Central heating - this is such a heating system, a heat source in which it is located in a separate room, for example, at a thermal power plant. Moreover, the thermal station is often located far from residential buildings - about 10-20 km. Such a system has its advantages, but also some disadvantages. An overview of the main types and devices is presented below.
The content of the article
- Heating system device
-
Types of central heating system
- Single pipe
- Two-pipe
Heating system device
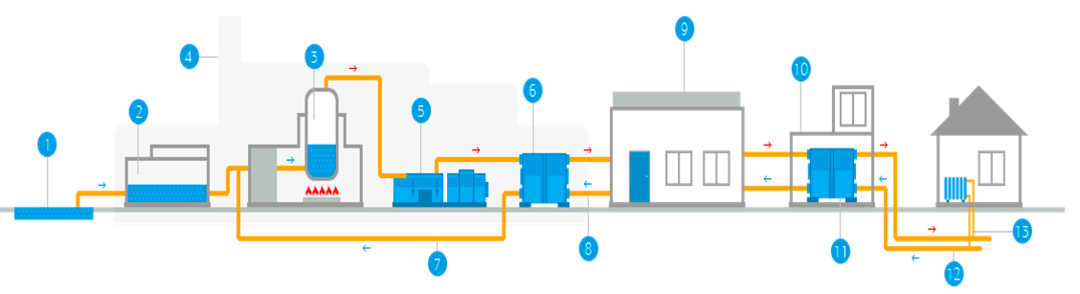
A heating system is a collection of many elements of heating, water supply, temperature and pressure control. It provides a complete cycle of coolant circulation from the boiler house to the consumer and vice versa. The main elements of such a system are shown in the diagram.
Here the numbers are:
- Actually water, which is used as a heat carrier.
- Chemical shop for water purification. As a rule, local heating is a thermal power plant, which independently selects and prepares the liquid, and then lets it through the pipes in an already filtered form.
- Space heating involves heating water to a certain temperature. This happens directly at the CHP in installed boilers. They can run on solid fuels such as fuel oil, liquid or gaseous.
- Chimney - for the removal of gases that are formed during the combustion of fuel.
- A turbine is a plant that rotates under the influence of heated steam. It then drives a generator to produce electricity.
- A heat exchanger is a container in which water is heated and then moves through pipes to radiators. This is how dynamic heating works.
- Steam return - a system for removing excess volumes of evaporation. After cooling, the steam condenses again, turns into a liquid and enters the pipes.
- Main pipes - bring the coolant from the CHP for local heating. Their length cannot exceed 40 km (usually up to 20 km). Otherwise, the water will be very cold.
- Thermal pumping station - a system for pumping water in pipes under a certain pressure.
- The central heating point is a transit hub for receiving water from the CHP and further transfer to the houses.
- The second heat exchanger, after which the liquid goes directly to the house.
- Quarterly pipes are used to bring the coolant directly to the houses. This is how buildings and structures are heated.
- The distribution of pipes inside the house distributes the coolant over floors, apartments and other rooms.
Types of central heating system
From the described scheme it is clear how the heating system works. But for a complete review, it is necessary to consider what types it happens. The main classification is related to the method of supply and discharge of water. According to this criterion, 2 schemes are distinguished:
- Single pipe.
- Two-pipe.
Single pipe
This scheme got its name due to the fact that it provides for the installation of one pipe to which radiators are connected. Water comes to the batteries from this pipe and goes into it. Then, from the last battery in the circuit, it moves along the return line to the boiler, heats up, and the cycle repeats many times.
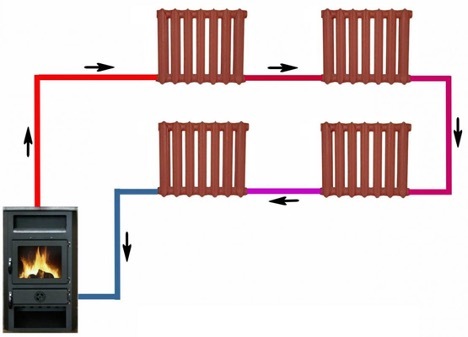
This type of circuit has quite a few advantages:
- saving on materials - only one pipe is installed;
- outwardly it looks more aesthetically pleasing - it is quite easy to hide in a niche, floor or wall;
- simpler and more affordable installation.
But there are also disadvantages, and significant ones:
- radiators heat up unevenly - the first is faster, the second and subsequent longer;
- due to an accident in one fragment of the site, for example, in a battery, the entire circuit has to be turned off;
- such a system is less resistant to hydraulic shocks and other emergency situations.
Two-pipe
The classification of water heating systems also involves the allocation of a two-pipe scheme. It involves the supply of water to the battery through one pipe, and the discharge through another. This system fundamentally differs from a single-pipe system, as can be seen in the figure.
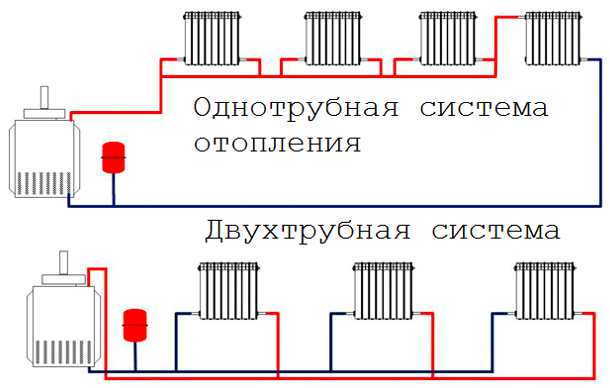
Due to the separation of the supply and exhaust flows, a two-pipe circuit provides quite a few advantages:
- all radiators are evenly heated, regardless of their proximity to the boiler;
- you can put a thermostat on each battery to set the temperature (for example, you can make it hotter in one room, cooler in another);
- the system is much more resistant to pressure and temperature changes;
- if repair is necessary, it is enough to block only one radiator without touching the entire circuit.
At the same time, there are also disadvantages:
- the price is higher because more materials are required;
- installation work is more difficult, and therefore also more expensive;
- in such a scheme, 2 pipes are used, so outwardly it does not look as compact and attractive as a single-pipe one.
In general, it is central heating that shows the greatest reliability and efficiency. Even in the event of a serious accident, it is possible to restore working capacity within a day (usually in a few hours). In practice, in the construction of apartment buildings, a two-pipe system is almost always used. This is a universal design that can be used in private homes.


