Sellers of condensing-type heat generators declare that the efficiency of the innovative equipment offered to us exceeds 100%. But you must admit that this slightly contradicts the law of conservation of energy, which is familiar to all of us from the school physics course. So what's the mystery?
On the one hand, such statements are a trick of marketers. However, on the other hand, there is a grain of truth in their assurances that convince the buyer. We will analyze in detail how a condensing boiler works: the advantages and disadvantages, its specific operation and design deserve a detailed study.
In order to get a complete picture of the condensing type of equipment, let us compare it with the classic type of thermal energy generator. Here are the features of its connection and operation. Let's uncover the secrets of ultra-high performance.
The content of the article:
-
Gas condensing boiler
- Device and principle of operation
- Nuances of operation: condensate and chimney
- Where does the efficiency come from above 100%?
- Pros and cons of condensing heater
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Gas condensing boiler
The high efficiency of the condensing gas heat generator is ensured by the presence of an additional heat exchanger in its design. The first heat exchange unit, standard for all heating boilers, transfers the energy of the combusted fuel to the heat carrier. And the second adds to this also the heat from the exhaust gas recovery.
Condensing boilers operate on "blue fuel":
- main (gas mixture with a predominance of methane);
- gasholder or balloon (mixture of propane with butane with a predominance of either the first or second component).
Any gas option can be used. The main thing is that the burner is designed to work with one or another type of fuel.
Condensing gas boilers are more expensive than conventional convection models, but they outperform them in terms of fuel costs by reducing gas consumption by 20-30%
The condensing heat generator shows the best efficiency when burning methane. The propane-butane mixture is slightly inferior here. Moreover, the greater the proportion of propane, the better.
In this respect, the “winter” gas for the gasholder gives a slightly higher efficiency at the outlet than the “summer” one, since the propane component is higher in the first case.
Unlike a condensing gas boiler, in a convection boiler, part of the heat energy goes into the chimney together with the combustion products. Therefore, for classical designs, the efficiency is in the region of 90%. You can raise it higher, but technically too difficult.
This is not economically justified. But in condensation tanks, the heat obtained from gas combustion is used more rationally and fully, since the heat released during processing of steam is accumulated and transferred heating system. In this way, the coolant is additionally heated, which makes it possible to reduce fuel consumption per 1 kW of heat received.
Device and principle of operation
By design, a condensing boiler is in many ways similar to a convection analogue with a closed combustion chamber. Only inside it is supplemented with a secondary heat exchanger and a recuperation unit.
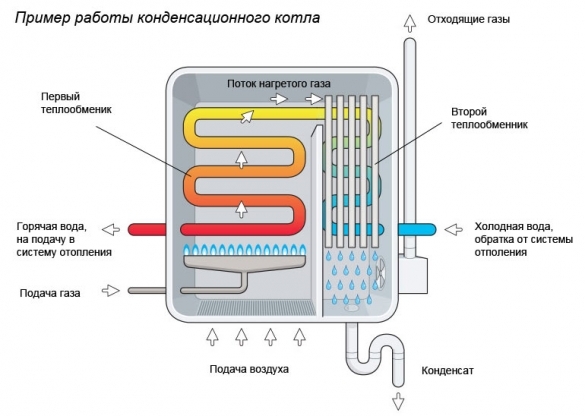
The main features of the condensing heat generator device are the presence of a second heat exchanger and a closed combustion chamber with a fan
The gas condensing boiler consists of:
- closed combustion chambers with modulating burner;
- primary heat exchanger No. 1;
- exhaust gas cooling chambers up to + 56–57 0C (dew point);
- secondary condensing heat exchanger No. 2;
- chimney;
- air supply fan;
- condensate tank and drainage system.
The equipment in question is almost always equipped with a built-in circulation pump for coolant. The usual version with a natural flow of water through the heating pipes is of little use here. If there is no pump in the kit, then it will definitely need to be provided when preparing a boiler piping project.
Additional percentages of efficiency for a condensing boiler are formed as a result of heating the return flow by cooling the exhaust gases in the chimney
Condensing boilers on sale are single-circuit and double-circuit, as well as in floor and wall versions. In this they do not differ from classical convection models.
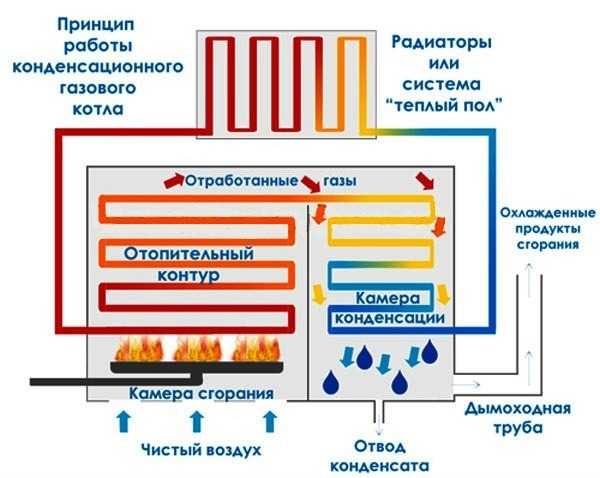
The principle of operation of a condensing gas boiler is as follows:
- The heated water receives the main heat in heat exchanger No. 1 from gas combustion.
- Then the coolant passes through the heating circuit, cools down and enters the secondary heat exchange unit.
- As a result of condensation of combustion products in heat exchanger No. 2, the cooled water is heated by recovered heat (saving up to 30% of fuel) and goes back to No. 1 in a new circulation cycle.
In order to accurately control the flue gas temperature, condensing boilers are always equipped with a modulating burner with an output rate of 20 to 100% and an air supply fan.
Nuances of operation: condensate and chimney
In a convection boiler, the combustion products of natural gas CO2, nitrogen oxides and steam are cooled only to 140-160 0WITH. If you cool them below, then the draft in the chimney will drop, aggressive condensate will begin to form and the burner will go out.
Such a development of the situation, all manufacturers classic gas heat generators strive to avoid in order to maximize operational safety as well as extend the life of their equipment.
In a condensing boiler, the temperature of the gases in the chimney fluctuates around 40 0WITH. On the one hand, this reduces the requirements for heat resistance of the material. chimney, but on the other hand imposes restrictions on its choice in terms of resistance to acids.
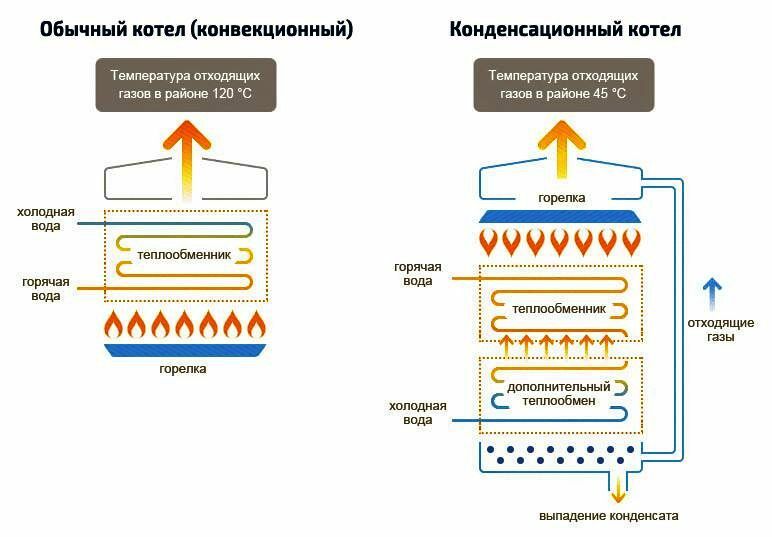
Exhaust gases from a gas boiler during cooling form an aggressive, highly acidic condensate that easily corrodes even steel
Heat exchangers in condensing heat generators are made from:
- stainless steel;
- silumin (aluminum with silicon).
Both of these materials have enhanced acid resistance properties. Cast iron and common steel are completely unsuitable for condensers.
The chimney for a condensing boiler may only be installed from stainless steel or acid-resistant plastic. Brick, iron and other chimneys are not suitable for such equipment.
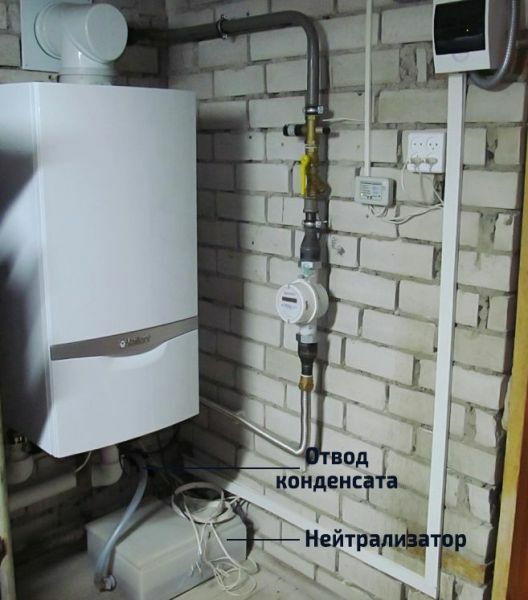

During recuperation, condensate forms in the secondary heat exchanger, which is a weak acidic solution and must be removed from the water heater
When operating a condensing boiler with a capacity of 35–40 kW, about 4–6 liters of condensate are formed. Simplified, it comes out about 0.14-0.15 liters per 1 kW of thermal energy.
In fact, this is a weak acid, which is forbidden to be discharged into an autonomous sewage system, since it will destroy the bacteria involved in waste processing. Yes, and before dumping into a centralized system, it is recommended to first dilute with water in a ratio of up to 25: 1. And then you can already remove it without fear of destroying the pipe.
If the boiler is installed in a cottage with a septic tank or VOC, then the condensate must first be neutralized. Otherwise, it will kill all microflora in an autonomous purification system.
"Neutralizer" is made in the form of a container with marble chips with a total weight of 20-40 kg. As it passes through the marble, the condensate from the boiler increases the pH. The liquid becomes neutral or low alkaline, no longer dangerous for bacteria in the septic tank and for the material of the sump itself. It is required to change the filler in such a neutralizer every 4–6 months.
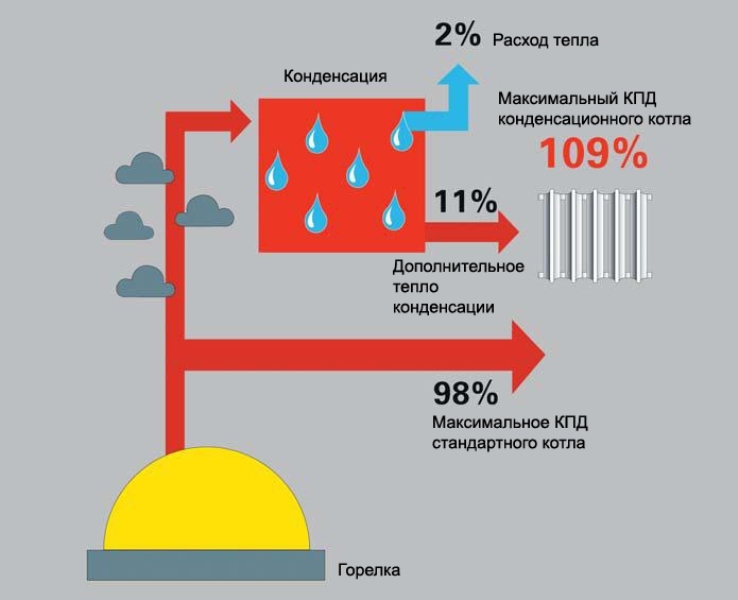
Where does the efficiency come from above 100%?
When indicating the efficiency of a gas boiler, manufacturers take as a basis the indicator of the lowest calorific value of gas without taking into account the heat generated during condensation of water vapor. In a convection heat generator, the latter, together with approximately 10% of the heat energy, completely goes into chimney, therefore, it is not taken into account.
However, if you add the condensation secondary heat and the main one from the burnt natural gas, then more than 100% efficiency will come out. No scams, just a little trick in the numbers.

When calculating the efficiency for the highest heat of combustion for a convection boiler, it will be in the region of 83-85%, and for a condensing boiler - about 95-97%
In fact, the "wrong" efficiency above 100% arises from the desire of heat generating equipment manufacturers to compare the compared indicators.
It's just that in a convection device "water vapor" is not considered at all, but in a condensation device it must be taken into account. Hence, there are small discrepancies with the logic of basic physics, which is taught at school.
Pros and cons of condensing heater
Among the advantages of a condensing boiler are:
- Reduction of harmful emissions by 60–70% (most of the carbon dioxide and nitric oxides go into condensate).
- In comparison with convection models, savings of up to 30% of gas fuel per generated 1 kW.
- Smaller dimensions of gas heating equipment with the same power.
- Low temperature of combustion products in the chimney (only about 40 0WITH).
- Possibility of installing a cascade of several boilers.
- Versatility (suitable for both heating radiators and "warm floors").
- Smart automation and full autonomy of the gas heat generator without human intervention.
A cascade system of two or three heat generators allows you to install low-power boilers that make less noise and vibrate during operation than more powerful models.
This simplifies the installation of the entire heating system and allows you to reduce the size home boiler room. Plus, due to the possibility of more flexible regulation of the heat generation process, the overall efficiency of the use of heat generating equipment increases.

The costs of a condensing boiler in comparison with a conventional convection boiler are recouped in 5-6 years due to savings on natural gas
Of the disadvantages of condensing heat generators, it should be mentioned:
- High price tag for equipment (1.5–2 times higher than that of models of the classic convection type of similar power).
- Condensate disposal problems.
- Decreased efficiency when using the boiler in high temperature heating systems.
- Volatility - the fan, automation and circulation pump require electricity to operate.
- Prohibition of use with antifreeze.
Despite the significant initial costs, the condensing boiler is economically justified. During operation, it more than returns all the money initially spent.
In Russia, such equipment is still not widespread. Gas recovery boiler is still too unusual and little studied in our market. But interest in such heat generators is gradually growing.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
How a condensing heat generator works:
Installation of gas boilers with steam recovery:
All the advantages of condensing boilers:
If you carefully understand how and according to what principles a gas condensing boiler works, then at first glance the "incorrect" 108–110% efficiency becomes quite understandable and justified figures.
A heat generator with exhaust gas recuperation is indeed more efficient than a conventional design. Its only serious drawback is condensate with high acidity, which must be disposed of somewhere.
Please write your comments in the block form below. It is possible that you own information that can replenish the stock of information presented in the article. Ask questions, share your own experience in the selection and operation of condensing boilers, post photos on the topic of the article.


