Thanks to its high energy efficiency and environmental friendliness, natural gas, along with oil, is of paramount importance. It is widely used as a fuel and also serves as a valuable raw material for the chemical industry.
And although the use of gas has become everyday and habitual, it still remains difficult in composition and a rather dangerous substance - to get into the burner of a gas appliance, it passes a long and difficult way.
In this article, we will analyze the main issues related to natural combustible gas - we will talk about its composition and properties, we will describe the stages of production, transportation and processing of gas, its scope. Let's consider modern ideas about the origin of hydrocarbon reserves, interesting facts and hypotheses.
The content of the article:
-
What is Natural Combustible Gas?
- Features of the chemical composition
- Physical properties of gas
-
Where does the gas in the bowels of the earth come from?
- Basic theories of origin
- Interesting facts and hypotheses
- How is mining and transportation going?
- Processing and scope
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
What is Natural Combustible Gas?
There is an opinion that gas lies underground in cavities and is easily extracted from there, for which it is enough to drill a well. But in reality, everything is much more complicated: gas can be inside a porous rock, it can be dissolved in water, liquid hydrocarbons, oil.
To understand why this happens, it is enough to remember that the word “gas” comes from the Greek “chaos", Which reflects the principle of substance behavior. In the gaseous state, the molecules move chaotically, trying to uniformly fill the entire possible volume. Due to this, they are able to penetrate and dissolve in other substances, including denser liquids and minerals. High pressure and temperature greatly enhance the diffusion process. It is often in the form of such a "cocktail" that natural gas is contained in the bowels.
But first, let's talk about what gas consists of and what it is - consider the chemical composition and physical properties of natural combustible gas.
Features of the chemical composition
Gas extracted from the subsoil, which is called "natural", is a mixture of various gases.
According to its composition, it is divided into three groups of components:
- combustible - hydrocarbons;
- non-combustible (ballasts) - nitrogen, carbon dioxide, oxygen, helium, water vapor;
- harmfulimpurities - hydrogen sulfide and mercaptans.
The first and main group is a set of methane hydrocarbons (homologues) with the number of carbon atoms from 1 to 5. The largest percentage in the mixture is methane (70 to 98%), which has one carbon atom. The content of other gases (ethane, propane, butane, pentane) ranges from units to tenths of a percent.
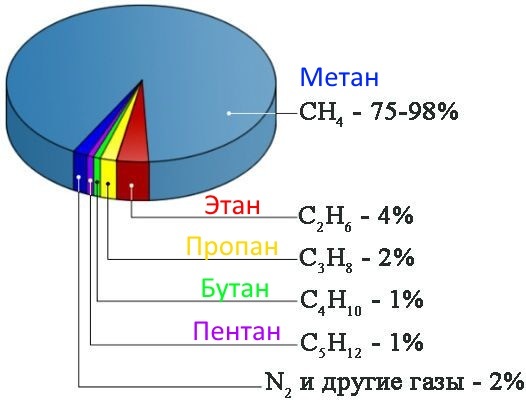
Gas produced from the fields is characterized by a high concentration of methane. In the associated, extracted from oil, the proportion of methane is much lower: 30 - 60%, and the homologues are higher: 10 - 20%
In addition to hydrocarbons, small amounts of incombustible substances may be present in the mixture: hydrogen sulfide, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, hydrogen and others. But, depending on the field, the proportions of hydrocarbons, like the composition of other gases, can vary significantly.
Physical properties of gas
According to the physical properties, methane СН4colorless and odorless, very flammable. At concentrations in air over 4.5% - explosive. This property, combined with its lack of odor, poses a great threat and problem. Especially in mines, as methane is absorbed by coal.
We wrote about the causes of gas explosion in domestic conditions in this material.
To give the gas a smell, in order to detect its leaks, special substances with an unpleasant odor are added to it before transportation - odorants. Most often, these are sulfur-containing compounds - ethanethiol or ethyl mercaptan. The proportion of the impurity is selected in such a way that a leak is felt at a gas concentration of 1%.
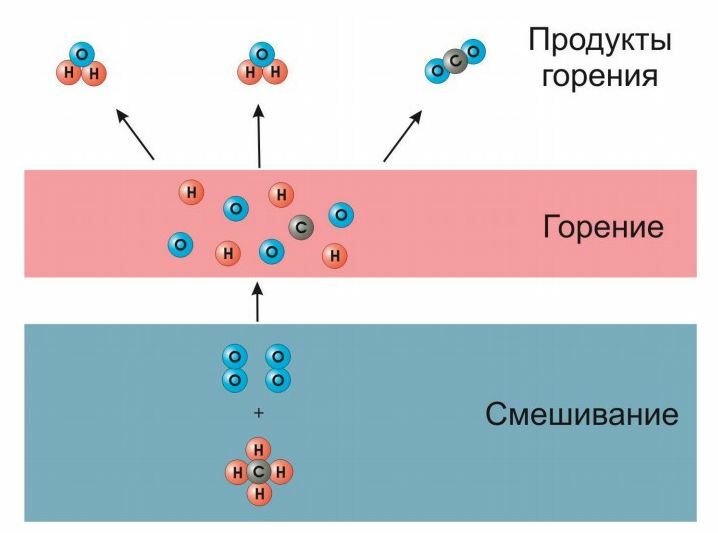
The main advantage of blue fuel is its high specific heat of combustion - 39 MJ / kg. In this case, harmless substances are released: water and carbon dioxide. It is also an important factor that allows methane to be used in everyday life.
Where does the gas in the bowels of the earth come from?
Although people learned to use gas more than 200 years ago, there is still no consensus about where the gas comes from in the bowels of the earth.
Basic theories of origin
There are two main theories of its origin:
- mineralexplaining the formation of gas by the processes of degassing hydrocarbons from deeper and denser layers of the earth and raising them into zones with lower pressure;
- organic (biogenic), according to which gas is a decomposition product of the remains of living organisms under conditions of increased pressure, temperature and lack of air.
In a field, gas can be in the form of a separate accumulation, a gas cap, a solution in oil or water, or gas hydrates. In the latter case, the deposits are located in porous rocks between gas-tight clay layers. Most often, these rocks are compacted sandstone, carbonates, limestones.
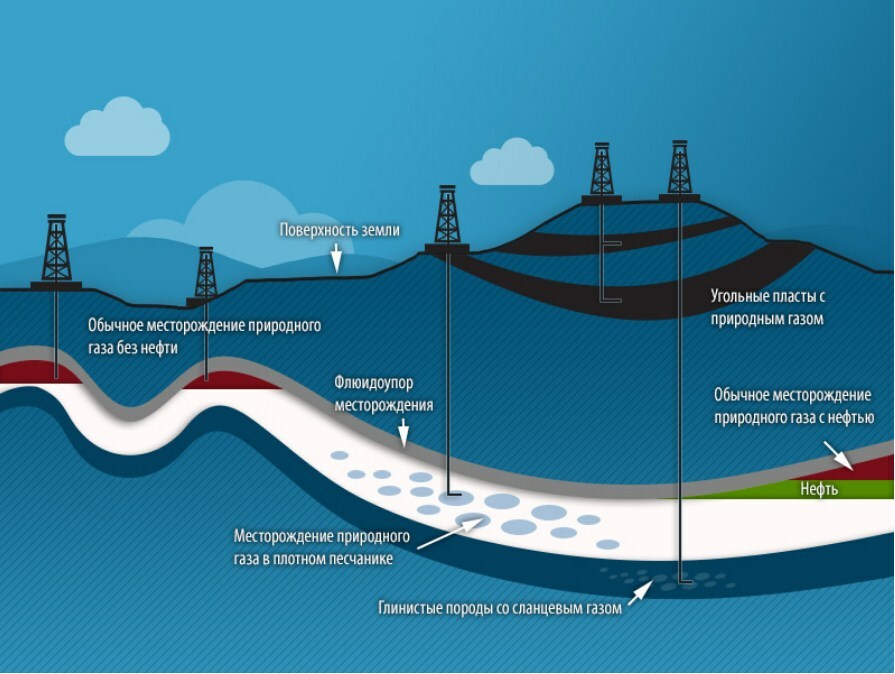
The share of conventional gas fields is only 0.8%. A slightly larger percentage is accounted for by deep, coal and shale gas - from 1.4 to 1.9%. The most common types of deposits are water-dissolved gases and hydrates - in approximately equal proportions (46.9% each)
Since gas is lighter than oil and water is heavier, the position of the fossils in the reservoir is always the same: gas is on top of oil, and water is supporting the entire oil and gas field from below.
The gas in the reservoir is under pressure. The deeper the deposit, the higher it is. On average, for every 10 meters, the pressure increase is 0.1 MPa. There are formations with abnormally high pressure. For example, on the Achimov deposits of the Urengoyskoye field, it reaches 600 atmospheres and higher at a depth of 3800 to 4500 m.
Interesting facts and hypotheses
Not so long ago it was believed that the world's oil and gas reserves should be depleted at the beginning of the 21st century. For example, the authoritative American geophysicist Hubbert wrote about this in 1965.
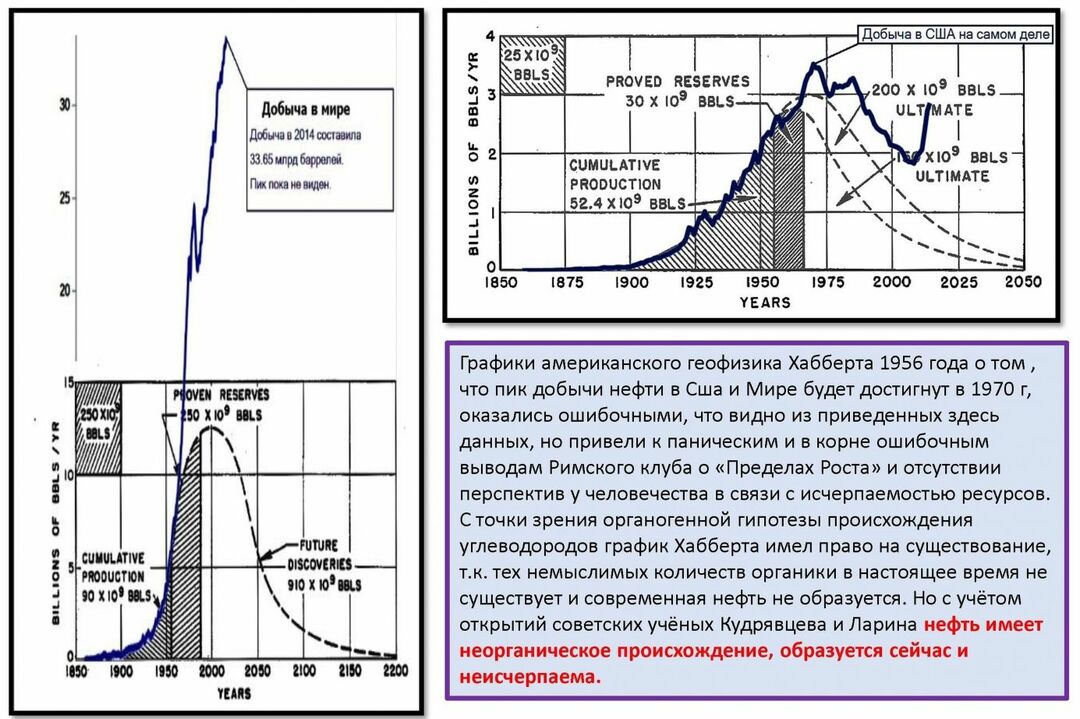
Until now, many countries continue to increase the rate of gas production. There are no real signs that hydrocarbon reserves are running out.
According to the doctor of geological and mineralogical sciences V.V. Polevanov, such delusions are caused by the fact that the theory of the organic origin of oil and gas is still generally accepted and dominates the minds of the majority scientists. Although D.I. Mendeleev substantiated the theory of the inorganic deep origin of oil, and then this was proved by Kudryavtsev and V.R. Larin.
But many facts speak against the organic origin of hydrocarbons.
Here is some of them:
- deposits were discovered at depths of up to 11 km, in crystalline basements, where the existence of organic matter cannot be even theoretically;
- with the help of organic theory, only 10% of hydrocarbon reserves can be explained, the remaining 90% are inexplicable;
- The Cassini space probe discovered in 2000 on the satellite of Saturn, Titan, gigantic hydrocarbon resources in the form of lakes, several orders of magnitude larger than those on Earth.
The hypothesis of an initially hydride Earth put forward by Larin explains the origin of hydrocarbons by the reaction of hydrogen with carbon in the depths of the earth and the subsequent degassing of methane.
According to her, there are no ancient Jurassic deposits. All oil and gas could have formed between 1 and 15 thousand years ago. As the extraction proceeds, the reserves can be gradually replenished, which has been noticed in long-depleted and abandoned oil fields.
How is mining and transportation going?
The process of extracting natural combustible gas begins with the construction of wells. Depending on the occurrence of the gas-bearing layer, their depth can reach 7 km. As drilling progresses, a pipe (casing) is lowered into the well. To prevent gas from escaping through the space between the pipe and the borehole walls, plugging is done - filling the gap with clay or cement.
Upon completion of construction, the drilling rig is retracted and the Christmas tree is installed on the casing head. It is a design of gate valves and valves, and is used to extract gas from the well.
The number of wells can be quite large.
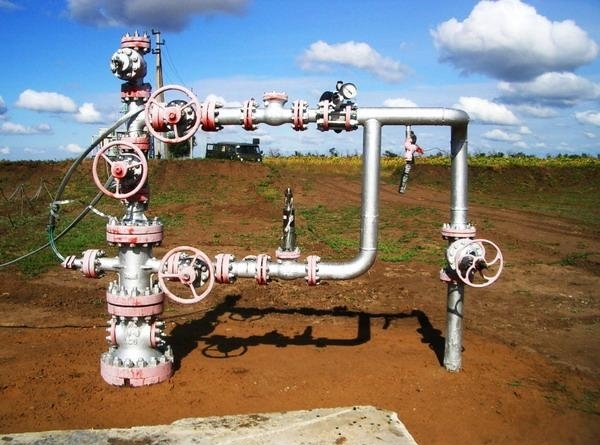

The Christmas tree has several functions: it keeps it suspended in the well tubing, controls operating modes, measures the parameters of the external and internal parts wells
The entire production cycle of natural combustible gas takes place in three stages:
- Gas field development. As a result of drilling, a pressure difference is created. Due to this, the gas moves through the formation to the wells.
- Operation of gas wells. At this stage, the gas travels along the casing.
- Collection and preparation for transportation. Gas from all X-mas tree is supplied to special technological complexes of the UKPG. Gas dehydration takes place on them, cleaning from harmful impurities.
Even small concentrations of hydrogen sulfide, water vapor or solid particles lead to rapid corrosion, hydrate formation and mechanical damage to the inner surface of the pipeline.
Final preparation for transportation takes place at the head facilities. It includes post-treatment and removal of hydrocarbon condensate, gas cooling to reduce its volume.
The main type of gas transportation over long distances is main gas pipeline. It is a system of complex engineering structures from the pipelines themselves to underground storage.
There are gas distribution stations (GDS) at the end point of the mainline. Here, the last cleaning of dust and liquid impurities takes place, pressure is reduced to the level required by consumers, its stabilization, gas consumption metering and the addition of an odorant.
Another common type of methane transportation is sea transportation by special vessels - gas carriers.
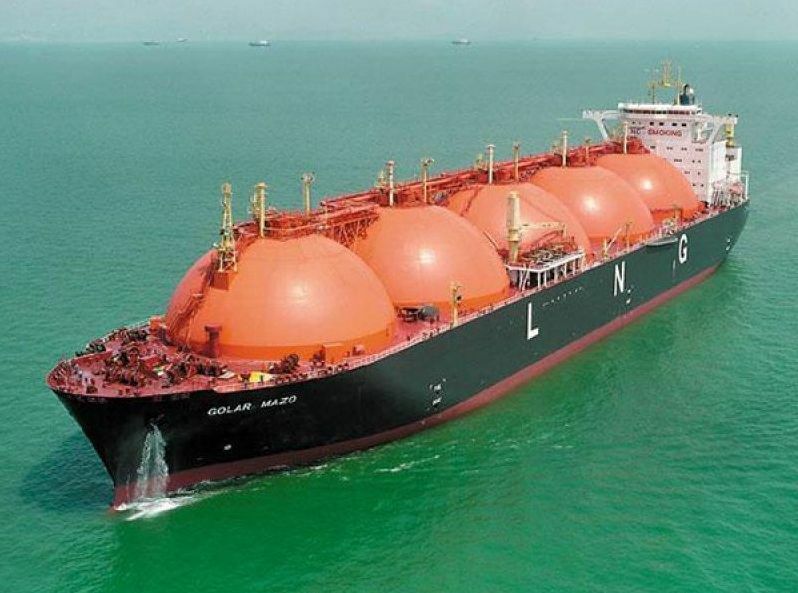

Huge spherical tanks will not allow the LNG carrier to be confused with other types of vessels. They are thermoses that maintain a constant required temperature for liquid methane -163 ° С
The transformation of gas into a liquid state is carried out in special LNG plants. The process takes place in two stages: first, the methane is cooled to -50 ° C, and then to -163 ° C. At the same time, its volume decreases 600 times.
Processing and scope
The high flammability of natural gas determines its main application. It is used as a fuel in factories, factories, thermal power plants, boiler houses, offices, residential buildings, agricultural facilities and many others. We recommend that you read the rules use of gas in everyday life.
Oil production and processing is always accompanied by the release of associated gas. In some cases, its volumes can be impressive and amount to 300 cubic meters per one cubic meter of crude oil.
But there are a large number of fields where natural associated gas is not used, but is burnt in flares. For example, up to 25% of useful raw materials are lost in this way throughout Russia.
Part of the associated gas is supplied to gas processing plants. From it, purified dry gas is obtained, which is used for heating. Another valuable ingredient is a mixture of light hydrocarbons.
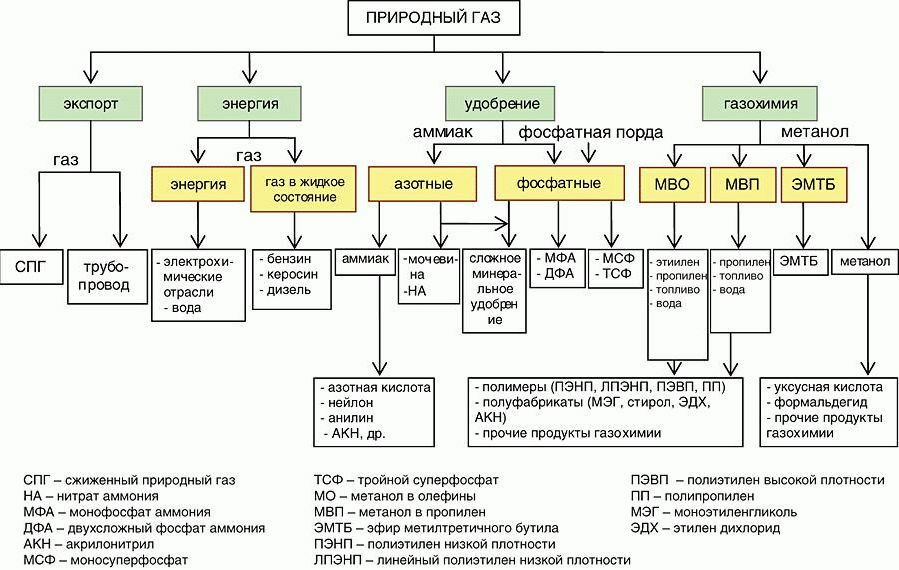
The diagram shows a general picture of the gas processing process. The role of end products for the modern chemical industry cannot be overemphasized
Further, it is divided into fractions in special installations. The result is hydrocarbons such as propane, butane, isobutane, pentane. To reduce the volume, ease of transportation and storage of them liquefy.
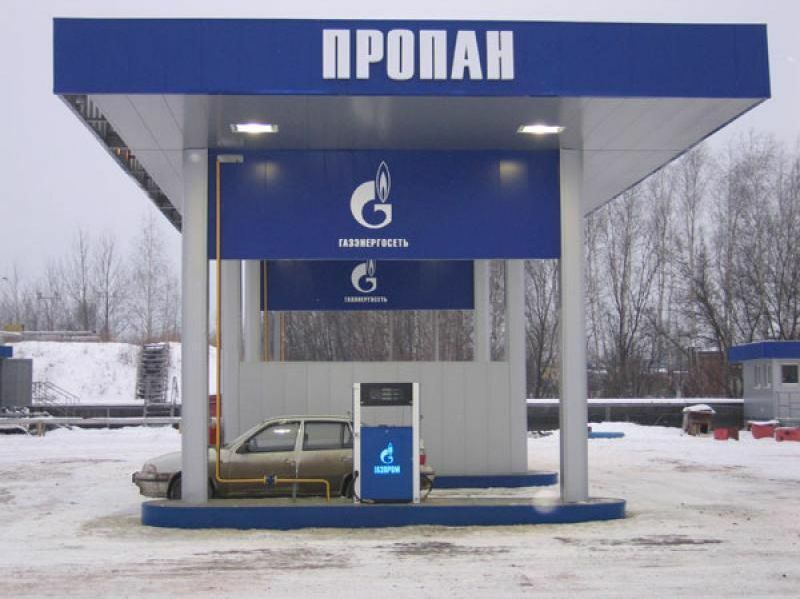

Converting vehicles to gas quickly pays for itself and provides tangible cost savings. Expansion of the network of gas filling stations contributes to an increase in the fleet of vehicles with LPG. It is not only drivers who win, but also pedestrians who do not have to breathe harmful fumes
Propane and butane are used for heating houses bottled gas either for cars. But most of it goes for further processing at petrochemical plants.
By means of high-temperature heating (pyrolysis), the main raw material for all synthetic materials is obtained from them - monomers: ethylene, propylene, butadiene. Under the action of catalysts, they combine to form polymers. The output is such valuable materials as rubber, PVC, polyethylene and many others.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The documentary tells about gas in an accessible and visual way:
This educational film is dedicated to the main gas transportation:
We still do not know everything about natural gas - its origin is still fraught with many mysteries. We can only hope that blue fuel is a truly inexhaustible gift that will be enough for both us and our descendants.
Do you have any questions after reading the above material? Or would you like to supplement the article with useful comments, interesting facts or photographs? Write your comments, ask questions, participate in the discussion - the feedback form is located below.


