The heating battery is a structure of the upper and lower collectors connected by vertical pipes. Also included are valves, faucets and other fittings. The presented material shows and describes in detail the radiator in section, the types of equipment, their pros and cons.
The content of the article
- Radiator device
- How the battery works
-
Types of radiators
- Cast iron
- Aluminum
- Steel
- Bimetallic
- Copper
- Battery designs
Radiator device
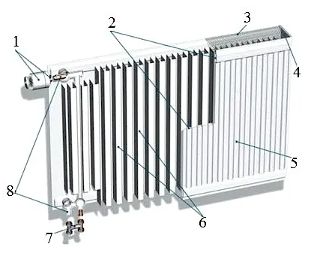
One of the common types of batteries is made of stainless steel. It is used in many multi-apartment and private houses, it is characterized by efficient heating, corrosion resistance and a relatively affordable price. The device of a heating radiator can be considered precisely on the example of this model.
The equipment is represented by 2 steel plates, which are interconnected by rib channels (2) running in vertical and horizontal directions. In fact, these are pipes inside which water or other coolant circulates. Each ribbed plate is closed with a grate (3) for effective air circulation. The outer plate is covered with corrugated metal leaves (6). They have enough area to heat the air to the maximum.
The way a heating radiator is arranged depends on its type. For example, in some cases, batteries do not have ribs - they simply connect together to form a common panel. The plates can have both smooth and corrugated surfaces (5). Not always, but quite often, batteries are equipped with a control valve. The thermostatic head (1) is fixed to it.
Both steel and aluminum heating radiators in the section are connected to the heating system through 4 connecting pipes (8). In some cases, it is necessary to turn off the hot water supply - a special valve (7) is provided for this.
How the battery works
The sectional view of the heating radiator shown allows you to understand the principle of operation of this device. Regardless of the type of material or design features, the battery operation scheme is approximately the same. It is a sealed system of pipes through which hot water is supplied to heat the air. Moreover, heat transfer occurs due to 2 phenomena:
- Thermal radiation - the space is heated due to the hot surface of the equipment.
- Convection - when air is heated, it rises, then cools and moves down. After that, the cycle repeats many times.
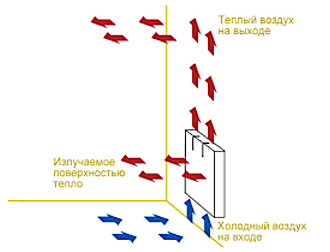
The principle of operation of a heating radiator allows you to use only one of these phenomena, and most often it is thermal radiation. Although modern bimetallic type batteries are designed to use both processes. Thanks to this, even a large room warms up as quickly as possible.
Types of radiators
The rate of heat transfer directly depends not only on the design, but also on what the heating battery consists of. For example, old cast-iron batteries take longer to heat up, but they heat the air for a long time even when disconnected from the heating circuit. Nevertheless, in modern homes, bimetallic and steel models are more often used. There are other varieties - the most common are:
Cast iron
The way a heating radiator works depends little on the material of manufacture. For example, cast-iron batteries also heat the room due to thermal radiation and convection. These are old models that are now being replaced by modern materials everywhere. They are very strong and durable, but corrode over time. Outwardly, such equipment looks already obsolete.
Aluminum
As already mentioned, the device of a cast-iron heating battery practically does not differ from a metal one. However, the material greatly affects heat dissipation and performance. According to this indicator, aluminum devices are more preferable than the same cast iron ones. They are light, not susceptible to corrosion, although they can become clogged from dirty water, so it is advisable to install filters.
An aluminum radiator in a section looks about the same as a classic steel one. But it is worth remembering that the material is softer. Therefore, in houses with strong pressure in the heating circuit, it can leak, especially during a jump, an emergency.
Steel
A common type of battery with panel or tubular design. The first is cheaper and at the same time is characterized by good heat transfer. This is an unpretentious equipment, resistant to corrosion and clogging. The device of an aluminum heating radiator in a section is approximately the same as a steel one. But steel models are much stronger and last at least 20 years.
Bimetallic
This is a modern type of equipment, made from 2 metals at once - steel and copper. The device of this type of heating battery is classic, but due to the presence of a copper insert, strength is significantly increased. In addition, the models are characterized by high heat transfer, although they have the disadvantage of high cost.

Copper
As already mentioned, what the heating radiator consists of affects its reliability, as well as technical characteristics. In terms of durability, strength and resistance to corrosion, copper batteries are in the lead. They serve 30-40 years or more, while they do not rust and have good heat dissipation. Such equipment allows you to use not only water, but also antifreeze. The main disadvantage is the high cost.
Battery designs
Sectional heating radiators, the photo of which is shown above, are a system of pipes of various designs. Depending on this important indicator, the following types are distinguished:
- Sectional - a classic version, made up of several separate sections. Their number can be both reduced and increased, adjusting to the required power and niche size.
- Tubular - one-piece metal construction, has a lower and upper collectors, which are connected by pipes running vertically. The principle of how this type of heating battery works is based on convection and thermal radiation.
- Panel - mostly steel, but there are also concrete (the latter are mounted in the thickness of the wall). They heat the air with radiation.
- lamellarOn the contrary, they work on the principle of convection. The design is represented by a core and metal plates or ribs.
Thus, the battery device is quite simple. The radiator is equipped with several sections, and the upper and lower collectors are connected by pipes, due to which they form a single system. Water, flowing through the supply pipe, heats the air due to radiation and convection. Then, cooling down a little, it goes into the return pipe, from where it enters the boiler and again into the batteries. Such cycles are repeated many times, so that even large areas can be heated.


