The complex of works on the construction of a residential cottage without fail includes the device of a ventilation system. It has a number of important functions. With the help of a constant inflow of clean atmospheric air into the premises of the house and the removal of polluted air, one's own house remains dry, and the air in it is fresh and healthy.
The system will work properly only if the ventilation standards of a private house are observed and accurate calculations are made. They are produced during the development of the project in the part "Ventilation". The calculated values will help you select the components of the system that provides the standard air exchange.
We will tell you about the specifics of the organization of ventilation. We will show you on the basis of which building codes and regulations developed and approved by government agencies, design and calculations are carried out. Here you will find examples, using which you can calculate the system yourself.
The content of the article:
- Regulations for the low-rise sector SP 55.13330.2016
- General sanitary requirements in GOST 30494-2011
-
Designer's Guide to JV 60. 13330.2016
- The main postulates of the normative collection
- Intake ventilation devices
- Calculation of air inflow
- Air exchange organization rules
- Equipment and its placement
- Form and material of air ducts
- Specificity of energy saving and automation
- Air exchange in multi-storey buildings in SP 54.13330.2016
- Requirements for air exchange in MGSN 3.01-01
- Hygienic justifications in SanPiN 2.1.2.2645
-
An example of calculating natural ventilation at home
- Calculations for the frequency and number of residents
- Calculation according to sanitary standards
- Calculation of the cross-section of air ducts
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Regulations for the low-rise sector SP 55.13330.2016
This is one of the main sets of rules applied to the design of single-apartment residential buildings. The ventilation standards for a private house collected in it relate to the design of autonomously located residential buildings, the height of which is limited to three floors.
A comfortable microclimate is created in the inner space of the building with the help of ventilation equipment. Its characteristics are given by GOST 30494-2011.
In most cases, an individual house is heated by an autonomous heating boiler. It is installed in rooms with good ventilation on the ground or basement floors. Accommodation in the basement of the cottage is possible. With power heat generator up to 35 kW it can be installed in the kitchen.

The design of any building, regardless of its area, number of storeys, purpose, without fail includes the section "Ventilation" with the development of a scheme, calculations and recommendations for construction
If the heating unit runs on gas or liquid fuel in the boiler room, measures are taken to insulate equipment and pipelines in accordance with the terms of SP 61.13330.2012.
The collection offers three principles of ventilation:
- Exhaust air is removed from the premises by natural draft along ventilation ducts. The inflow of fresh air is due to the ventilation of the rooms.
- Air supply and removal by mechanical means.
- Air intake by natural means and the same removal by ventilation ducts and incomplete application of mechanical force.
In individual houses, air outflow is most often arranged from the kitchen and bathrooms. In other premises, it is organized on demand and need.
The flow of air from kitchens, bathrooms, latrines with strong and not always pleasant odors is removed immediately outside. It must not enter other rooms.
For natural ventilation, windows are equipped with vents, valves, transoms.
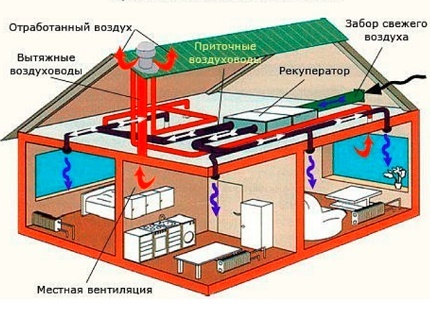
An important advantage of the supply and exhaust system is the stability of operation, regardless of the temperature and air density within the room and outside the window.
The efficiency of the efficiency of ventilation equipment is calculated taking into account a single change of air within one hour in rooms with a constant presence of people.
Minimum volume of air evacuation in operation:
- from the kitchen - 60 m3/час;
- from the bathroom - 25 m3/час.
The air exchange rate for other rooms, as well as for all ventilated rooms with ventilation, but when it is turned off, is taken as 0.2 of the total cubic capacity of the space.

The open-cut air ducts are fixed to the building structures with brackets. To reduce sound vibrations, the holders are equipped with noise-dampening elastomer pads
Cylindrical or rectangular air ducts are attached to building structures using various devices: hangers, brackets, lugs, brackets. All fastening methods must ensure the stability of the ventilation ducts and exclude sagging of the ventilation pipes or ducts.
Duct surface temperature limited to 40O WITH.
Outdoor appliances are protected from low negative temperatures. To all structural parts ventilation systems free passage is provided for preventive inspection or repair.
In addition, there are also collections of standards such as NP ABOK 5.2-2012. These are regulatory guidelines air circulation in the premises of residential buildings. They were developed by specialists of a non-profit partnership. ABOK in the development of the normative acts discussed above.
General sanitary requirements in GOST 30494-2011
A collection of state-approved standards for creating a comfortable living environment in residential buildings.
Indicators for air in residential apartments:
- temperature;
- travel speed;
- proportion of air humidity;
- total temperature.
Depending on the stated requirements, admissible or optimal values are used in the calculations. You can familiarize yourself with their full composition in Table 1 of the above standard. A condensed version is shown below for an example.
For a living room, the following are admissible:
- temperature - 18O-24O;
- moisture percentage - 60%;
- air movement speed - 0.2 m / sec.
For kitchen:
- temperature - 18-26 degrees;
- relative humidity - not standardized;
- speed of air mixture advance - 0.2 m / sec.
For bathroom, toilet:
- temperature - 18-26 degrees;
- relative humidity - not standardized;
- the rate of movement of the air is 0.2 m / sec.
In the warm season, microclimate indicators are not standardized.
The assessment of the temperature environment inside the rooms is carried out according to the usual tO air and the resultant. The latter value is a collective indicator of tO air and radiation tO premises. It can be calculated using the formula in Appendix A by measuring the heating of all surfaces in the room. An easier way is to measure with a ball thermometer.
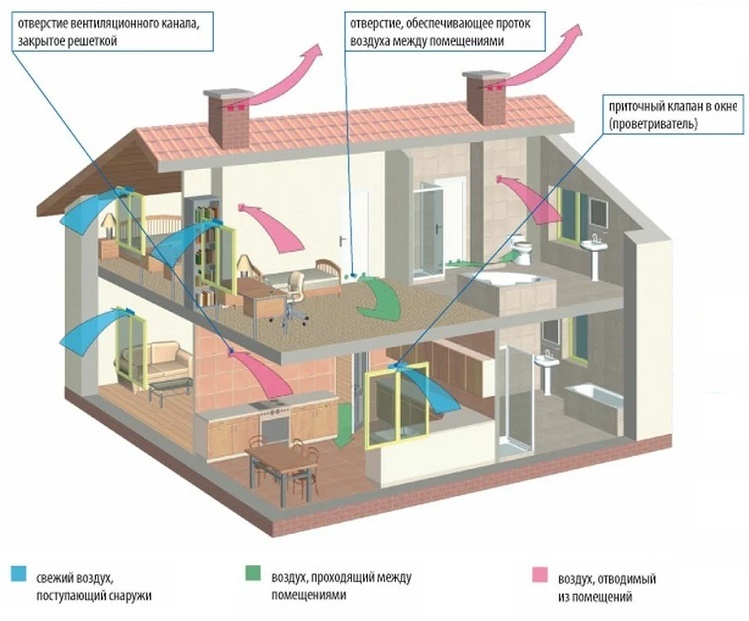
For the correct measurement of temperature data and sampling to determine the organoleptic parameters of the air mass, the direction of the flows of the supply and exhaust parts of the system should be taken into account.
Air pollution inside a home is determined by the amount of carbon dioxide, a product breathed out by people when they breathe. Harmful emissions from furniture, linoleum are equated to the equivalent amount of CO2.
According to the content of this substance, the internal air and its quality are classified:
- Grade 1 - high - carbon dioxide tolerance 400 cm and below3 in 1 m3;
- Grade 2 - medium - carbon dioxide tolerance 400 - 600 cm3 in 1 m3;
- Class 3 - permissible - CO tolerance2 - 1000 cm3/ m3;
- Class 2 - low - carbon dioxide tolerance 1000 and higher cm3 in 1 m3.
The required volume of outside air for the ventilation system is determined by calculation using the formula:
L = k × Ls, where
k - coefficient of efficiency of air distribution is given in table 6 of GOST;
Ls - estimated, minimum amount of outdoor air.
For a system without forced traction, k = 1.
He will acquaint you in detail with the performance of calculations for providing the premises with ventilation. next article, which is worth reading for both the customers of the construction site and the owners of problem housing.
Designer's Guide to JV 60. 13330.2016
This set of rules is the main document for the designers of a ventilation complex in a private house. This document establishes design rules ventilation system for all types of buildings. They also build on the state standards for the microclimate of residential premises.
Sanitary and epidemiological indicators of residential buildings are used according to SanPin 2.1.2.2645.
The main postulates of the normative collection
The rules prescribe materials for air ducts and other parts of ventilation structures purchase only if there are certificates confirming their compliance with sanitary and hygienic requirements.
To exclude the appearance of condensation, the air ducts are insulate according to the standards of SP 61.13330. To protect against aggressive air components inside and outside the house, anti-corrosion materials are used or the surface of the boxes is covered with special compounds.

Thermal insulation of pipelines is used to prevent the formation of condensate and to protect against the aggressive effects of chemicals contained in the condensate
Installation and commissioning work is carried out in accordance with SP 73.13330.
Mechanically driven ventilation is used:
- if there is not enough natural air exchange;
- if the area is not equipped with devices for air intake.
Mechanical ventilation is turned on when there is not enough natural circulation of the air mass at certain time periods.
Ventilation system based on natural air circulation calculated based on the difference in the density of street air at a temperature of 5O C and the density of indoor air at the standard temperature in the cold season of the year.
If at the above temperatures the air is not completely renewed, do supply and exhaust systems with mechanical motivation.
Intake ventilation devices
They should not be located less than 8 m from waste collection areas, parking lots with more than three cars, roads and other sources of harmful emissions and unpleasant odors.
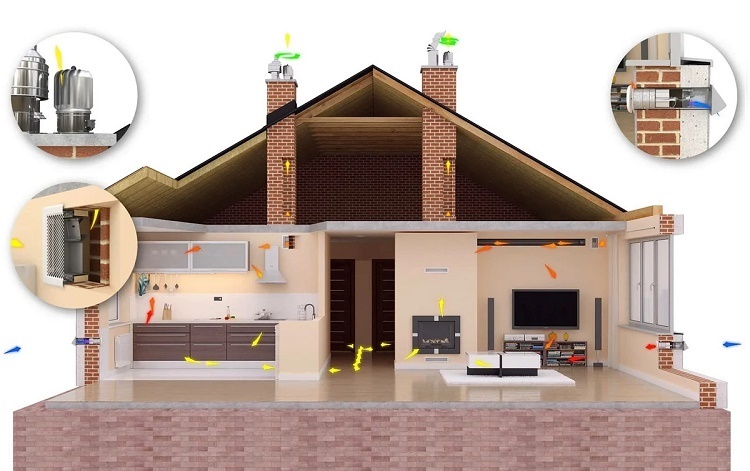
The inlet openings for the intake part of the air exchange system are located in the area of the basement or foundation of the house
In the upper zone of the building, receiving structures are placed on the windward side. On hot days, they are protected from direct sunlight and overheating.
The lower boundary of the ventilation receiving compartment runs at a level not exceeding 1 m from the snow surface, but not lower than 2 meters from the average ground elevation.
Calculation of air inflow
The calculation is made according to Appendix G of the current set of rules. From the results of the calculations, more importance is taken to guarantee compliance with sanitary standards and safety in relation to fires and explosions. The debit of the air entering the room should not be less than the minimum consumption calculated according to Appendices G and I.
The calculation of air costs is carried out separately for the summer, winter and off-season according to the formulas Ж1-Ж7, choosing the highest value obtained:
- excess heat;
- by weight of harmful and hazardous elements;
- excess moisture;
- by multiplicity air circulation;
- by consumption for 1 person.
The minimum consumption of outdoor air cubic meters / hour per person is given in Table I1 of Appendix I.
Air exchange organization rules
Air is supplied to the living quarters through special distributors in the upper part of the house. Receiving chambers for air outflow are made under the ceiling of the room at least 2 m from the floor to the bottom side of the hole to remove excess heat, excess moisture and gases.
Equipment and its placement
Fans are selected according to two indicators: resistance ventilation networks at a given speed of the air mixture in it and according to the calculated air consumption. In this case, the arrival and consumption of air through the leaky fit parts in factory devices and air ducts at the request of p. 7.11.8.

The air flow is forced to move by the fan. Axial models are installed in the exhaust and inlet openings, providing local ventilation
Transit distances of air ducts are designed in accordance with GOST REN 13779 for tightness class B, in other cases for class A.
Air leaks and leaks through fire dampers and ventilation ducts are accepted according to SP 5.13130.2009, to fulfill the settings of the Federal Law of July 22, 2008. No. 123-FZ "TR on the PB requirements".
Cleaning filters are selected taking into account the duration of operation, the amount of collected dust, the degree of air purification. Outside air diffusers must have devices for regulating the air flow vector and its flow rate.
In rooms with gas installations, grilles and valves with air flow regulators are installed near the fans. Their device guarantees incomplete closing.

Axial and centrifugal types of fans are installed in the air ducts. They stimulate the movement of flow through the system. The choice of model is determined by the volume of supplied air and the specifics of the operation of the room
Premises for the location of ventilation equipment, including technical floors and attics of residential buildings, are selected in accordance with the terms of SP 54.13330 "Residential apartment buildings". Room category by explosively- and fire hazard is determined by Federal Law No. 123-FZ.
Form and material of air ducts
In low-rise residential buildings, the union of air ducts general exchange ventilation in a warm attic is ineffective. To prevent smoke, fire dampers and air dampers are installed on the air ducts.
Ventilation ducts with limited fire resistance are made of non-combustible materials. Fire-resistant materials are also used for transit areas ventilation system and air ducts in rooms for placing equipment in basements and attics.
Materials with a flammability group above G1 are allowed:
- for air ducts of premises, except for the above;
- for flexible inserts of transit sections.
Ventilation ducts and pipes are made from unified standard parts. The use of asbestos cement in supply systems is not allowed. Air ducts must have coatings that are resistant to aggressive environments.

For the assembly of the duct ventilation system, pipes and fittings are produced from galvanized steel and plastic.
The thickness of sheet steel for the manufacture of air ducts is selected according to Appendix K of the considered regulatory collection.
At a permissible temperature not exceeding 80 degrees with a circular cross-section diameter:
- up to 200 mm inclusive - sheet thickness 0.5 mm;
- from 250 to 450 mm - 0.6 mm;
- from 500 to 800 mm - 07 mm;
- from 900 to 1250 mm - 1.0 mm.
For rectangular air ducts:
- up to 250 mm - 0.5 m;
- from 300 mm to 1000 mm - 0.7 mm;
- from 1250 to 2000 mm - 0.9 mm.
With the established standard of fire resistance not less than 0.8 mm. It is not allowed to lay transit air ducts through kitchens and living rooms coming from premises for other purposes.
Gas pipelines, cables, wires, sewer pipes are allowed to be laid at a distance of more than 100 mm from the walls mounted air ducts. V air vent mines are not allowed to place domestic sewage pipelines.
The ducts and pipes of the general exchange exhaust ventilation are mounted with a rise of 0.005 in the direction of movement of the air mass. To remove the resulting condensate, drainage devices are provided.
Specificity of energy saving and automation
For private households, energy savings play a significant role.
The total energy saving in the design of ventilation systems is due to:
- selection of advanced equipment;
- solutions energy efficient tasks;
- the use of mechanical systems;
- secondary use of the heat of the removed air;
- an individual approach to the regulation of air exchange.
Electrical installations are selected taking into account the standards PUE (7th edition) "Electrical Installation Rules". If there is a fire extinguishing and fire alarm system in the cottage, an automatic blocking of the power supply of ventilation systems is designed in accordance with SP 7.13130.
In the event of a fire, it is envisaged to disconnect centrally or individually the ventilation systems, and turn on smoke protection. Remote control of smoke dampers, windows, transoms should be automated.
Air exchange in multi-storey buildings in SP 54.13330.2016
The postulates of this set of rules intended for the construction of apartment buildings up to 75 meters high will be useful in the design of ventilation of individual houses. Construction is carried out according to the working drawings made on the basis of the project.
A residential building can have built-in, built-in-attached, attached general-purpose premises and use: swimming pools, gyms, garages, parking lots, subject to the relevant rules security. The placement of industrial units in residential buildings is not allowed.
Design rules MKD, designed on the basis of sanitary requirements SanPiN 2.1.2.2645, GOST 30494, taking into account climatic zones according to SP 131.13330.
Noise protection is regulated by the terms of SP 51.13330. The project of a residential building includes instructions for use, including a ventilation complex.
An individual house is designed for one family. The composition of the premises and their number is provided at the request of the customer. Main premises: common living room, bedrooms, kitchen, bathrooms. Accommodation of living rooms in basement floors is not allowed.
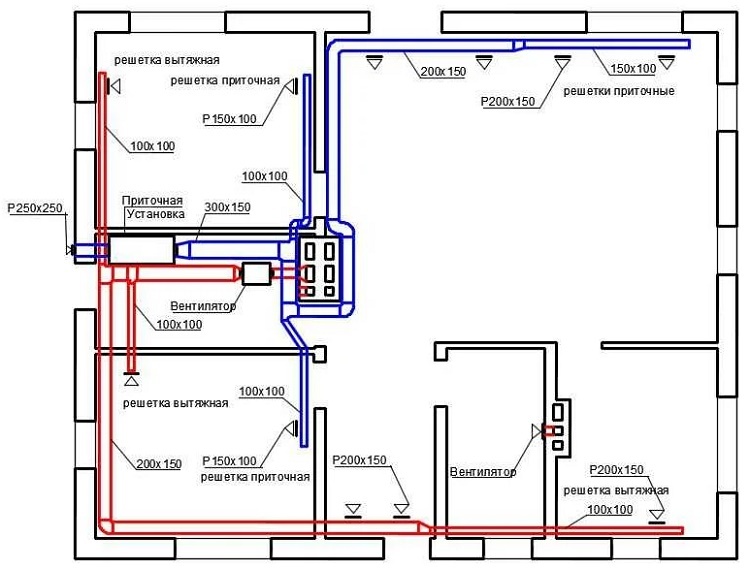
If a supply and exhaust ventilation is installed in a house with a typical layout, an air supply unit and an exhaust fan are used in the system
When designing saunas ventilation ducts equipped with fire dampers. Ventilation openings and pipeline entries in the foundation and basement structure of the building are provided with rodent protection devices.
Air exchange rate:
- bedroom, living room with a total area of the mansion for 1 person. less than 20 sq.m. - 3 cubic meters / hour for 1 sq. meter of living space;
- more than 20 sq.m. - 30 cubic meters / hour for 1 person;
- kitchen with electric stove - 60 cubic meters / hour;
- room with gas equipment - 100 cubic meters / hour;
- a room with a heating boiler up to 50 kW with an open and closed firebox - an hourly consumption equal to the volume of the room.
- bathroom, toilet - 25 cubic meters / hour.
In the outer walls of the basement technical underground, cold attic that do not have a hood, make air vents evenly distributed around the perimeter of the house. The area of one opening is not less than 0.05 sq.m.
Requirements for air exchange in MGSN 3.01- 01
All-Russian standards for the construction of residential buildings are concretized and partially repeated.
The rate of air exchange increases hoods from kitchens with gas equipment, depending on the number of gas burners:
- 2 pcs. - not less than 60 cubic meters / hour;
- 3 pieces - not less than 75 cubic meters / hour;
- 4 pieces - at least 90 cubic meters / hour.
Gym in working mode - 80 cubic meters / hour, non-working - 16 cubic meters / hour;
For built-in objects, an autonomous ventilation system is made. In the presence of a warm attic space, the exhaust shaft is provided with a height of at least 4.5 meters from the surface of the slabs covering the upper floor.
Hygienic justifications in SanPiN 2.1.2.2645
The collection dictates hygienic requirements for the ventilation device of the house, the internal climate, and the state of the air. In accordance with its norms, the release of the contaminated mixture from kitchens and bathrooms in general is not allowed. ventilation duct with living rooms.
Exhaust ventilation shafts rise above the roof ridge or flat roof to a height of at least 1 meter.
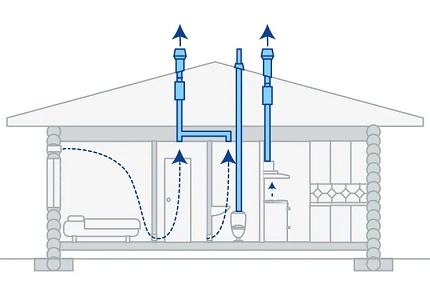
The height of the ventilation risers above the roof is determined by the distance between them and the ridge rib. If it is less than 1.5 m, then the channel must be brought out at least 0.5 m above the ridge.
The permissible norms of temperature, relative humidity, speed of air movement in the premises of the house in the cold and warm seasons of the year are listed.
An example of calculating natural ventilation at home
The current regulatory enactments offer three calculation methods:
- by the frequency of air exchange;
- for sanitary and hygienic characteristics;
- by the total area of the rooms.
The calculation is based on two indicators: air flow in m3/ hour and hourly rate of air exchange. These data are taken from the sets of rules SP 54.13330 and SP 60.13330.
Multiplicity air circulation means the number of complete room air updates in 1 hour. Taken according to so 9.1 SNiP 31-01-2003.
According to the standard settings, the following air consumption is assumed:
- living room, bedroom - 1 time / hour;
- kitchen with electric stove - 60 cubic meters / hour;
- sanitary facilities - 25 m3/час;
- room with a solid fuel boiler - multiplicity 1 + 100 m3/час.
For kitchen in a house with a gas stove a scheme is adopted: a volume of air equal to the standard turnover is removed using natural exhaust, and the added 100 m33/ hour are removed by forced ventilation in the form of a kitchen hood.
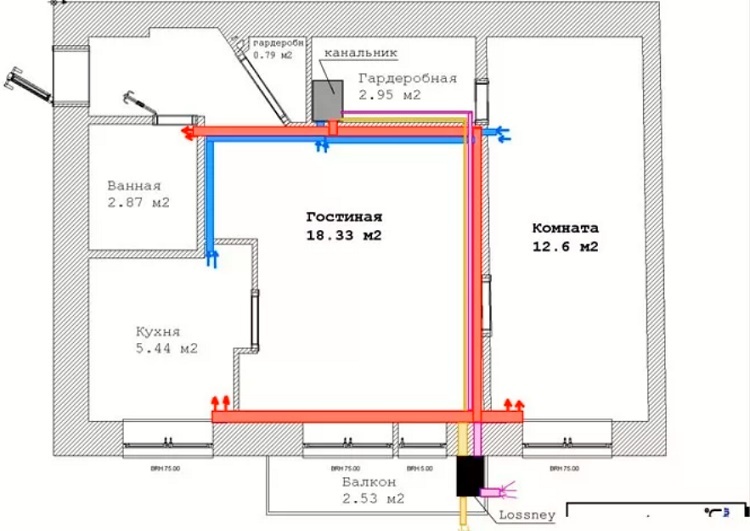
To perform calculations on the frequency of air exchange, to ensure the flow in systems without recuperation, to supply air mixture in systems with a recuperator, a house plan with the exact dimensions of the premises is needed
Exchange rate for boiler rooms with gas heat generator taken equal to 3+ the volume of air for gas combustion.
Calculations for the frequency and number of residents
It is carried out for each room of the cottage according to the formula:
L = S × h × n,
S - room area in m2;
h - room height m;
n - the frequency of air exchange within an hour, taken from SNiP.
The standard volume of air mass and the frequency of its change per day depends not only on the area of the space equipped by the system, but also on the number of residents. The hood calculation uses the following formula.
L = m × N, where
L - volume of air extract in m3/час;
m - the amount of air mixture per person m3/час;
N - the number of people present in the room for at least 2 hours.
Considered as an example, a conditional house with a composition of premises:
- living room - 27 m2;
- bedroom 1 - 15 m2;
- bedroom 2 - 18 m2;
- kitchen - 16 m2;
- corridor - 10 m2;
- bathroom - 8 m2;
- bathroom - 4 m2.
Total - 98 m2.
If we assume that so many people live in the house that there is less than 20 m2 for each2 total area, then the hourly air flow is determined at the rate of 3 m3/ hour for 1 m2 area. 98 × 3 = 294 m3/час.
Air volumes are determined by cubic capacity of rooms with a height of 2.8 m:
- living room - 27 × 2.8 = 75.6 m3/час;
- bedroom 1 - 15 × 2.8 = 42 m3/час;
- bedroom 2 - 18 × 2.8 = 50.4 m3/час;
- kitchen - 16 × 2.8 = 44.8 m3/час;
- corridor - 10 × 2.8 = 28 m3/час;
- bathroom - 8 × 2.8 = 22.4 m3/час;
- bathroom - 4 × 2.8 = 11.2 m3/час.
The obtained values, taking into account the frequency of air exchange, are rounded up to a multiple of five. The corridor used by the SNiP table is not standardized, therefore it is excluded from the calculation.
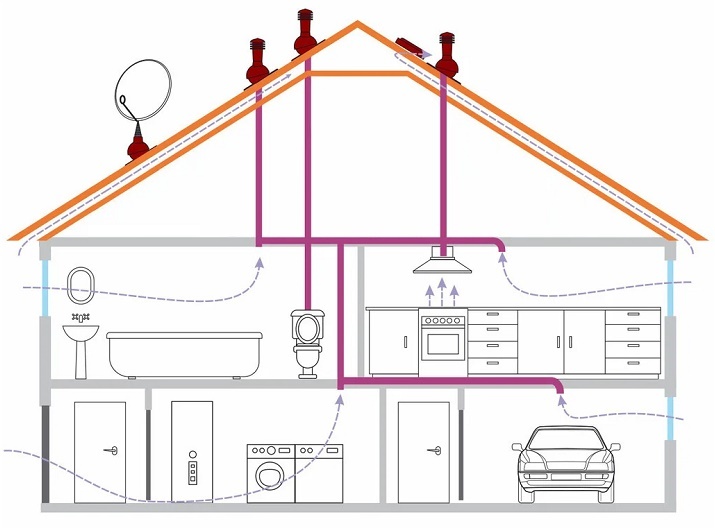
Layout of ventilation ducts in a mixed ventilation system: exhaust from the kitchen, bathroom and toilet is produced through separate channels, the inflow is carried out naturally through leaks in window and door structures
The resulting volumes are summed up separately for the air intake and exit.
Extracted rooms:
- kitchen - 44.8 at least 90 m3/час;
- bathroom - 22.4 at least 25 m3/час;
- bathroom - 11.2 at least 25 m3/час.
Total - 140 m3/час.
Rooms from which fresh air comes in:
- living room - 75.6 × 1 = 80 m3/час;
- bedroom 1 - 42 × 1 = 45 m3/час;
- bedroom 2 - 50.4 × 1 = 55 m3/час;
Total - 180 m3/час.
The inflow volume exceeds the outflow volume by 40 m3/час. To balance the air flows, the volume of the hood is increased by the missing amount, adding it to the volumes of the kitchen and bathroom.
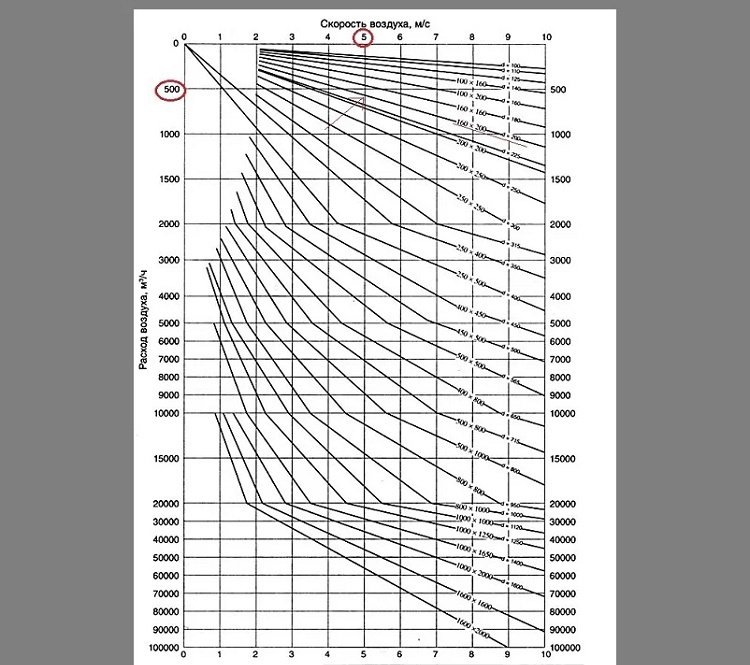
The diameters of pipes for the assembly of ventilation ducts are determined from a diagram in which typical values are collected and plotted.
After the adjustment, the exact values of the arrival and departure are obtained.
Coming:
- living room - 75.6 × 1 = 80 m3/час;
- bedroom 1 - 42 × 1 = 45 m3/час;
- bedroom 2 - 50.4 × 1 = 55 m3/час;
Total - 180 m3/час
Care:
- kitchen - 44.8 at least 105 m3/час;
- bathroom - 22.4 at least 25 m3/час;
- bathroom - 11.2 at least 50 m3/час.
Total - 180 m3/час.
The volumes are balanced according to the multiplicity calculation.
Accommodates 3 people + 2 guests are intermittent. Norm - 60 m3/ hour for 1 resident person, 20 m3/ hour for 1 temporary tenant.
Calculations:
- living room - 3 × 60 + 2 × 20 = 220 m3/час;
- bedroom 1 - 2 × 60 = 120 m3/час;
- bedroom 2 - 1 × 60 = 60 m3/час.
Total - 400 m3/час.
The hood, calculated above according to the multiplicity standards, is increased to the total volume of the air flow, spreading the difference 400 - 180 = 220 m3/ an hour for the exhaust from the kitchen, bathroom and toilet.
Receive:
- kitchen - 105 m3/ hour = 280 m3/час
- bathroom - 25 m3/ hour = 60 m3/час;
- bathroom - 50 m3/ hour = 60 m3/час.
Total - 400 m3/час. The calculated value of the diameter of the hood should provide a full-fledged change of air mass in a private house.
Calculation according to sanitary standards
The area of the house is 98 sq.m. Supply air exchange taking into account the norm of 3 m3 1 m2 area. 98 × 3 = 294 m3/час.
This result is distributed over all rooms with a hood:
- kitchen - 90 m3/ hour = 174 m3/час;
- bathroom - 25 m3/ hour = 60 m3/час;
- bathroom - 25 m3/ hour = 60 m3/час.
Total - 294 m3/час.
Achieving equilibrium air exchange is the basis for calculating ventilation.
Calculation of the cross-section of air ducts
Now the task is to distribute the threads. The hood will consist of four channels: two in the kitchen and one each in the bathroom and toilet.
You can count using two formulas:
but) F = L / 3600 × V, where
F - cross-sectional area of the air duct m2;
L - consumption of the exhaust mixture m3/час;
V - air flow speed m / sec.
b) F = 2.778 × L / V, where
2.778 is the conversion factor from meters to centimeters.
In ducts with natural draft air mass movement rate limited to a range of 0.5 to 1.5 m / s. Accepted for the selected house - 0.8 m / sec.
100 cubic meters the air in the kitchen will go out through the duct with the exhaust fan when cooking on the stove. For natural air exchange in the kitchen, 180 cubic meters remains. Calculate the circular cross-section of the natural draft kitchen duct.
F = 2.778 × 180 / 0.8 = 625 cm2.
Area of a circle = n × R2where n = 3.14.
625 = 3.14 × R2, R = 14.1 cm, the calculated diameter of the hood in a private house is 282 mm.
Likewise, the channels for the bathroom and the toilet will have a section of 163 mm each.
F = 2.778 × 60 / 0.8 = 208 cm2.
Area of a circle = n × R2.
208 = 3.14 × R2, R = 8.13 cm, the value of the section is determined ventilation ducts in a private house with a diameter of 163 mm.
You can select air ducts according to special diagrams with two coordinate axes: the flow rate of the air mixture and the speed of air transportation. At the intersection of the perpendiculars from these values for a specific duct, the values of its diameter are found.
Within a series of ventilation pipes, connectors, elbows, bends, etc. elements of standard sizes are produced. Their acquisition significantly increases the rate of system assembly.
The selection of the standard size of ventilation ducts is carried out in accordance with GOST, taking into account the calculation performed. For example, GOST 14918-80 is used for galvanized steel air ducts, and GOST 17079-88 for reinforced concrete.
Designers use reference books and computer programs developed on the basis of building codes and regulations: calculation algorithm ventilation Vent–Calc, selection of air ducts - Ducter 2.5, drawing ventilation SVENT, CADvent.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The following video will acquaint you with the rules for designing installations and systems for standard air exchange:
Ventilation standards are not only designed to make it easier for designers. Knowing them is useful for customers of construction and homeowners who are not provided with an adequate supply of fresh air. If the owners independently identify violations in the project, they will be able to correct the errors or at least receive compensation.
Do you want to talk about how the ventilation system works in your own house / apartment / cottage? Please leave your comments in the block form below. In it, you can share useful information on the topic, ask a question and post a photo.


