It is not enough to grow a crop in a country house or a personal plot in a village; it still needs to be somehow saved until spring. And almost the only correct option here is a personal vegetable store. Moreover, often such a cellar is set up in the garage under the inspection pit. So it comes out cheaper, and everything is in one place, and the temperature inside does not drop below zero.
But you must admit that if you dig a pit under the garage building and pour potatoes and carrots there, then the vegetables will not even last until winter. Due to excess moisture, they will simply rot. Only properly equipped ventilation in the vegetable pit in the garage is a guarantee of the safety of supplies.
We will tell you how to properly equip a storage for crops under the garage with an impeccably functioning ventilation system. All the nuances and rules are detailed in our article. Our tips will help independent home craftsmen achieve excellent results.
The content of the article:
- How much ventilation is needed for a vegetable pit
-
Ventilation system design
- The choice of pipes for air ducts in the garage
- Condensation and ice control
- Installation of ventilation in a vegetable store
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
How much ventilation is needed for a vegetable pit
A classic vegetable storehouse under a private garage (box) is a room 2–2.5 meters wide / long and up to 2 meters high. The descent into it is usually arranged from the observation pit using a ladder.
As a result, the cellar for vegetables and jars of pickles is deliberately below the level of freezing of the soil, which guarantees that the temperature in it remains above zero even in winter.
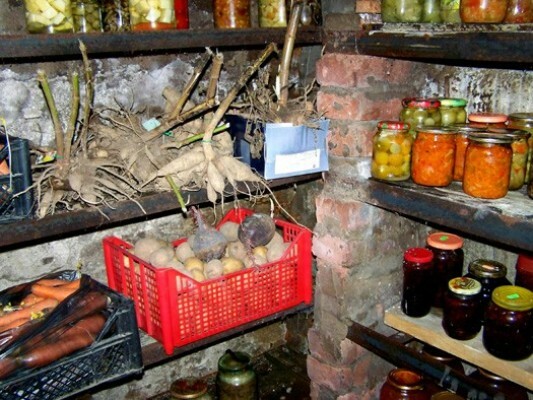

The moisture content in the vegetable store should be at the level of 80–95%. If it turns out to be lower, then the vegetables will begin to dry, and at higher rates, potatoes, beets and carrots will quickly begin to rot
Ventilation in the garage vegetable store is equipped to:
- keep the air temperature in the pit at a level from 1 to +10 0C all year round;
- remove excess moisture and carbon dioxide with ethylene from the cellar;
- ensure constant air exchange with the inflow of clean street air inside.
During storage, vegetables "breathe" and continue to ripen or gradually begin to rot. As a result of these processes, heat and moisture are constantly generated. And if they are not taken out of the vegetable store, then the humidity inside will reach 95-100%, and the temperature will rise above 10-15 0WITH. As a result, this leads to condensation and the development of rot, followed by a loss of yield.
Ideally, the following conditions should be met in the vegetable pit under the garage:
- temperature - plus 1-5 0WITH;
- humidity - 85–90%;
- air exchange - 1 time / hour (about 50-100 m3/ ton of vegetables * hour);
- light - darkening with the absence of direct sunlight, the lighting is turned on only when people are in the cellar.
In reality, these indicators can be achieved only when a ventilation system with forced aira. Moreover, it will have to include automation in its composition for stable maintenance of the microclimate.
This ventilation option will cost several hundred thousand rubles. It is completely unprofitable to spend such sums. Therefore, most often, ventilation in a garage vegetable storehouse is built in the usual natural pattern of a pair of pipes.
Ventilation system design
Ventilation in a garage vegetable store can be natural and forced. The first option is cheaper, while the second is more efficient. Another nuance - in the second case, the garage must be electrified without fail, the fan for blowing air runs from the mains.
If everything is done according to SNiPs, then when preparing a project for a ventilation system in a vegetable pit, it is necessary to take into account:
- Winter and summer temperature readings for the region.
- Groundwater level and the level of soil freezing.
- The presence of underground utilities next to the garage building (especially heating mains and water pipes).
- Types of vegetables and root crops that are supposed to be stored in the cellar.
- The volume of the stored supplies and the storage capacity.
- Presence / absence of insulation and concrete floor in the pit.
To keep potatoes, cabbage in forks, carrots, radishes and beets in the vegetable store for as long as possible, they should be kept in different compartments, if possible with a different microclimate.
But in a small personal garage, such conditions cannot be created due to the limited space available. Therefore, in the case under consideration, natural ventilation is usually organized. It is cheaper, easier to install with your own hands and does not require electricity.
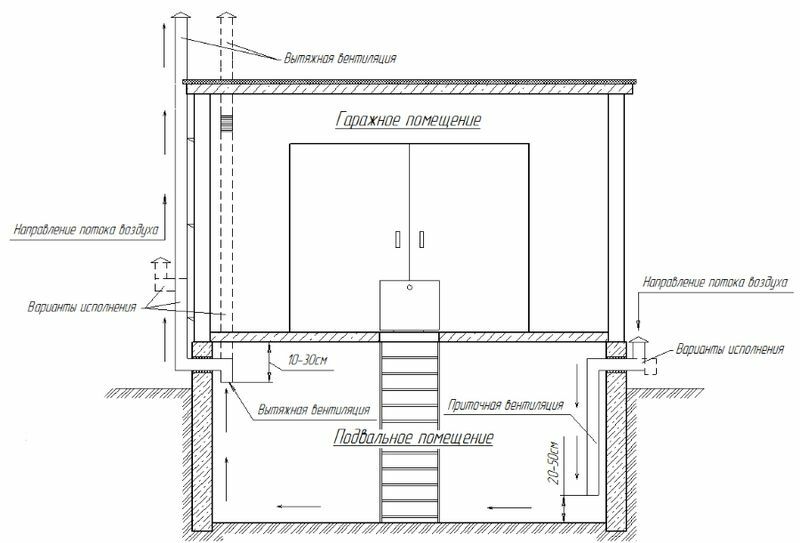
Natural ventilation is simpler and cheaper in a building. The main thing here is to correctly position the inlets and exhaust pipes. Mechanical ventilation with automation guarantees the safety of vegetables, but many times more expensive than a simpler version with natural air exchange
When organizing ventilation in a vegetable storehouse under the garage, the following points should be considered:
- The air from the garage with the exhaust from the car should not enter the vegetable pit.
- The air from the cellar, saturated with moisture from vegetables, should not enter the inspection hole and rise under the car.
- The forced ventilation system needs electricity and constant supervision.
- The system with natural air exchange in summer in the heat practically stops working, and in winter in severe frosts (if the inflow is not blocked) it can freeze the cellar.
The vegetable pit is a constant source of moisture. But the descent into it in a private garage is usually organized through a viewing pit.
If there is no maximally airtight door between these two rooms, then moist air from the bottom of the vegetables will rise under the bottom of the machine. As a result, the car from such a microclimate will begin to rust and rot.
The ventilation systems in the garage and the vegetable store must be separate, otherwise the exhaust from the car will harm the products in the pit, and the excess moisture from vegetables will lead to corrosion of the body
Cold air descends to the floor, and warm air rises to the ceiling. This is pure physics. And the higher the temperature difference, the faster such a circulation of air masses occurs.
If the supply pipe from the street is brought to the floor of the vegetable pit, and the exhaust pipe is mounted outside under the ceiling or connected to a common garage hood, then a natural draft is formed in such a duct system.
And if the ventilation ducts are calculated correctly, then the air exchange will be more than sufficient to remove excess heat and moisture from the vegetable storehouse to the street.
When the intake and exhaust pipes are narrowed, the air exchange rate in the garage cellar will be low. And if you set them too wide, then the circulation will be excessive. In the first case, it will be too warm and humid in the pit, and in the second vegetable store during the winter it may freeze.
The optimal variant of the duct diameter for a natural ventilation system in a garage cellar with an area of 3–6 m2 - 100-150 mm.
The choice of pipes for air ducts in the garage
To organize natural ventilation in the garage box itself, it is enough to build one ventilation duct in it for the exhaust through the roof of the building. In this case, the air supply will be carried out through an open door and air vents on both sides of it at the bottom of the wall.
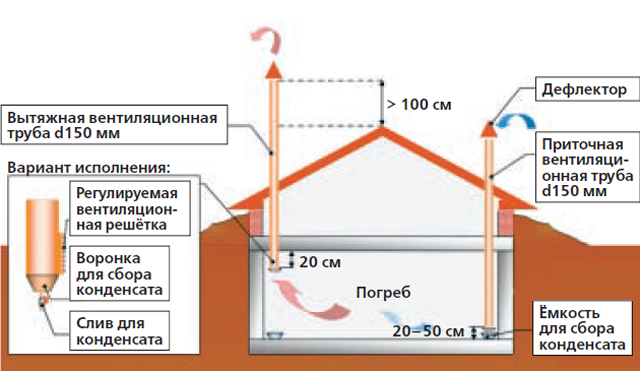
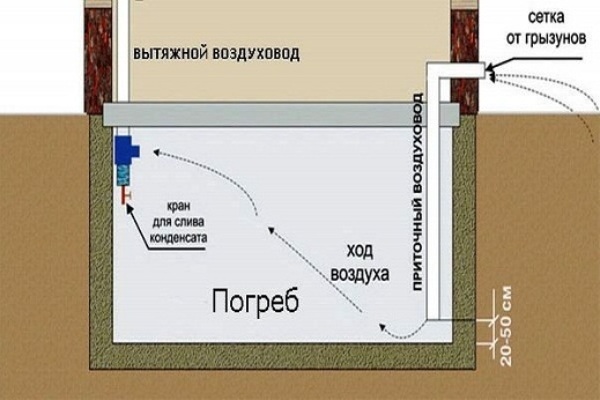
To ventilate the garage vegetable pit, it is necessary to mount two ventilation pipes with a diameter of 100-150 mm - supply from the street to the floor of the cellar and exhaust from its ceiling upwards with an outlet to the roof
For the ventilation device for vegetable storage in the garage, the following are used types of air ducts:
- plastic (PVC or polyethylene);
- iron galvanized;
- asbestos;
- aluminum.
The asbestos and PVC options are the cheapest. Moreover, if the first is non-combustible, then the second does not absorb moisture. Metal pipes are more expensive, but they are more durable and tolerate frost more calmly.
Condensation and ice control
It is impossible to completely get rid of the constantly forming moisture in the vegetable store. It comes from vegetables, ground underfoot and condensation from the walls in the pit. At the same time, it is also not recommended to dry the air in the cellar unnecessarily. This is harmful to stored supplies.
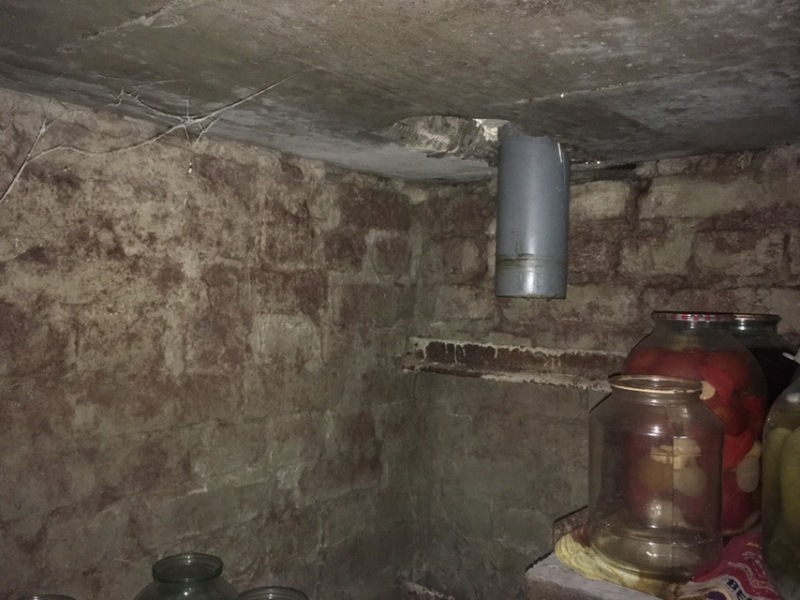

One of the main tasks of ventilation in the vegetable pit is to remove excess moisture from the underground room under the garage and keep the air humidity inside at the level of 85-90%
When warm air enters a cold cellar, condensation instantly falls on the walls and everything in the vegetable store. If the hood does not work well, then the latter will remain inside and contribute to the development of mold on the vegetables. And with a sharp cold snap, it will instantly turn into ice, which is also unpleasant.
The wider the ventilation pipes, the stronger the air exchange takes place. However, this is good in summer, but completely unnecessary in winter. In winter, the air flow, on the contrary, must be reduced as much as possible so as not to unnecessarily lower the temperature inside.
To provide yourself with maximum control over what is happening in the vegetable pit, you should provide:
- control valve on the supply pipe;
- the ability to completely shut off the inflow and exhaust air in case of severe frosts;
- insulation of both air ducts;
- the possibility of installing an electric exhaust fan for forced drying of the cellar.
Also, if there is lighting in the basement, condensation can lead to a short circuit. Therefore, the better the vegetable pit itself is insulated, the garage above it and the ventilation pipe, the better.
Installation of ventilation in a vegetable store
Before you start doing ventilation in the vegetable pit of the garage, everything should be calculated and all the necessary materials should be prepared in advance. Also, one should not neglect the drawing up of a small room plan indicating the points of the location of the air ducts.
It seems that you only need to make a couple ventilation ducts. But without a preliminary drawing, even with their installation, you can trick something.
To organize natural ventilation in the room under consideration, pipes 8–9 meters long will be required (3.5–4 m for the inflow and at least 4 m for the exhaust). This is taking into account the presence of a viewing hole.
If it is not there, then it is necessary to build on the depth of the cellar and the height of the ceiling of the garage box. Plus, you will need a glass for condensate with a drain valve, metal grilles for ventilation openings from the street and a cap or a deflector.
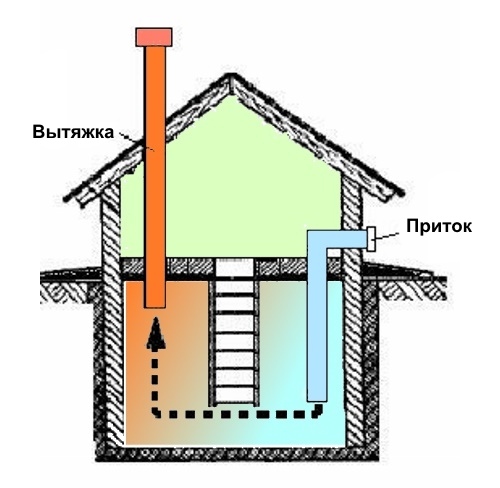
The supply and exhaust pipes should be bred diagonally to opposite corners of the vegetable store so that air circulation captures all its corners
Installation of ventilation in the garage and vegetable pit is as follows:
- Holes for a supply pipe are made in the wall near the garage door with an indent from the ground of 20-30 cm and through the ceilings down into the cellar.
- Holes for the hood are made in the roof of the garage and the ceiling of the pit.
- Ventilation pipes are mounted (a condensate collector is installed at the bottom of the hood).
- A valve is installed on the air intake pipe.
- If necessary, ventilation ducts are insulated with moisture-resistant foam or foam.
- A rain hood is installed on top of the exhaust pipe.
To prevent rodents from getting in through the ventilation in the vegetable store, a metal grate should be installed on the vents of the air flow from the street. In this case, the distance from the edge of the exhaust pipe to the ceiling of the vegetable pit should not exceed 20 cm, and the supply pipe should rise above its floor by a maximum of 50 cm.
The inflow duct in the pit should be positioned so that the incoming outside air does not get onto cans and vegetables. It is cold in winter and should warm up a little at first.
Otherwise, the total temperature in the cellar will be at +5 0C, and locally near the ventilation pipe everything will freeze. For the same reason, this ventilation duct should be removed from the wall by at least 30-50 cm so that a frost coat does not grow next to it.
The rules and formulas for calculating the area of air ducts will acquaint next article, which we recommend to independent home craftsmen.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Ventilation in the vegetable store under the garage:
How to make ventilation in a vegetable pit:
The owners who decide how best to arrange ventilation in the garage vegetable pit have only two options at their disposal. You can make a forced system with a fan or organize air exchange with natural air circulation. The first method is volatile and expensive, but also effective in any weather.
In the overwhelming majority of cases, just the second is used. A pair of pipes for the supply and exhaust, spaced diagonally in the cellar in different corners, are usually quite enough to provide the required level of air exchange in the room in question.
You still have questions on the topic or have your comments on how to properly ventilate in a vegetable store in the garage - write below. We will definitely help you understand all the nuances of ventilation in a vegetable cellar.


