Surely you have already repeatedly heard that gas boilers have no competitors in terms of efficiency. But, you see, healthy skepticism never hurts - as they say, trust, but verify. Therefore, before deciding on the installation and operation of gas equipment, you should thoroughly calculate and think over everything.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the calculation steps and formulas by which the gas consumption for heating a house is determined 100 m2 taking into account all significant factors. After reviewing the calculations, you can draw your own conclusion on how profitable it is to use blue fuel as a source of thermal energy.
The content of the article:
- Heat load and gas flow formulas
-
Gas consumption by specific examples
- Heat load calculation
- Main gas consumption
- How much propane-butane is needed for the heating season
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Heat load and gas flow formulas
Gas consumption is conventionally denoted by the Latin letter V and is determined by the formula:
V = Q / (n / 100 x q), where
Q is the heat load for heating (kW / h), q is the calorific value of the gas (kW / m³), n is the efficiency of the gas boiler, expressed as a percentage.
Main gas consumption is measured in cubic meters per hour (m³ / h), liquefied gas - in liters or kilograms per hour (l / h, kg / h).
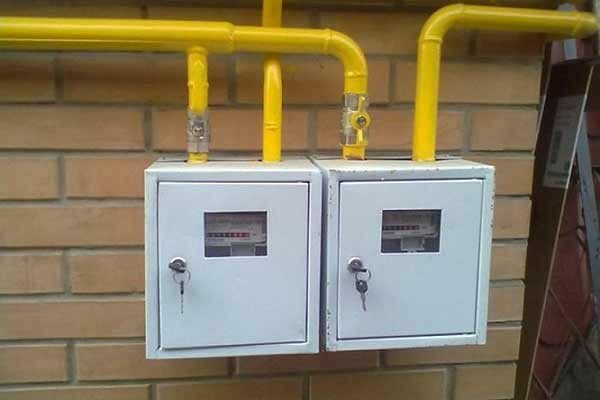

Gas consumption is calculated before designing a heating system, choosing a boiler, energy carrier, and then easily controlled using meters
Let's consider in detail what the variables in this formula mean and how to define them.
The concept of "heat load" is given in the federal law "On heat supply". Changing the official wording a little, let's just say that this is the amount of heat energy transferred per unit of time to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
In the future, we will also use the concept of "thermal power", therefore, at the same time, we will give its definition in relation to our calculations. Thermal power is the amount of thermal energy that a gas boiler can produce per unit of time.
The heat load is determined in accordance with MDK 4-05.2004 by means of heat engineering calculations.
Simplified formula:
Q = V x ΔT x K / 860.
Here V is the volume of the room, which is obtained by multiplying the height of the ceiling, the width and length of the floor.
ΔT is the difference between the air temperature outside the building and the required air temperature in the heated room. For calculations, the climatic parameters given in SP 131.13330.2012 are used.

To obtain the most accurate gas consumption indicators, formulas are used that even take into account the location of the windows - the sun's rays warm the room, reducing heat loss
K is the heat loss coefficient, which is the most difficult to determine precisely due to the influence of many factors, including the number and position of external walls in relation to the cardinal points and the wind regime in winter period; number, type and size of windows, entrance and balcony doors; the type of building and thermal insulation materials used and so on.
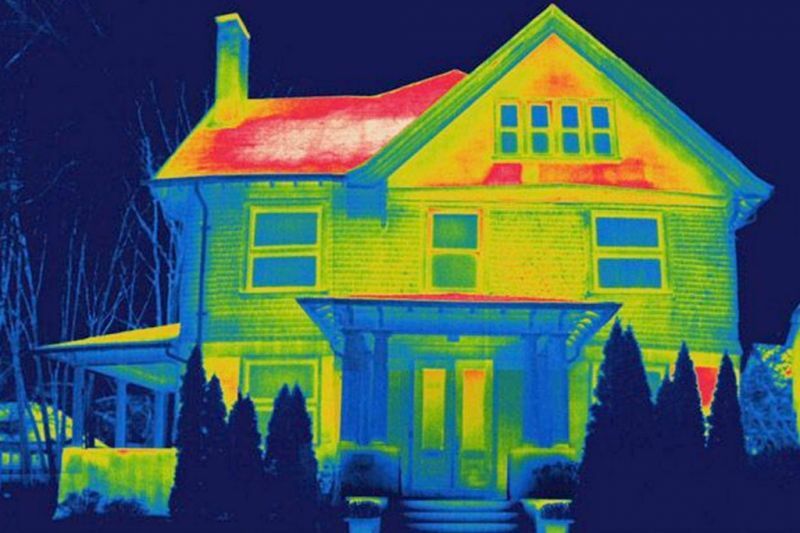

On the enclosing structures of the house there are areas with increased heat transfer - cold bridges, due to which fuel consumption can significantly increase
If it is necessary to perform a calculation with an error within 5%, it is better to conduct a thermal audit of the house.
If the requirements for the calculations are not so stringent, you can use the average values of the heat loss coefficient:
- increased degree of thermal insulation - 0.6-0.9;
- medium thermal insulation - 1-1.9;
- low thermal insulation - 2-2.9;
- lack of thermal insulation - 3-4.
Double brickwork, small windows with three-chamber double-glazed windows, insulated roofing system, strong foundation, thermal insulation using materials with low thermal conductivity - all this indicates the minimum heat loss coefficient of your home.
With double masonry, but with normal roofing and double glazed windows, the coefficient rises to average values. The same parameters, but single brickwork and a simple roof are a sign of low thermal insulation. Lack of thermal insulation is typical for country houses.
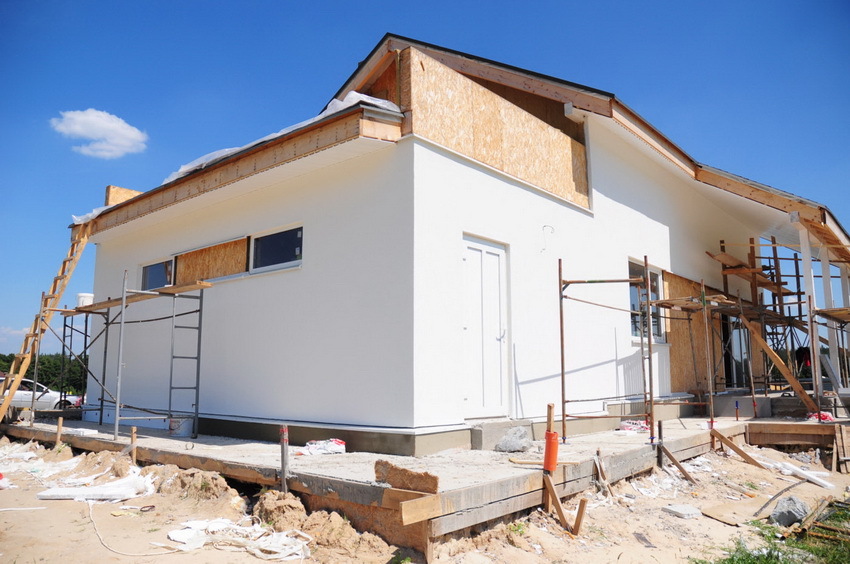

It is worth taking care of saving thermal energy already at the stage of building a house by performing insulation of walls, roof and foundation and installing multi-chamber windows
Having chosen the value of the coefficient that most closely matches the thermal insulation of your house, we substitute it into the formula for calculating the heat load. Next, using the formula, we calculate gas consumption to maintain a comfortable microclimate in a country house.
Gas consumption by specific examples
To determine what the natural gas consumption will be when heating a one-story house of 100m2, first you need to determine the heat load.
Heat load calculation
To obtain the most accurate data on the heated volume of the house, the volume of each room and auxiliary rooms where it is necessary to maintain heat is calculated separately. Length and width measurements are taken along the skirting boards using a standard or laser tape measure.
We will do it easier: we take the height of the ceilings as 2.5 meters, multiply it by the indicated area and get the volume of the house V = 250 m3.
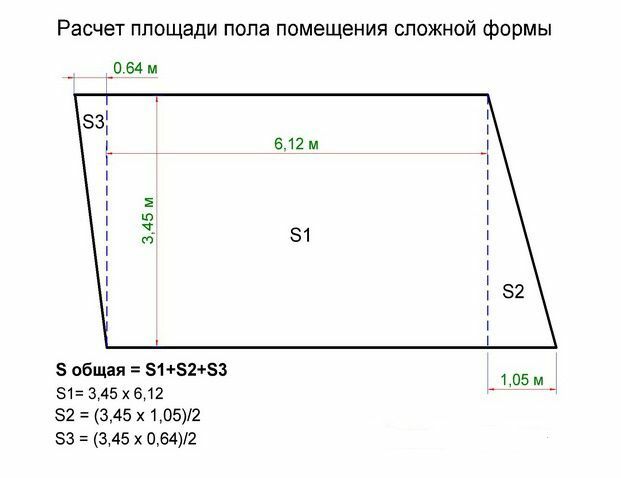
If the room has a complex architectural shape, it is divided into rectangles, triangles, circles, the area of each of them is calculated and summed up
To determine ΔT, column 6 in table 3.1 of SP 131.13330.2012 is used. The air temperature of the coldest period is indicated here, calculated based on the average monthly temperatures.
We find the name of the settlement where the heated object is located. Let's say this is Bryansk, therefore, the desired value is -12 ° C. The temperature in living rooms according to GOST R 51617-2000 should be within 18-24 ° C. Taking an average value of 22 ° C, we get ΔT = 34 ° C.
We determine the degree of thermal insulation of the house and apply the appropriate coefficient. In the face of rising heat carrier prices, most homeowners are looking to improve heating energy efficiency by improving thermal insulation of your home, therefore, it is quite reasonable to apply the first indicator of the average degree of thermal insulation, which is equal to 1.
We summarize all the values according to the formula:
250 m3 × 34 ° C × 1/860 = 9.88 kW / h.
We apply the rule of rounding to the nearest integer and get Q = 10 kW / h.

Do not neglect automatic control - set different heating modes for night and day time to provide a comfortable microclimate regardless of the temperature outside the window and at the same time save up to 30% gas
Recall that we have only done heat engineering calculation at home and now the next step is the calculation of gas consumption. But for now, it will be appropriate to make a small digression and clarify that the heating load can be calculated in a simplified way.
notice, that gas boiler power can be calculated for a specific object, taking into account all the technical nuances. According to averaged data, there is 100 W / h of thermal energy for each meter of standard living space. Therefore, for a house with an area of 100 m2 this figure will be 100 W / h × 100 m2 = 10,000 W / h or 10 kW / h.
In this case, calculations using the formula and the simplified method gave the same result, but this is not always the case, and the difference often reaches 20% or more. Moreover, heating engineers recommend buying turbocharged and atmospheric boilers always with a margin of 20-25% with the expectation of the possibility of covering heat losses on days with critically low temperatures.
Main gas consumption
For the calculation, you need to know the efficiency of the gas boiler. You can see it in the specifications stated in the accompanying documentation. We will choose the model that is suitable for the house of the specified area.
The main selection criterion will be the heat output of the unit. Its value is very close to the value of the heat load and can be calculated using the same formula, but the temperature of the temperature itself is taken into account for the calculation. cold five days or a multiplying factor of 1.3 is applied, because the boiler must have enough power to maintain heat in the house even in the most severe frosts.
Therefore, for heating 100 m2 a boiler with a capacity of about 13 kW is required. Efficiency (n) of many models wall mounted gas boilers, for example units of the NEVA brand, is 92.5%. We will use this value in our calculations.

Due to the design features of the combustion chamber, increased efficiency of heat exchangers, the use of latent heat of water vapor, the efficiency of modern gas boilers exceeds 90%
The calorific value, or, in other words, the specific heat of combustion (q) depends on the type of gas used. What kind of gas is supplied to your home, it is better to check with the gas supply company.
By default, we will substitute in the formula the rounded value corresponding to the G20 gas with a net calorific value of Hi, namely 9.5 kWh / m³. Pay attention to the units of measurement - kilowatts are used, not megajoules.
All the necessary values are determined and it remains to reduce them to the formula:
V = 10 / (92.5 / 100 × 9.5). V = 1.1 m³ / h.
Thus, the consumption of main gas when heating a house with an area of 100 m2 with a ceiling height of 2.5 meters, it is just over 1.1 cubic meters per hour. A day, respectively, 24.2 cubic meters.
Now it is easy to find out how much gas will be required for the entire heating season. According to state regulations, during the heating season, the average daily outdoor temperature does not exceed 8 ° C. In the middle lane, this period lasts from October 15 to April 15 (183 days).
Since there are significant temperature fluctuations at this time, the daily gas consumption is divided by 2 and then multiplied by 183. That is, about 2214.3 cubic meters of main gas will be required for the heating season.
How much propane-butane is needed for the heating season
Modern gas boilers are designed to use not only mains gas, but also liquefied gas. To stock up on the required volume of fuel, they use not ordinary gas cylinders, but more capacious tanks - gasholders.
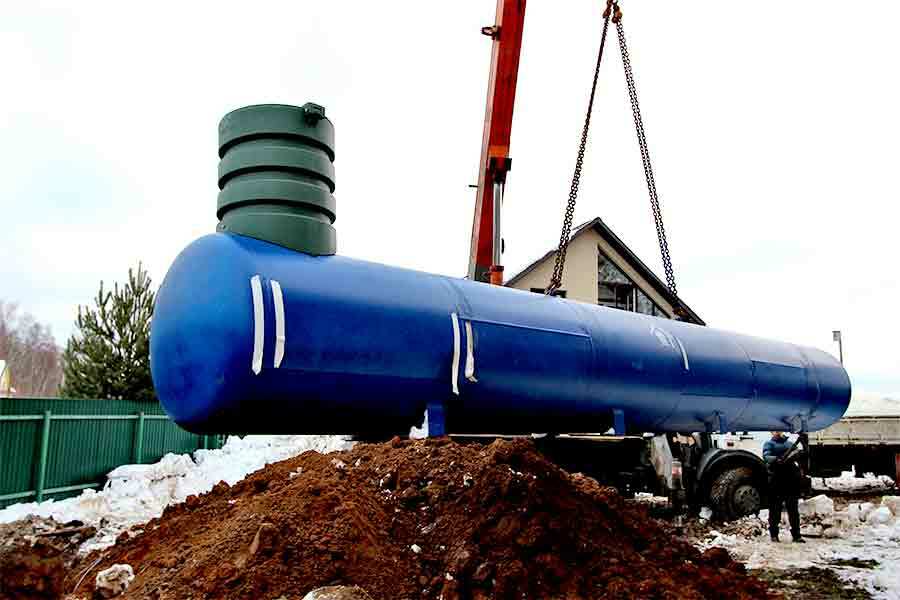

The use of gas tanks solves the problem of storing liquefied hydrocarbon fuel, sufficient to heat a house of 100 sq. m, throughout the entire heating season in a temperate climatic zone
When calculating the consumption of liquefied gas required for heating a house of 100m2, the same technique is used, but the values of some variables in the formula change.
A liquefied propane-butane mixture is supplied for household needs.
Its heating value is 12.8 kW / kg. We substitute this parameter into the formula and we get:
V = 10 / (92.5 / 100 × 12.8). V = 0.8 kg / h.
When operating on liquefied fuel, the efficiency of the equipment decreases, so the gas consumption increases by about 10% and amounts to 0.88 kg / h per day. The correction may be different for your boiler model. The specific value is indicated in the accompanying documentation.
Now we calculate the required amount of gas for the heating season: 0.88 × 24 × 183 = 3865 kg. This value must also be divided by 2 due to temperature fluctuations. The final result: 1932.5 kg of propane-butane are required for the heating season.
It will be helpful to convert kilograms to liters. Based on the reference data, 540 grams of liquefied propane-butane mixture corresponds to 1 liter. That is, 3578 liters of liquefied gas will be required for the entire heating season.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
You are economical with thermal energy, but your neighbor still has less consumption? The author of the video decided to share his own experience of using LPG for home heating. Perhaps this information will be useful to you.
Can a thermostat and a temperature sensor help to significantly reduce gas costs during the heating season? The video demonstrates how this happens in practice.
To determine the upcoming gas consumption for heating, a higher education is not required. Knowing how the simplest mathematical operations are performed, you will calculate the required parameters with an acceptable error.
Along the way, you will be able to identify weak points in your home, minimize heat losses, exclude heat leakage to the outside and, as a result, take advantage of all the advantages of blue fuel.
Please comment on the information provided by us with calculation balls and formulas for determining the gas flow rate. You can share useful information on the topic of the article, ask a question or post a photo in the block below. It is possible that your recommendations will be useful to site visitors.


