The underground laying of gas pipelines has many advantages. They do not spoil the exterior of city buildings and the suburban landscape, do not interfere with the movement of vehicles, do not force existing buildings to be displaced. But they have a significant drawback - this is the complexity of monitoring both the pipe itself and the medium moving along it.
We will tell you how a control tube on a gas pipeline helps to monitor the state of the system. Let's get acquainted with the design features of this device. Let's analyze the location options and installation rules.
From the article presented by us, you will find out where and in what sequence control pipes are installed on the gas pipeline system. Get acquainted with the peculiarities of attaching them to cases and semicircular casings. You will understand how necessary it is to monitor the technical condition of an underground pipeline.
The content of the article:
- The purpose of monitoring the condition of an underground gas pipeline
- What is the case for the gas pipeline?
- Test tube design
- Rules for installing and fixing the tube
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The purpose of monitoring the condition of an underground gas pipeline
Gas pipelines laid in trenches need regular inspection no less than overground routes. Of course, they are not threatened with purely mechanical damage, as happens with openly arranged communications. However, gas workers have no less reason to worry about their condition.
If the pipe carrying blue fuel is submerged in the ground:
- It is difficult to monitor the mechanical state of a gas pipeline, but its walls are affected by soil pressure, weight structures and pedestrians, as well as passing vehicles, if the highway passes under a highway or railway branch.
- Corrosion cannot be detected in a timely manner. It is caused by aggressive groundwater, the soil itself, which contains active components. The loss of the initial technical characteristics is facilitated by technical fluids that penetrate to the depth of the route.
- It is difficult to determine the loss of tightness resulting from the failure of the integrity of the pipe or weldment. The reason for the loss of tightness is usually oxidation and rusting of metal pipelines, banal wear of polymer structures or violation of assembly technology.
Despite the fact that the laying of gas pipelines in trenches provides for the complete replacement of aggressive soil with soil with neutral properties, and the device in places of possible spillage of technical fluids is completely prohibited, without special devices they cannot be considered completely protected from chemical aggression.
Image gallery
Photo from
The underground laying technology is used in the construction of high, medium and low pressure gas pipelines. Pipes laid in trenches do not spoil the landscape, do not interfere with movement
Pipes laid in closed trenches require regular inspection and maintenance no less than surface gas lines
Despite the complete replacement of aggressive soils in the trench, corrosion of metal pipes and gradual wear of polymer pipelines is virtually inevitable.
It is necessary to constantly monitor the welds connecting both polyethylene and electric-welded pipes, installation points of fittings and other places of possible gas leaks
Low pressure gas pipeline device
High pressure gas pipeline construction
Gas pipeline construction
Welding of polyethylene pipes before laying
As a result of the loss of tightness, gas leaks, which, as it should be for all gaseous substances, rushes upward. Penetrating through the pores in the soil, the gaseous toxic substance comes to the surface and creates negative zones for the entire living area above the gas pipeline.
A gas leak can easily become the cause of a serious catastrophe if the blue fuel that left the pipe "finds" any cavity in the ground for accumulation. When heated, for example, the elementary effect of sunlight in the sultry summer, the explosion of the accumulated gaseous fuel is almost inevitable.

The occurrence of a gas leak from the pipeline threatens not only with a violation of the ecological balance, but also with serious catastrophic consequences: explosions, destructions, fires.
In addition, a gas leak entails considerable financial losses for the gas production and gas transportation organization. Moreover, disagreements may arise between them, with which it is not even worth going to court, if a control tube for monitoring was not installed on the gas pipeline case.
What is the case for the gas pipeline?
In the device of underground gas communications, as a rule, steel or polyethylene gas pipescapable of withstanding the pressure of the medium passing through them. Their strength characteristics are designed for the load created by the soil thickness up to 2.0-2.2 m. However standard pipe-rolling is not designed for a possible transport load from above, i.e. over the gas highway.
It is also not taken into account that the pipelines through which the gas moves to the consumer, it is undesirable to pass under other communication lines. There are also geological and hydrogeological restrictions, in accordance with which the gas pipeline has to be laid above the established norms.
If it is impossible to find a laying route that does not cross other engineering structures, according to the requirements of SNiP 42-01-2002 between the pipelines, it is necessary to ensure a safe distance along vertical. This is 0.2 and more meters, which, as a result, changes the depth of the gas pipeline.

On difficult sections of the gas pipeline route, requiring protection of the pipe from damage, laying is carried out in cases
The depth of the gas pipe is also changed if rocky rocks or unstable groundwater level interfere with the laying at the standard depth mark.
How to protect a gas pipeline if an additional load on the line is unavoidable? In all these cases, cases are used, which are a rigid round or semicircular casing made of steel alloy, polyethylene or fiberglass in cross section. It is he who protects the path of blue fuel from possible damage.
It should be noted that it is even more difficult to monitor the state of the pipe laid in the case when protecting a gas pipeline. To facilitate the hard work of linemen, employees of the mining industry and gas supply structures, a control tube is installed on the gas pipeline.
Image gallery
Photo from
The purpose of the case is to protect the gas pipeline from possible mechanical, biological and chemical negative influences
Protects areas with multiple welded joints - potential gaseous fuel leakage areas
Cases are used in cases of a decrease in the standard depth of pipeline laying due to unfavorable geological and hydrogeological conditions.
If, to control the operation of the gas pipeline system, inspection wells are arranged on the route, cases are installed at the entrance and exit to the monitoring point.
Protection is used if the gas pipeline route passes next to a residential building, industrial or public facility
The use of a case to protect underground gas pipeline branches is recommended in areas with uncontrolled traffic and pedestrian traffic.
Before the withdrawal and after the introduction of a part of the gas pipeline to the surface, 2 m of underground laying is installed in a case
The laying of gas and other communications under the railway, tram and automobile tracks is carried out in cases. In this case, the depth of the pipe can be increased.
Gas pipeline device in a protective case
Potential pipe depressurization point
Unfavorable hydrogeological conditions
Checkpoint on the underground highway
Close proximity to residential building
Suburban area with uncontrolled movement
Exit of the underground gas pipeline to the surface
A group of cases under a railway embankment
We list all the possible prerequisites for the installation of cases with control devices over gas pipelines:
- The close location of the underground gas main to a residential building or a public building.
- Shallow gas pipeline laying.
- Device under transport routes: automobile, tram, railway tracks.
- The presence of a threaded joint or weld on electrically welded metal pipes and polyethylene analogues.
- "Intersection", i.e. passage 0.2 m above or below the heating network and other communication lines.
- Input gas supply pipe to the house through the load-bearing wall and the vertical intersection of the slabs.
- Construction of a control and measuring point with a protective carpet. They are installed along the entire route every 200 m within cities and other settlements. On an area free from residence, they arrange after 500 m.
All of the above options, except for the crossing of the ceiling by the gas pipe, as well as the arrangement of the entrance and underground line exit on the surface provide for the installation of a control tube on one of the edges of the case.
Even in the case of installation over a problematic weld, it is allowed to use not the cases as a base for fastening the tube, but a semicircular metal casing.
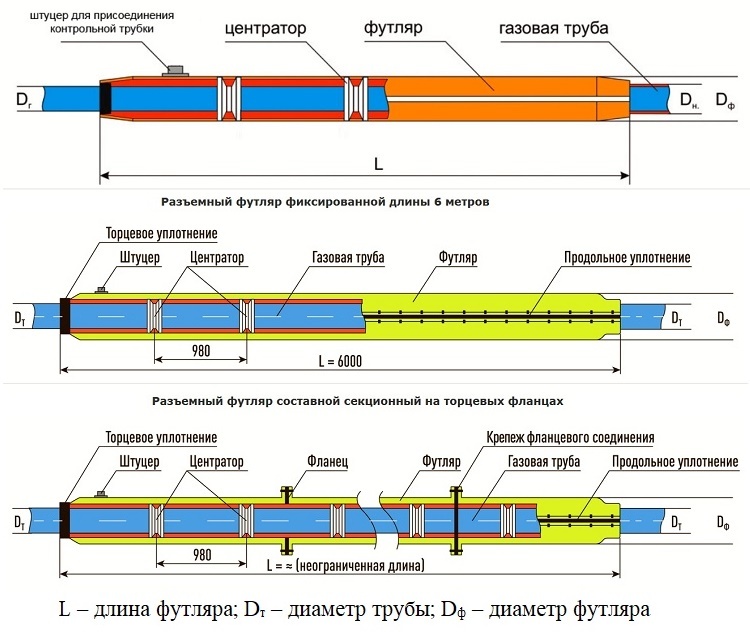
In the arrangement of underground gas pipelines, steel, polyethylene and fiberglass cases are used. Structurally, they are one-piece pipes, connected by two halves of the pipe or one semicircular casing
The test tube is placed in a place convenient for monitoring. Those. from the side from which the approach of the gas worker for monitoring operations is possible, safe and does not require obtaining permits.
If two gas pipelines are laid in one trench, which is allowed by building codes, then the location of the cases with the pipes connected to them should ensure that both systems are monitored.
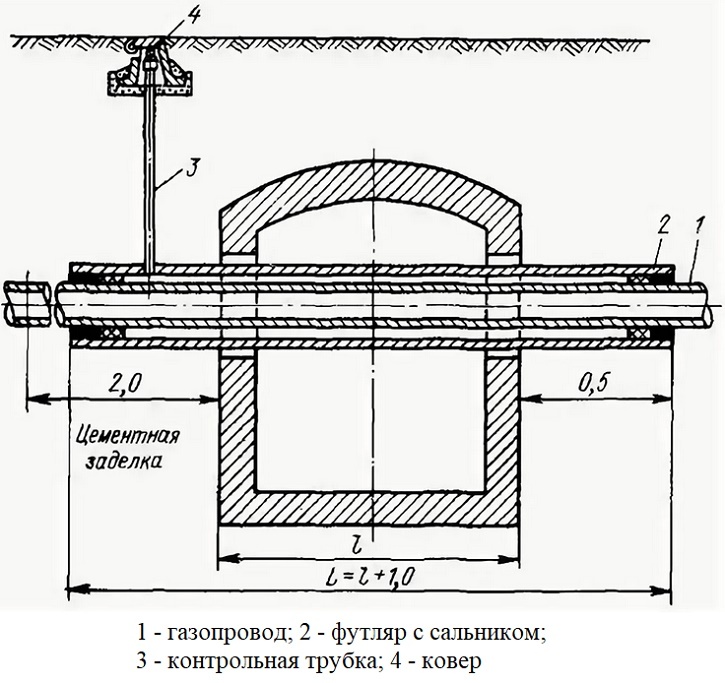
A control tube is installed on each case designed to protect the gas pipeline, necessary for monitoring the technical condition of the underground system and determining the moment of fall pressure
Cases are installed both on newly laid gas pipeline lines and on existing branches by puncturing or pushing through the soil. They should go beyond the boundaries of highways, highways, load-bearing walls and other structures by 2 m from both edges.
Test tube design
According to the standards, the minimum distance from the top of the case to the daytime surface is 0.8 m, the maximum distance is 3.0 m. In places where transport load is not planned, the minimum thickness of the soil above the case can be reduced to 0.6 m. surface.
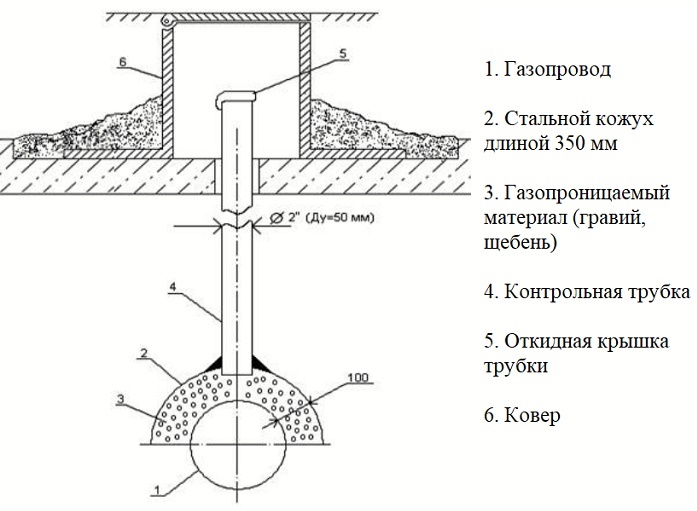
If the control tube is installed not on a case, but on a semicircular casing, which is the upper half of the pipe, it is fastened after filling the gas pipeline with a layer of sand at least 10 to 20 cm
Structurally, this control device is literally a tube fixed with one end on the case or semicircular casing of the gas pipeline. The second is brought to the surface and supplied with either a clapper cover or a sleeve with a tightly screwed screw plug.
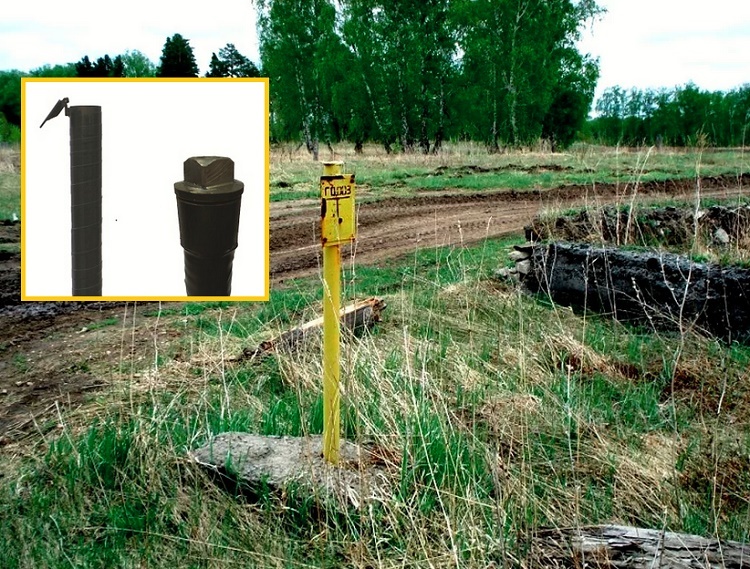

The upper end of the control gas tube is closed either by a flip-top cover or by a screw-type plug. All devices coming out to the surface of the gas pipeline shut-off and control devices are painted in bright yellow
The diameter of the control tubes, which are installed on the case or casing of the gas pipeline, according to technical standards, is 32 and 57 mm. However, they can be produced according to the sizes required by the customers. In this case, for the production of a series of tubes, a project is developed and technical specifications with quality requirements are approved.
Rules for installing and fixing the tube
Fastening of the control tube to the case or semicircular casing of the gas pipeline is carried out in accordance with the material of the pipe and the protective system.
There are three main methods used in installation:
- Installation of a control tube with a semicircular metal casing welded to its base. They are placed as an ordinary control point on the gas pipeline route without a case after laying a steel or polyethylene pipe and partially filling it with sand up to 0.2 m.
- Fastening to a polyethylene case using a saddle and resin-to-steel adapter. A hole for fixing the control tube is drilled before installing the case.
- Welding the base of the tube to the steel case. The welded assembly is arranged along a hole pre-drilled in the gas pipe.
If the pipe is not welded directly to the gas pipeline, then there is always a layer of sand between its base and the pipe. The tube itself is wrapped in plastic wrap or covered with a waterproofing primer.
Image gallery
Photo from
The test tube is easiest to install on a case with a pre-made mounting hole for it. It is great if it is equipped with a branch pipe that plays the role of a guide
Upon completion of the assembly of the gas pipeline section in the case with the mounting hole, the control tube is simply installed in the hole. Tighten if threaded or welded
On polyethylene pipelines, control tubes are installed mainly with the use of a saddle branch, which ensures the tightness of the assembly
In most cases, control tubes are welded to metal cases and semicircular housings.
Mounting the Pre-Hole Case
Fitting the tube to the case
Fastening via saddle outlet
Welding the test tube on site
In the new generation cases made of fiberglass, the attachment point of the control tube is laid during the manufacturing process. This solution greatly facilitates the installation process. The pipe is screwed on before installation and the joint is sealed, after which the foundation pit with the gas pipeline is filled with soil.
The design and arrangement of the top of the control tube is carried out in accordance with the type of surface through which it is removed. In the presence of a hard surface (concrete slab, asphalt), a protective cap, a carpet is placed over the top. In the absence of a hard coating, the tube is taken out 0.5 m above the ground and smoothly bent through 180º.
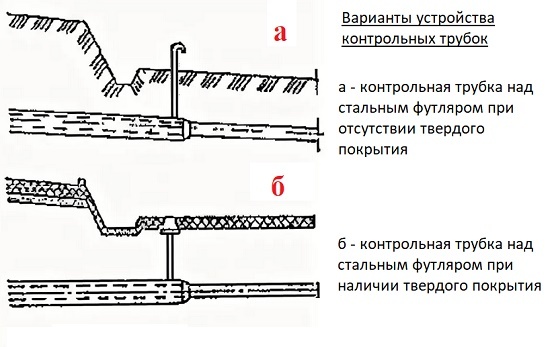
The scheme of arrangement of the exit of the control tube to the surface depends on the type of this particular surface. If it passes through asphalt or concrete, a carpet is installed, if there is loose soil around it, the tube is bent
Through the control tube, a lineman who is obliged to monitor the technical condition of the gas pipe and density of the transported gas, inserts the gas analyzer hose or the pressure gauge sensor and takes readings devices. The data taken by him are recorded in the survey log.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The following video will acquaint you with all types of structures and devices intended for servicing the gas pipeline and monitoring its technical condition:
Information about the nuances of laying and arranging gas pipelines will be useful to owners of suburban areas who want to connect their property to a centralized gas supply.
Of course, the information will be extremely useful to those who intend to organize an autonomous network with a gas tank and pipes laid from it. With the installation of a control tube, it will be much easier to monitor the status of the underground system.
Please leave comments in the block form below the text of the article, ask questions, post photos on the topic. Tell us about your own experience in arranging control devices for monitoring the operation of a gas pipeline at your own site. Share useful information that may be useful to site visitors.