas consumption by eliminating errors associated with house insulation. Real example:
Gas consumption at a known thermal power:
All calculations of heat loss can be carried out independently only when the heat-saving properties of the materials from which the house is built are known. If the building is old, then first of all it is necessary to check it for freezing and eliminate the identified problems.
After that, using the formulas presented in the article, you can calculate the gas consumption with high accuracy.
Please leave your comments in the feedback box below. Post photos on the topic of the article, ask questions on points of interest. Share useful information that may be useful to visitors to our site.