Are you going to gasify your home? Perhaps you are equipping an autonomous gas supply system with a gas holder? In this case, you need to know about gas condensate traps.
They will help to avoid many problems in the use of gas and will extend the life of equipment that consumes gas, as well as the gas pipeline itself and chimneys. A properly selected and installed condensate trap significantly improves the quality of the gas and ensures the safe functioning of the entire system.
In this article we will tell you what functions are performed by condensate traps on a gas pipeline, what is deposited in them, what they are and how they differ, what is the principle of operation of these valves, how to install them and service.
The content of the article:
- Why do you need a condensate trap on a gas pipeline?
- The structure and principle of operation of the collection
-
Recommendations for the selection of condensate traps
- Criterion # 1 - the shape of the condensate collector
- Criterion # 2 - pressure in the gas pipeline
- Criterion # 3 - other equipment parameters
- Condensate trap installation procedure
- Nuances of equipment maintenance
- How to do without gas condensate traps?
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Why do you need a condensate trap on a gas pipeline?
Both methane and liquefied propane-butane mixture require additional treatment. This is due to the conditions of storage and use, imperfection of gas distribution systems.
There are various impurities in gases:
- Water can get into a gas pipeline during its construction, checking and purging, as well as through the smallest holes or slots. It corrodes the steel and destroys the chimney
- Butane (liquid) can be recondensed from a propane-butane mixture. It does not evaporate and does not rise through the gas pipeline at subzero temperatures, in frost. Liquid butane in a gas burner forms a torch, and in a boiler it provokes a shutdown or explosion.
- Fine solid particles can get into the gas from the tanks and pipelines of the system, especially if they are not new and the process of corrosion has begun inside. Because of them, the nozzles are clogged.
Each of these types of impurities is dangerous in its own way. Water, liquid butane in a gas burner forms a torch, and in a boiler it provokes an explosion; solid particles clog the nozzles.
The condensate collector is engaged in filtration, accumulation and removal of foreign inclusions.
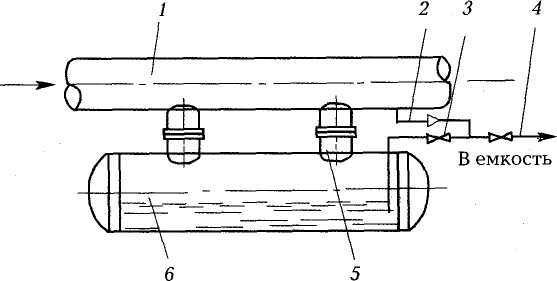
The condensate trap consists of the following components: 1) gas pipeline; 2) pressure equalization line; 3) shut-off valves; 4) purge pipe; 5) condensate drain; 6) a condensate collector installed under the gas pipeline
Everything heavy, including liquid butane, collects in the condensate trap, preventing dangerous situations that it can provoke.
The structure and principle of operation of the collection
Low pressure condensate traps are fundamentally different from fittings designed for operation with medium or high pressure gas pipelines.
This is a vertical cylindrical container with a convex or conical bottom, to the upper part of the walls of which are welded on both sides nozzles for connecting to the gas pipeline, and through the lid a tube is brought to the surface of the earth, under a special visor - a carpet for pumping condensate.
Gas passes through the top of the glass from one branch pipe to another, and all liquid or solid impurities from it settle at the bottom. In such systems, the gas pressure is not enough to push the liquid through the tube of the unit, and it must be pumped out with a pump, just like you drink a drink from a glass through a straw.
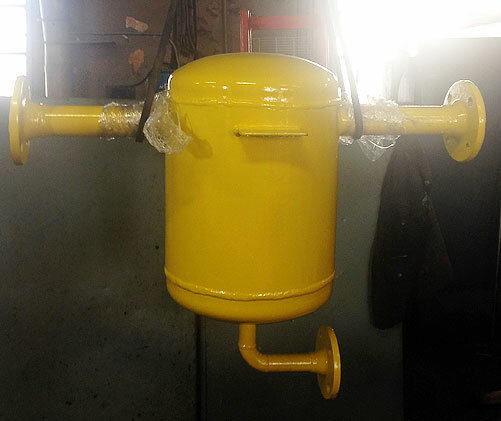

In aboveground condensate traps, sometimes the drain pipe is located at the bottom, and the condensate is simply drained off when the tap is opened under the force of gravity
Medium and high pressure condensate collectors are expansion tanks in which the gas is, as it were, settled. Due to a significant increase in the cross-sectional area, compared to gas pipes, the flow rate decreases, and all heavy liquid and solid particles have time to settle.
The main part of the unit - the collection - is a cylindrical container with convex ends, like a tank. Two branch pipes are diverted from it from above: in the first, the condensate flows by gravity from the pipeline, and in the second, the gas that has entered the condenser together with the liquid returns to the pipeline.
The blowing tube for removing condensate in medium or high pressure devices is necessarily equipped with a valve - and not a plug, as in the first version. In some cases, the gas pressure in the system may be sufficient to remove all condensate when the valve is opened. This is more often the case with condensate traps installed on the surface of the earth.
In underground tanks, only at a pressure of at least 15-20 kPa, the accumulated liquid rises independently along the discharge tube and splashes out of it into a special tank. At the same time, at the surface of the earth, it can freeze, from which not only the removal of condensate stops, but the tube in which this happens, up to rupture, can also be damaged.
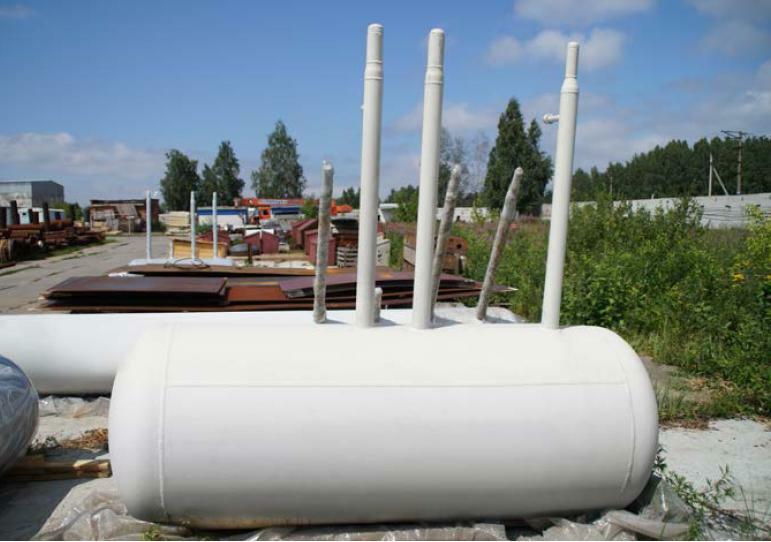

To avoid freezing in winter, there is another gas-filled riser in the underground high and medium pressure condensate traps, installed parallel to the discharge pipe. It is connected to the main one at the surface of the earth and creates back pressure in it, not releasing liquid in frost.
In addition, such condensate accumulators are usually equipped with additional equipment. It could be pressure gauge to control the pressure inside the tank, liquid level sensorwhich will show how much condensate has already been collected, filling indicatorcommanding the unit to service and drain the collected fluid.
Not uncommon in such installations - automatic liquid removal device. On the condensate trap installed in front of the compressor, the full indicator automatically switches it off.
Recommendations for the selection of condensate traps
Depending on the parameters of your gas pipeline, there is a huge range of condensate traps for gas pipeline on the market. Some manufacturers are ready to manufacture a unit of any modification according to your personal order, which exactly meets all the requirements, if a suitable model is not in the presented product line.
Gas systems are varied in shape, pressure, operating conditions, filling, operating conditions - there are many options for combining these parameters. Therefore, there are no less options for condensate traps for gas pipelines.
An incorrectly selected unit will not cope with the tasks assigned to it or it will be unreasonably large and expensive, so we advise you to entrust the final choice to specialists. And in order to orient ourselves a little in this variety, we will understand their main differences and the principles of choice according to these parameters.
Criterion # 1 - the shape of the condensate collector
The container itself for collecting condensate can be placed horizontally, like a tube or a small cistern, or vertically, resembling a pot. It is possible to determine how the selected condensate trap should be located not only by its shape, but also by the location of the connection pipes: they are always directed horizontally.
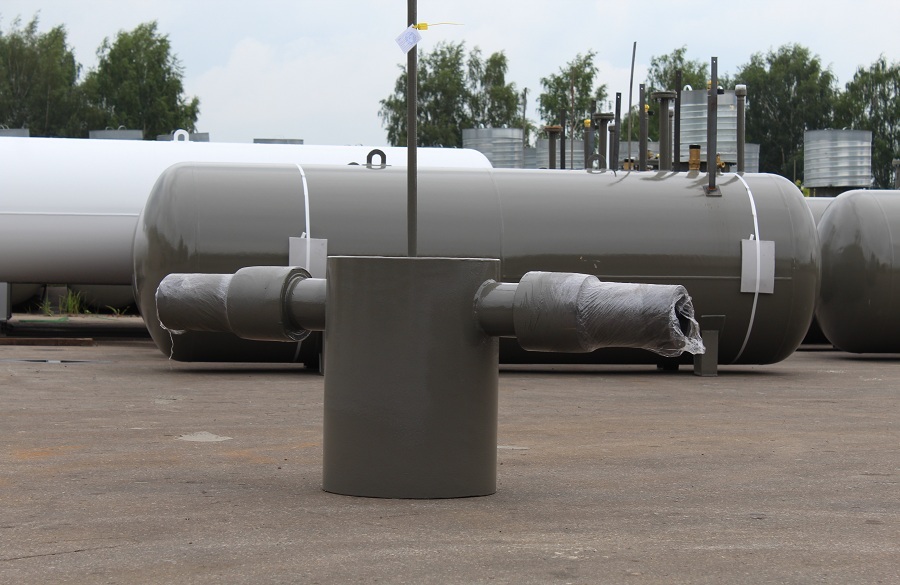

The shape of the condensate trap does not always depend on the design pressure: there are vertical ones for main pipes, and mini-tanks for low pressure
Vertical condensate traps are most often used on gas tanks, they are connected to a tank and to a vertical pipe supplying gas to the house, while the condensate collection pot is located vertically, parallel to the pipe.
Horizontal models are usually hung or supported under a horizontal pipe, parallel to it. They are more often of high pressure and large volumes.
Criterion # 2 - pressure in the gas pipeline
It is important to purchase a condensate trap designed for the same pressure as the entire gas pipeline. There are 3 options: for low, middle and high pressure.

Sometimes condensate traps are produced already connected to a section of gas pipe - this allows you to minimize the amount of welding work in the field
They differ not only in the size and diameter of the connection nozzles, but also in the internal structure, the way of installation and maintenance. Therefore, a pressure mismatch can make installation and operation not only ineffective but also dangerous.
Criterion # 3 - other equipment parameters
In addition to the mentioned shape and pressure, they differ in the following parameters:
- Volume - from a couple of hundred milliliters to several cubic meters, depending on the tendency of the gas pipeline to form condensate, gas composition, climatic conditions, volume of transported gas and place of installation condensate trap.
- Material, from which the condensate receiver is made - as a rule, stainless steel. It can withstand the aggressive environment of moisture and liquid butane for a long time without additional processing. However, condensate traps, especially of large volumes, are often made of ordinary steel. For additional protection, it is treated not only outside, like the entire gas pipeline, but also inside - for example, with an epoxy compound.
- At the place of installation condensate collectors are underground and aboveground. On the second, the labeling "Gas", "Flammable" is required.
- External waterproofing should be the same as on the gas pipeline. Most often these are polyethylene adhesive tapes, but it can also be bitumen mastic or bitumen-polymer coating. For overhead equipment, protection with waterproof paint, always yellow, is sufficient.
- Connections to the gas pipeline differ in diameter, and can also be designed for a welded seam or permanent connection between steel and plastic.
- Optional equipment. In addition to the inlet and outlet nozzles, there is always a tube for draining or pumping out the collected condensate. There may also be connectors for a pressure gauge, a liquid level sensor, a tank filling indicator, for pressure equalization.
Private consumers, as a rule, purchase a condensate collector for private gas tanks when arranging an autonomous gas supply to the estate.
Gas tanks for a private house are of different volumes, the quality of gas and operating conditions also differ - this affects the choice of a condensate trap
For such purposes, usually small devices are used with a vertical, glass-like container and a long tube for pumping condensate. They are usually installed underground, directly at the gas tank inlet, and usually do not have additional equipment.
High pressure condensate traps are installed on main gas pipelines, at gas distribution points and in front of large industrial consumers. They have a large volume and shape of a tank, almost always equipped with additional sensors and alarms.
Condensate trap installation procedure
The method and procedure for connecting the condensate collector depends on the place of its installation.
The main places for collecting and draining condensate from gas are as follows:
- At the exit from the gas tank in autonomous gas supply systems.
- On low sections of the gas pipe or at the junction of pipes with the opposite slope.
- At the beginning ("head") of the gas pipeline - at an oil refinery, after a gas distribution station or a storage tank.
- In front of the compressor, in order to avoid disruptions in its work, as well as in front of factories and other industrial consumers.
- At the outlet of the gas from the compressor - here the condensate is collected if the compressor was stopped, or oil was pumped out from the tanks, filling them with gas.
The development of a plan for the location of condensate collectors is a task for the chief engineer of a company that transports and distributes gas to consumers.
It determines not only the installation location of such units and the distance between them, but also the type, size and other characteristics. After installation, the location of the equipment must be accurately signaled by special plates indicating the direction and distance to it.
The installed underground condensate trap should be located at a distance from water bodies, wells, trees and buildings, its location is indicated by signs
When choosing a place for the condensate trap, the convenience of further maintenance is also taken into account. There should be not only free access to the condensate drainage tube, but also the ability, if necessary, to dig it out for maintenance, repair or replacement. The device itself is located no less than 2 m from the nearest wall, and its connection to the pipe is no closer than 1 m from the wall. It is also prohibited to install such devices above the freezing point of the soil.
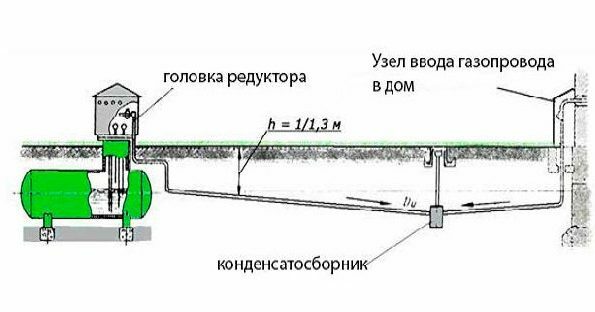
Private consumers may be faced with the need to install a condensate trap only on a gas tank - we will dwell on this issue in more detail. The gas tank is installed on distance from home, according to the requirements of the standards - at least 10 m, and therefore the pipe to the basement input is usually laid horizontally underground.
In such a scheme, this pipe is divided into 2 parts with an opposite slope, and a condensate collector is installed at their junction, at the lowest point. A small foundation is poured under it, and the unit itself is placed on legs to minimize corrosion. The inlet and outlet of the device are welded to the gas pipe, and the condensate pumping pipe is extended to the surface of the earth, plugged with a stopper and covered with a carpet.

The condensate trap can only be connected with permanent connections, welding, and threaded and flanged ones are not allowed. This ensures safe operation and reduces the risk of leaks.
If gas is discharged to the surface of the earth vertically, directly from the gasholder, then the place for collecting condensate is the very beginning of the pipe. In this case, one branch pipe is welded to the pipe, and the second - either to it, just below, or to the tank itself. The condensate drainage pipe runs parallel to the gas riser.
Nuances of equipment maintenance
According to the schedule developed by the engineer of the gas supply company, purge condensate traps and checking their technical condition. This work is considered hazardous because the condensate contains not only water, but also flammable liquid butane, which often makes up the majority of the liquid. Therefore, two specialists carry out maintenance, only during the day, not during a thunderstorm.
It is also forbidden to drain condensate directly into a tank truck - only into metal stationary containers with a fence or into a pit. If there is an oil pipeline nearby, you can drain the condensate into it.
To empty the low pressure condensate trap, you need a pump, motor pump or vacuum tank. A plug is removed from the end of the tube, a pump hose is connected to it, a tap is opened and the pump is started. Pumping is continued until the liquid stops flowing from the pump, and then it is turned off, the valve is closed, the hose is disconnected and the plug is returned to its place.
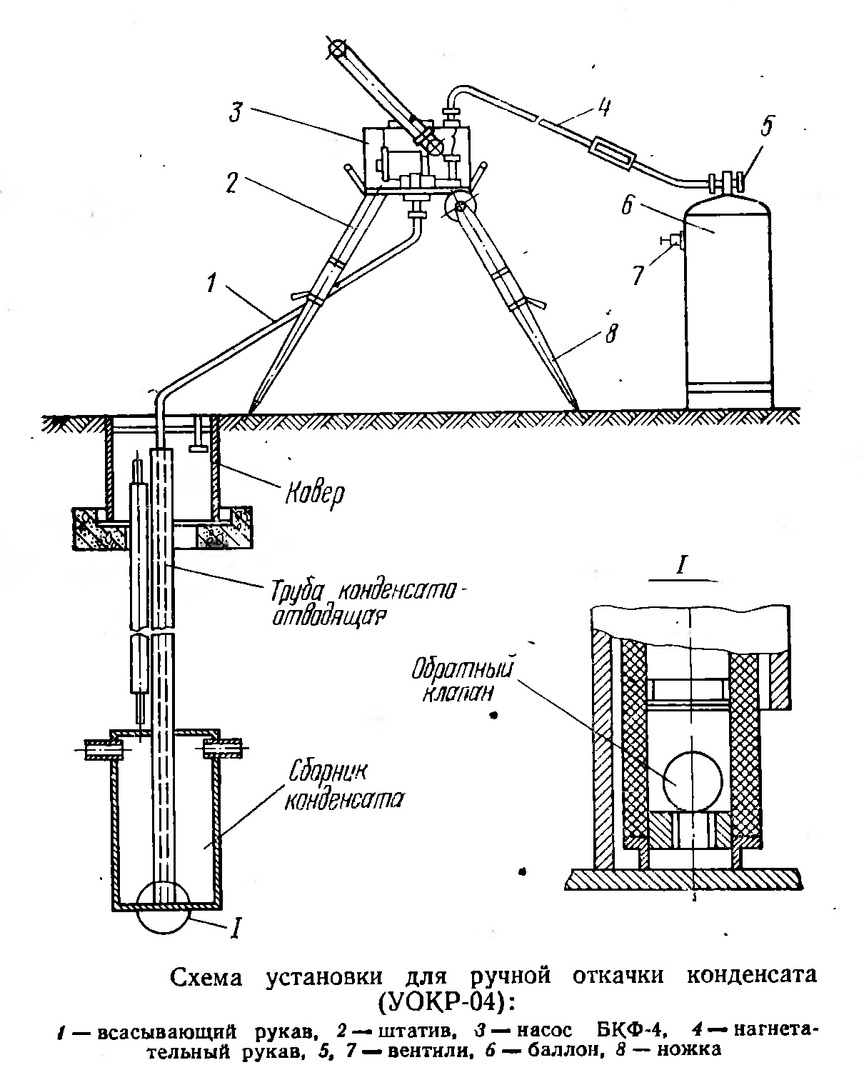
A small condensate trap can also be handled with a hand pump, and some models for aboveground installation drain the liquid by gravity
Condensate traps of medium and high pressure usually do not need a pump. They have 2 risers: with condensate and with gas, each has a tap, and usually only the one on the gas is open.
To free the reservoir from the liquid, both valves are turned: the gas valve is closed, and the condensation valve is opened. The liquid comes out under gas pressure from the line. To save time and labor costs, this process can be automated through instrumentation and automation.
If the condensate is not removed in time, a water hammer or plug can not only obstruct the gas supply, but also damage the pipe.
In addition to removing the collected condensate, pipeline crawlers check the presence and accuracy of the labels, indicating their location, as well as the serviceability of the unit itself and the associated shut-off fittings. If necessary, repairs are carried out immediately or an act is drawn up, according to which a special team later leaves.
How to do without gas condensate traps?
The condensate trap installed on the gas pipeline is a guarantee of the safety and security of the equipment.
But there are also alternatives. As a rule, they are aimed at preventing the formation of condensation. Among such funds - vaporizers, returning vaporous butane to the gas tank, thermal insulation and heating of the pipeline, laying it deeper than the freezing point, using pipes of a larger diameter.
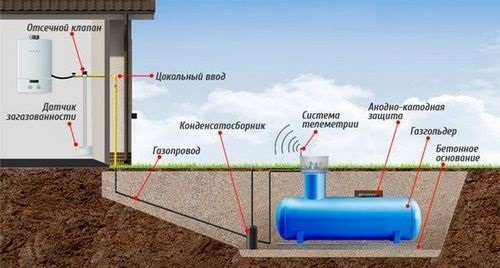
Heating the gas pipeline will prevent the formation of the most dangerous part of the condensate - the liquid phase of butane, but its construction and operation are not cheap
However, their use is not always possible and effective, moreover, it is usually more expensive than installing a condensate trap.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
To get a better idea of the principle of operation of the condensate trap, we suggest watching the following video:
A visual aid on what gas condensate is in the following story:
We have analyzed why gas condensate traps are needed, what they are and how they work, and what criteria to pay attention to when choosing a suitable container. We also talked about how and where they are installed and serviced by condensate traps and what are the alternative solutions.
Have you already encountered this equipment? With what and for what reason? Share your experience of use and other information on the topic - the feedback form is located below this publication.