Gas is not only an affordable fuel, but also an extremely explosive substance. Therefore, it is so important that each gasified facility meets safety requirements. Do you agree? After all, if a high temperature rises on the gas pipeline section (when something ignites) and the gas ignition limit is reached, then explosion is inevitable.
A thermal shut-off valve on the gas pipeline will help prevent such a development of the situation. This device cuts off the gas supply in the event of a fire, which means it eliminates the risk of explosion. Next, we will tell you how such valves are arranged, what types there are and how to properly install them on gasified objects.
The content of the article:
-
Why are thermal shut-off valves needed?
- The purpose of the thermal shut-off valve
- Where is the thermal shut-off valve used?
- KTZ device and principle of operation
- Types of thermal shut-off valves
- Basic installation rules
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Why are thermal shut-off valves needed?
Thermal shut-off valves are devices that are gas shut-off valves. They automatically shut off the gas pipeline to all gas powered appliances.
All "stubs" are marked as KTZ with a certain set of numbers after the letters. The second number indicates the diameter of the gas pipe for which this mechanism can be suitable.
The purpose of the thermal shut-off valve
The main purpose of the KTZ is to shut off the gas supply to the equipment in the event of a fire. That helps not only to protect against explosion, but also prevents the area of fire from increasing twice or more.
If the shut-off valve is in the open position, then the device itself does not in any way interfere with the passage of a combustible substance to devices and equipment.
Thermal shut-off mechanisms are mounted on pipelines, where the maximum pressure can be 0.6 MPa - 1.6 MPa.

Threaded type thermal shut-off valve. It is used for equipment with lower pressure (up to 0.6 MPa). They are most often used for household needs.
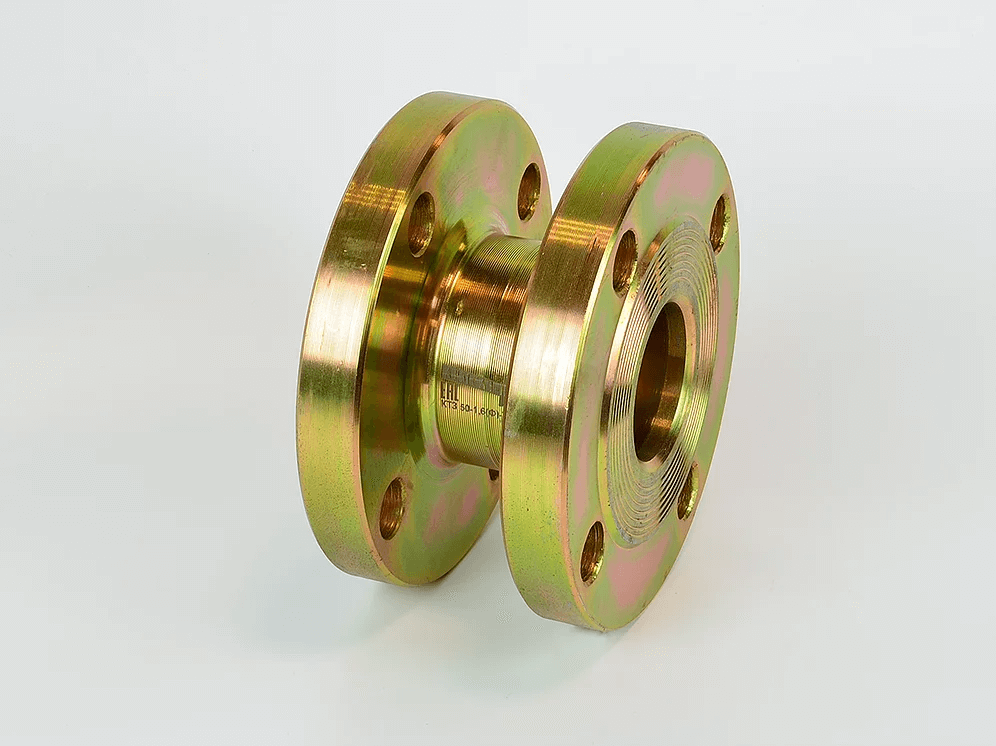

KTZ flange type, which is used in pipelines with high pressure (close to the maximum). More often used in industrial facilities
Next, we will designate the purpose of valves prescribed by the rules of fire authorities.
In the fire safety regulations, there is a regulation that involves the use of valves:
- On the equipment of all natural gas pipelines. Any types of systems (complexity, ramification), any number of consumer devices are assumed.
- To ensure the protection of various gasified facilities and devices operating from gas. In this case, valves are applicable that are designed to automate (act) when the room temperature reaches 100 ° C.
- Installation of thermo-locking modules at the entrance to the room.
In accordance with PPB-01-03 (Fire safety rules) thermal locking devices must be installed in all rooms where there is a gas pipeline. However, this does not include buildings of the V category of fire resistance.
Also, it is not necessary to install KTZ in buildings where pipelines are equipped with solenoid valves. They are usually placed outside the building, and if ignition occurs inside the building, they are triggered. gas analyzer, after which the gas supply stops.
It should be understood that KTZ is not another Russian "trend". The use of these devices at various economic facilities where gas equipment exists is mandatory in countries such as Germany, France, USA, etc.
Where is the thermal shut-off valve used?
The scope of application of thermal shut-off gas plugs is, first of all, pipelines supplying gas to appliances for different purposes in which gas is burned (household and industrial appliances, regardless of type).
Installation of KTZ on any gas pipeline is not permissible outside the premises, after the installation of any other gas fittings, also on bypasses, in adjacent rooms and where the operating air temperature during the operation of gas equipment can reach more than 60 ° C.
It is important not to violate the installation rules - the shut-off valve is installed first on the gas pipeline, and only after it the rest gas fittings, devices and equipment. The valve can be positioned in different positions, but you should pay attention to the arrow-pointer, applied by the manufacturer on the body.

Threaded shut-off valve. Arrows on the steel element when installing on a gas pipeline must correspond to the direction of gas flow
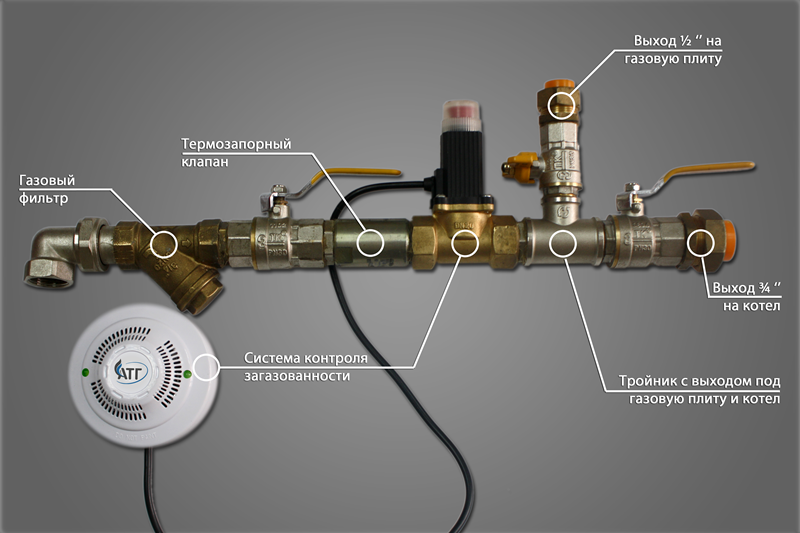
Here you can see the location of the KTZ on the pipeline. The valve must be installed first at the inlet of the gas pipeline, or at the branch from the riser
With respect to the horizon, the position of the installed valve can be any. We will describe in more detail the rules for installing KTZ in more detail below.
Thermal shut-off valves have a special design that allows the device to automatically shut off the gas supply at the right time. If you take a closer look at the design features of the valves, you can quickly understand the essence of their operation. Next, we will analyze everything in more detail.
KTZ device and principle of operation
The valve design includes a steel body with a threaded connection, a fusible insert, a spring element located inside the body, and a poppet or ball-shaped plug. It is this shutter element (indicated by the last) that serves as one of the main ones, since it closes the channel if necessary.
In the photo below, you can see two different types of thermal shut-off valves and the subtleties of their design.
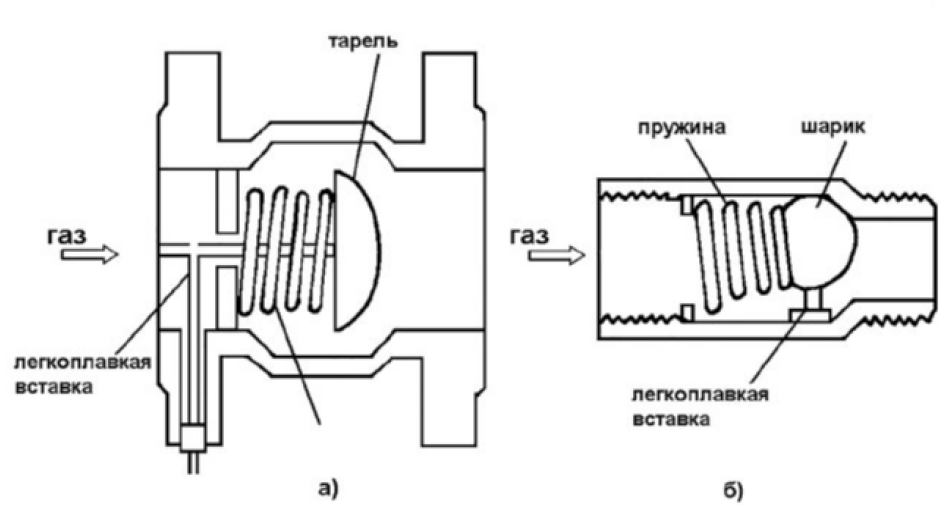
The principle of operation of both types of CTZ is very similar. Only valves with a seam connection are usually used in large enterprises (large buildings and facilities). The bore diameter of these valves is from 50 to 200 mm, the available pressure is 1.6 MPa.
Now let's talk about how the thermal shut-off valve works.
When the air temperature in the room is normal and there is no threat of explosion (ignition, fire, etc.), the valve closure part is cocked and is held by a fuse. If the ambient temperature in the building rises, reaching 80-100 ° C, then this entails the expansion of the insert we are talking about. This is the release of the shut-off mechanism, which in turn, due to the action of the spring, closes the gas access to the equipment.
The tightness of the actuated valve is ensured by mating the cones of the plug and the valve seat, in a word, like “metal to metal”.
Such shut-off devices can be supplied to the pipeline with different types of connections. It can be flanged, coupling (threaded) or wafer mount. Below we will analyze what types of thermal shut-off valves are in general.
Types of thermal shut-off valves
There are only two types of thermal shut-off valves on the market today. From the descriptions above it is clear that this is clutch valves and flanged.
Each type has its own standard size range. The main difference between one species and another is the scope of application. That is, threaded devices are used more often for domestic purposes, and flanged ones - in production.
This is due to the conditional pressure indicators that the locking mechanisms are able to withstand during operation:
- coupling valves - 0.6 MPa;
- flanged valves - 1.6 MPa.
Both types have the same design with the inclusion of a spring, shut-off element, fusible link and other elements. However, the difference is visible externally in the bore diameter.
If in more detail about the scope, then the following places and industries should be highlighted, depending on the type of KTZ:
- Threaded valves used in the installation of a gas pipeline in residential buildings, boiler houses, industrial facilities for various purposes.
- KTZ with flange connection are used when installing a gas pipeline in large boiler houses and at industrial facilities of a large area.
The second type of valves is more in demand in the industrial field due to the large diameter of the bore. If for threaded gates it varies between 15-50 millimeters, then for flanged gates this figure can be from 50 to 200 millimeters.

It is important to use a heat-resistant gasket when installing the valve. If this condition is not met, this can lead to the fact that the KTZ will work and cut off the gas supply, and the gasket, for example, made of paronite or other material, will burn out. Then the gas will begin to flow into the room through the wafer joint.
The connection of the inlet flange of the thermal shut-off valve with the counter flange of the pipeline must be sealed with a special heat-resistant gasket. It can withstand up to 900 ° C in case of fire.
The gaskets mentioned are made of a special heat-resistant material. The composition includes reinforced graphite in a foil sheath, as well as stainless steel from which this foil is made.
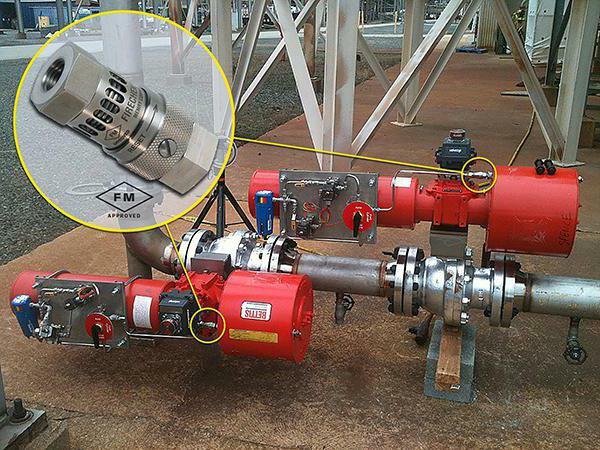
At the moment the clutch valve is activated, the tightness remains 100%. The indicator remains even with prolonged exposure to high temperatures (900 ° C)
What is the first, what is the second version of the shut-off devices can work with any gases. After the mechanism is triggered, the valve is changed, installing the same new one in its place. In some cases, it is sufficient to replace the fuse-link for further operation of the operated valve.
Basic installation rules
The quality of the subsequent operation of the valve depends on the installation process. Therefore, it is important to follow the rules when installing the thermal shut-off valve.
Next, we will consider the basic rules and norms for the installation of KTZ on a gas pipeline:
- Thermal locking devices for threaded connections should be installed only on lines with a pressure of no more than 0.6 MPa. Flanged valves can and should be used on pipelines with gas pressure from 0.6 to 1.6 MPa.
- The flow capacity of the gas line must match the flow capacity of the valve itself.
- Installation is only permitted indoors to protect fittings that are not designed for high heating.
- Installation of KTZ is not allowed where adjacent elements raise the temperature of their environment to 52 ° C and above.
- After completing the installation process, it is important to check the valve for leaks.
- The installed valve must be located in a place accessible to a person (for inspection and maintenance).
- The valve must not be subjected to various influences.
It should also be borne in mind that when transporting the thermal shut-off valves, an automatic triggering of the mechanism may occur. Therefore, when choosing a device, it is important to check the mechanism.
If the gas distribution is complex, and there are several fuel consumers, and the facilities are located in different parts of the building, then valves will need to be installed on each branch.
And although this valve has undergone thorough and numerous checks, it is also certified and approved for its intended use, every rule on their installation.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
What you need to know about KTZ for household use:
Every day, fires claim the lives of thousands of people around the world. Gas explosions during fires are no less terrible. If every user would be more responsible fire safety rules, then perhaps there would be fewer disastrous outcomes. Thermal isolation valves can be considered equipment that greatly enhances the safety of your home. But for this it is important to follow each rule for their operation and installation, which we described in this article.
Do you have any questions about the design or installation rules of the thermal shut-off valve? Or would you like to supplement the material with useful information? Write your comments in the comments block, ask your questions to our experts, take part in discussions.


