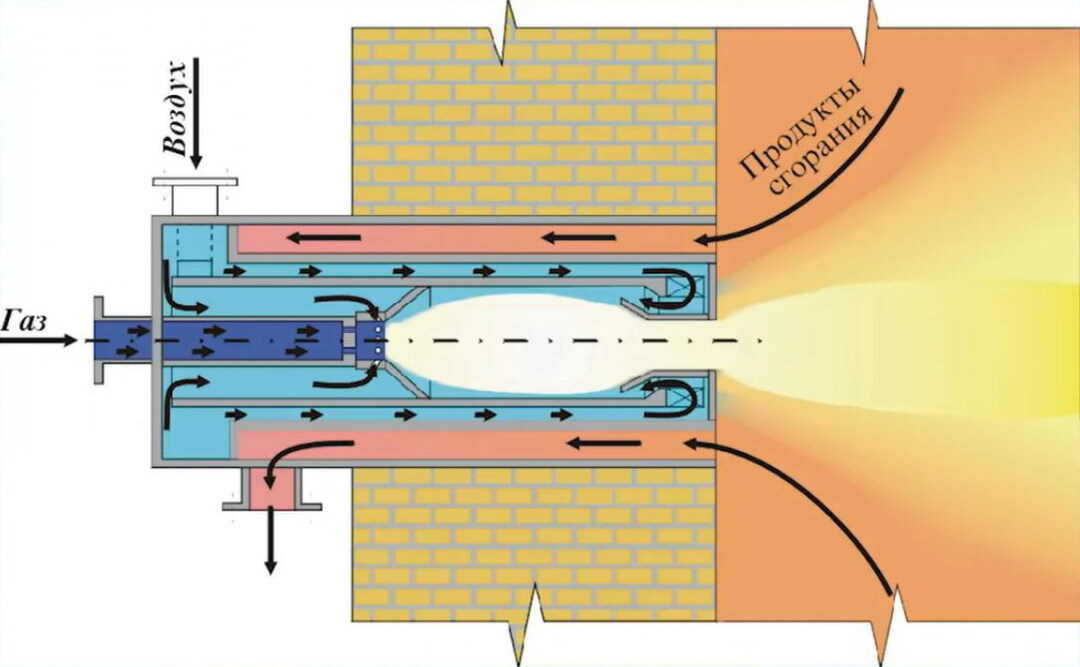
The operating parameters of the gas fuel in the system are controlled by various devices, among which the gas pressure relief safety valve is considered the simplest and at the same time effective. This device is mandatory for installation both in the main gas pipelines and in the local home network.
If a gas boiler or stove is installed in your house, we suggest that you get to know more about the PSK - a safety relief valve, in order to use it if necessary.
The content of the article:
- Purpose of the gas valve
- Design features and sizes
-
Types of trigger safety devices
- Classification # 1 - Diaphragm and Spring
- Classification # 2 - Low Lift and Full Lift
- UCS advantages and disadvantages
- Requirements for choosing a UCS
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Purpose of the gas valve
PSK is a safety valve element responsible for the safety of a gas pipeline and gas equipment connected to it. During operation, the valve is in a closed position, therefore it is referred to as a closed pipe fitting.
Such devices are installed not only on gas pipelines, they are an integral part of other communications -
plumbing, heating network. Everywhere they perform the same function - they stabilize the pressure in the network, provide the operating parameters necessary for the correct functioning of the system.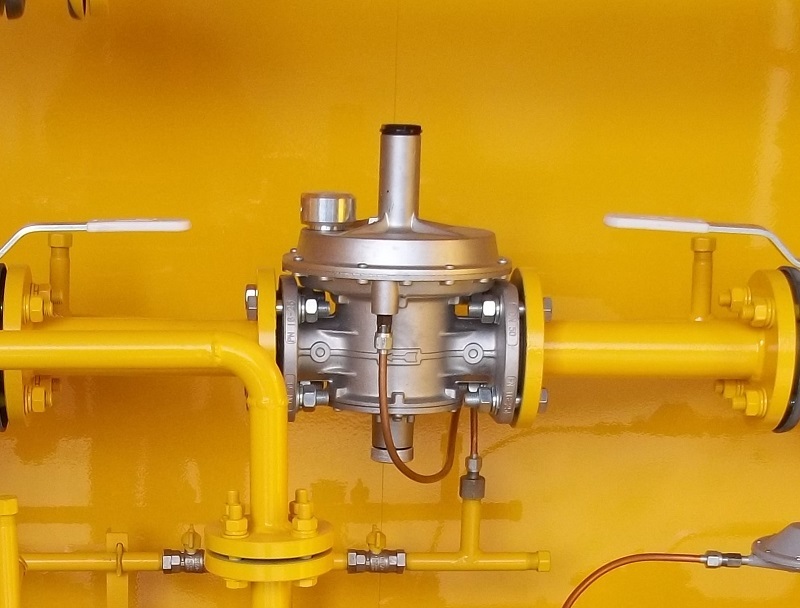
The valve serves to dump excess gas if the pressure parameters become critical. Fuel that creates an imbalance in the system is discharged into an auxiliary pipeline or discharged into the atmosphere
The pressure surge is usually short-lived and depends on a number of factors.
Causes that can cause overpressure in the system:
- breakdown of connected gas equipment - double-circuit boiler, instantaneous water heater or capacitive boiler, shut-off valves;
- use of fuel that is not suitable in composition;
- change in temperature indicators in the pipeline;
- failure in the thermomechanical circuit.
The installation location of the gas safety valve is standard, due to the effectiveness of the application: either in the pressure regulator, or immediately behind it. After the automatic actuation of the valve, it returns to the working - closed state.

In the gas network, the valve is a separate or integrated device in the pressure regulator. It is triggered if the working gas pressure exceeds the nominal level by 15%
What is the threat of the lack of the PUK in the network? The most common consequences are mechanical destruction of the pipeline or breakdown of connected equipment, which can cause gas leakage.

There is also a possibility of an explosion, therefore, it is necessary to constantly monitor the health of the device, to carry out maintenance on time and to replace the failed elements.
Along with relief devices, gas safety shut-off valves are also used, with the help of which the fuel supply is shut off. This happens automatically. The shut-off valve element is installed on the pipeline, in the gap between the filter and the pressure regulator.
The slam-shut response limit is indicated in the technical passport of the device. The upper critical parameter is usually equal to the formula: slave. pressure + 25%.
Design features and sizes
PSK cannot be made by handicraft, products are manufactured in a factory according to the requirements of GOST or TU.
The material must be strong, wear-resistant, not prone to deformation from changes in operating conditions, not amenable to the negative effects of corrosion. Most often it is brass or aluminum, but devices are also made from cast iron and stainless steel.
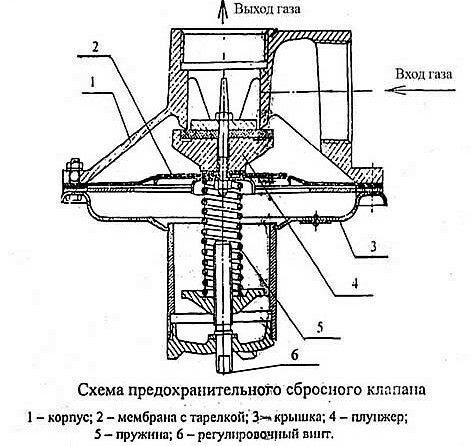
The design of products from different manufacturers may vary, but the most common type is a cone-seated device equipped with fasteners for installation in a pipeline.
There are two threaded holes in the body. Their diameter depends on the type of UCS and is usually 1 ″ or 2 ″. For household networks, mainly two types of valves are used, differing in section - by 25 mm or 50 mm.
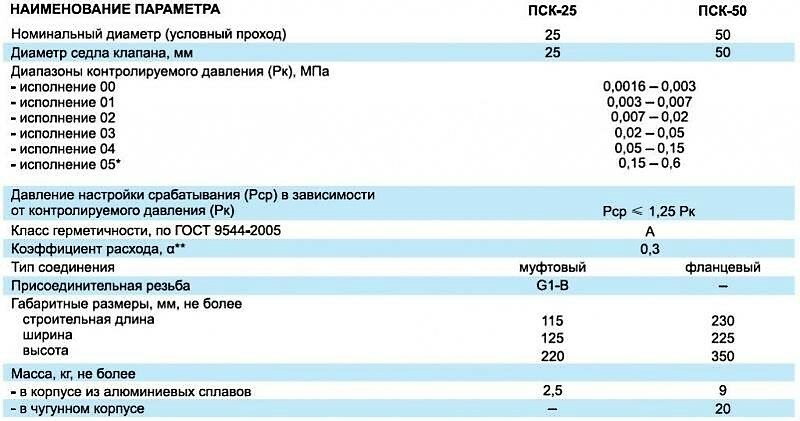
Table with the technical characteristics of the PSK. Devices can differ not only in cross-section, but also in the type of connection to the pipeline, operating pressure indicators, material of manufacture, body dimensions
The principle of operation of the safety gas valve is simple: as soon as excess gas enters the inside of the device and begins to press on the membrane, it acts on a spring that opens the outlet to the outside. As soon as the pressure drops to operating parameters, the spring closes the hole.
Although the devices work automatically, they are equipped with a forced opening mechanism. This is to check the performance of the valve.
To perform testing, you need to pull on a special element of the device - a rod. This manipulation should be repeated several times to make sure that the mechanism works.
The shut-off and control valve is mounted in tandem with the valve, so that, if necessary, if the valve suddenly does not work, quickly shut off the gas supply.
Types of trigger safety devices
UCS classification is based on design and function. There are two main groups that differ in the design of the working mechanism - membrane and spring, and two varieties that act differently at the time of increase pipeline pressure - low-lift and full-lift.
Let's consider what their differences are and what you need to know about the operation of various valves.
Classification # 1 - Diaphragm and Spring
Membranes are named after one of the main working elements - membranes. It is installed inside the housing and is responsible for the release of excess gas when the pressure rises. It is a sensitive detail, and one of its main qualities is elasticity. If the required flexibility is lost, the element needs to be replaced.
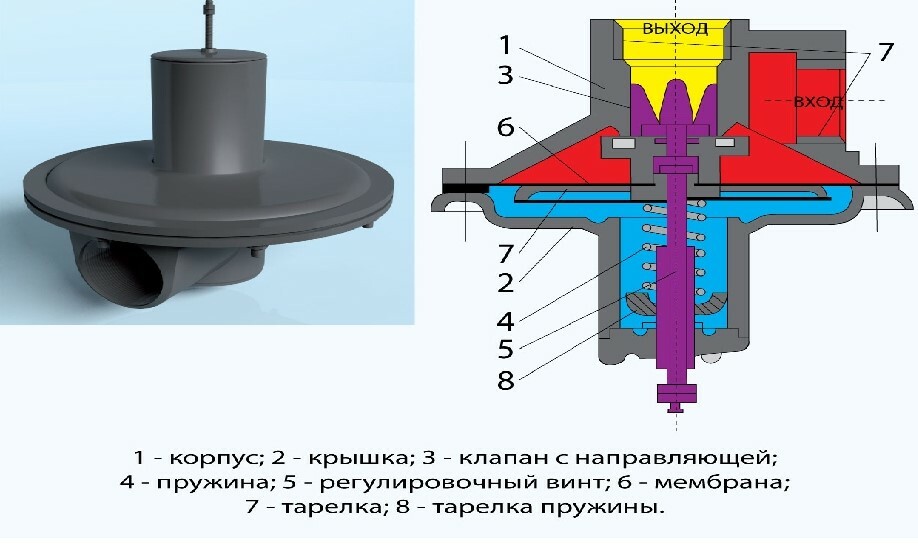
The presence of a diaphragm extends the range of action of the safety valves. The adjusting screw, which acts in tandem with the diaphragm, performs an additional, shut-off function
It is the membrane, more sensitive PSKs that are installed in gas systems with low pressure - that is, in household networks as well.
For the diaphragm valve to operate, the pressure in the system must increase by 15%.
Spring-loaded valves are characterized by the fact that the main active element is a spring-controlled spool. It simultaneously functions as both a sensitive and a shut-off part.

The spring is a dynamic element that opens the valve at the moment the gas rises in the system, and also serves to purge the PSC
Purging is a technical procedure that prevents the spool from sticking in the seat and also performs cleaning functions. Purge ensures that the seals last longer.
Classification # 2 - Low Lift and Full Lift
The difference between the valves is expressed in the way and speed of opening the shutter. In low-lift devices, it opens gradually, depending on the degree of pressure increase in the network, while in full-lift devices, it opens sharply, jerkily, across the entire width.
The second type of valves and closes accordingly - quickly, instantly. As soon as the pressure drops, the spool immediately hits the seat.
While the first type can have several open positions, the second has only two: “closed” and “open”. Another difference between low-lift PSKs is their low throughput.
UCS advantages and disadvantages
Regardless of the design features or the principle of operation, all types of relief valves have advantages, due to which they are actively used for equipment of gas communications.
Here are the main ones:
Image gallery
Photo from
If the device becomes unusable, thanks to the simple design, you can quickly find the fault, replace the seal, diaphragm or spring, and also clean or blow out the valve
Along with the main function - regulation of the standard working pressure in the gas pipeline - PSK provides sealing and protection
Installation method - threaded or flanged - assumes quick installation or dismantling of the device. This advantage is especially valuable if you need to quickly make repairs.
The material of manufacture, coupled with the design features, guarantee such product qualities as reliability, durability, long service life, resistance to all kinds of influences.
Simple design and principle of operation
Optional network sealing function
Easy installation and replacement
A set of required technical characteristics
Most of the models are universal - they can be used not only for equipment of gas pipelines, but also for heating system installation, plumbing, communications for the movement of steam.
The shock-absorbing function is performed by elastic seals, they are also responsible for sealing the joints of the reinforcement with pipes. The average service life of the seals is 5 years, after which replacement is required.
All PSKs are designed for increased loads and exposure to aggressive substances, however, they require maintenance and regular checks.
The disadvantages include only the need for additional installation work, but disappears if the UCS is integrated into the regulator.
Requirements for choosing a UCS
Before the installation of gas communications, a package of documents is being prepared, which details the requirements for all parts of the pipeline, including the relief valves.
The main requirements include the following:
- the valve plug should open as much as possible at the pressure set in accordance with the standards;
- the valve is closed automatically only after adjusting the pressure to the operating state (or below the operating state). parameters by 5%);
- when closed, the gate must ensure 100% tightness of the network.
If one of the requirements is violated, the pressure in the network will decrease or increase to critical levels, as a result of which the system will malfunction.
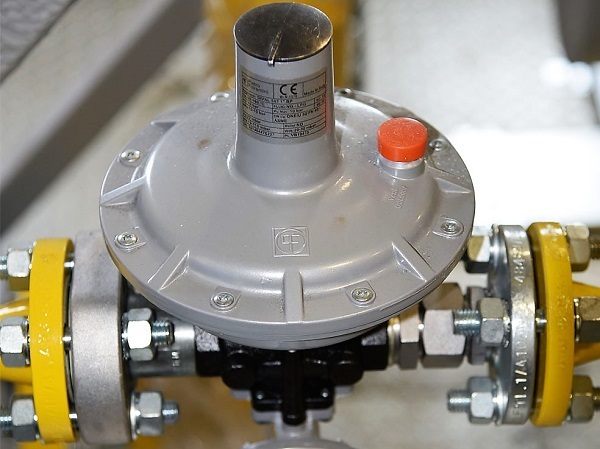
When choosing, you should take into account such parameters as the method of connection, throughput, diameter, tightness class, purpose, and also study the manufacturer's recommendations
In order for the device to perform its functions and not fail prematurely, it is necessary not only to choose a model, appropriate in terms of characteristics, as well as correct installation, and then strictly follow the rules exploitation.
A few helpful tips:
- To adjust the UCS, a flow meter (pressure gauge) is required, which is usually installed next to the valve.
- The hood of the device is always directed upwards, as well as the gas outlets, if they are present in the system.
- The movement of the gas flow must correspond to the arrow marked on the valve body.
- Stop valves are not installed between the PSK and the gas source.
- Ensure that all safety devices are clean and in good working order.
- The setting of the operating parameters should only be carried out by a gas service representative.
We remind you that for the correct functioning of all safety parts, both equipment and fuel must meet the requirements of regulatory documents.
For example, in GOST 5542-2014 the characteristics of the working medium are indicated - natural gas, in GOST 9544-2015 - requirements for fittings, in GOST 15150-69 - to the climatic environment, in GOST 6357-81 - to threads, in GOST 33259-2015 - to the flanges.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
What PSK-50 looks like:
Replacement of PSK and SZK - universal gas regulator:
Design features and assembly of the safety valve:
When installing a gas pipeline and connecting household units, one should not neglect the installation of a set of safety valves. A properly selected relief valve is responsible for regulating the pressure in the gas system - which means that it will work properly, and the residents of the house can be sure of their safety.
But do not forget that Gorgaz or Oblgaz is responsible for the installation and maintenance of gas equipment, so do not rely only on yourself and call gas workers in time.
Please leave comments, ask questions, post photos on the topic of the article in the block below. Tell us about how you selected and installed a safety valve in the heating system of your own house or apartment. Share useful information that may be useful to site visitors.