In the cold season, unpleasant interruptions in the operation of gas pipelines occur. They arise not only due to low temperatures. You can get a problem with a high degree of probability if the installation of communications was of poor quality. Then freezing with a stop of movement in the pipeline becomes a habitual phenomenon.
To resolve the issue, you will have to install a cable for heating the gas pipe, and preferably before the onset of frost. Next, we will tell you how to choose the right heating cable and share the intricacies of its installation.
The content of the article:
-
Heating cable structure
- Self-regulating heating wire
- Resistive heating cable model
- Choosing the ideal option by parameters
- Installation rules and guidelines
-
Installation methods for heating cables
- Longitudinal heating cable installation
- Spiral fixation around the pipe
- Important installation nuances
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Heating cable structure
The device for heating wires includes up to 5 elements - the presence of this or that part depends on the type of product, and there are only two of them, except for rarely used ones:
- self-regulating;
- resistive.
Self-regulating cablehas two conductors with different phases. These copper conductors carry electricity. They are located inside a conductive matrix, which heats the cable and acts as the brain of the system.
Every detail of this interior consists of an electrical circuit located exactly in the middle between the conductors. It is the matrix that heats and regulates the supply veins.
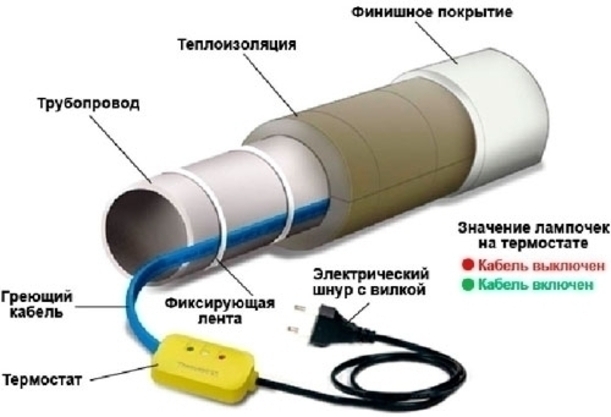

In addition to its own heat-insulating layer, the wires are used in tandem with external insulation. This is necessary in order to protect the cable from the external environment.
The main part of the cable is always threaded into a heat-insulating layer, which is also called thermal protection or insulating cover. The thermal insulation is wrapped with a shielding mesh made of flat copper plates. This braid is used to protect against electromagnetic waves from the outside, and also for grounding. The outer shell on the grid is a kind of shield against mechanical damage.
Resistive cables are single and double-core. Accordingly, they are distinguished by the number of conductors. The device resembles a self-regulating version, but only without a matrix system. Make another one instead thermal protective layer.
Self-regulating heating wire
Such a cable works like a normal conductor of electricity. Heating leads to an increase in resistance and, by a simple physical law, to a decrease in the current strength. In cold places of the pipe, the temperature of the wire is lower and the resistance is lower, and due to the higher current strength at these points, the heater works more and more intensively.
When the cable turns on, it gradually builds up power and at some point starts to work at full capacity. It turns out that heating the gas pipe accelerates this process.
The self-regulating cable does not stop working. There is no need to worry, because heating continues only until the desired temperature is reached, and then the cable functions with less power. Heater operation is built around a set temperature.

The self-regulating version of the heating cable has a variable resistance with a direct dependence on temperature, so the power of the wire can grow by itself
V gas pipes it is not the gas itself that freezes, but moisture, as a result of which it stops flowing. It is necessary to choose such a temperature of the pipe to make the probability freezing insignificant. A feature of self-regulating models is that the heating will not turn off or turn on as soon as the gas pipeline becomes warmer or colder than the optimal indicator. It's just that the intensity of work will change dramatically in the direction of decreasing or increasing.
In turn, the cost of power should not hit the wallet, because the cables consume about 10 watts per meter of length. There are weak models with energy costs within 5 W and powerful ones with an indicator of up to 150. Given the large selection, you can always find an acceptable option to afford to keep the equipment on at all times.
Resistive heating cable model
With a single-core variety, everything is more complicated, because you need power from both ends with subsequent design restrictions. The second end is returned to the connection point, or additional power is laid to the same, distant end. This is the crux of the inconvenience. Sheathed solid wire thermoplastic occupies the niche of the most budget heaters on the market.
On the principle of a single-core cable, a modification of HT was created with 50 watts per 1 meter. Its scope extends beyond pipelines. Together with the high energy consumption, the HT wire solves the issue of saving the material itself.
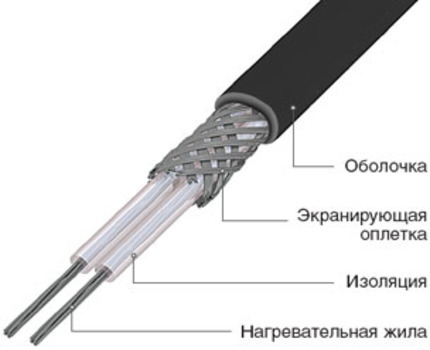
Resistive heating cables are manufactured only in a specific length, which cannot be shortened or lengthened in any way - such a wire cannot be cut
As the name suggests, a two-core heater consists of 2 cores. They do not perform the same function as with matrix cables. The heating core is paired with conductive, which is assigned a supporting role. On one side, power is supplied to the cable, and on the opposite side, a sealed sleeve is mounted.
Designing and installing the wire is straightforward, but the coupling is often a problem. Practice has shown a connection between breakdowns with this part in more than half of the cases. To gradually replace problematic products, manufacturing companies began to produce clutchless options.
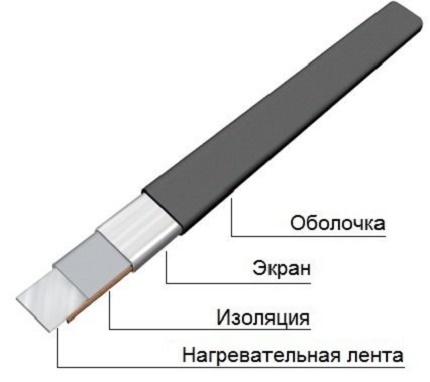
Flat single-core cable of the HT modification makes it possible to reduce material consumption by 1 m2 of the area of the gas pipeline that needs to be heated
Resistive heating cables offer the following benefits:
- stability of characteristics throughout the service life;
- high heat dissipation;
- low prices.
But in terms of reliability, they are somewhat inferior to self-regulating models, because in the event of a breakdown you have to replace the entire section with a problem area, they also often have a local overheat. The inconvenience lies in the fact that it will take time to select the sections of the optimal length.
Choosing the ideal option by parameters
For all outdoor models, the benefit is determined by the power and the uniformity of heat distribution. In theory, both types of cables are approximately the same, because the weaknesses of the resistive can be compensated for by the type of installation.
Depending on the minimum temperatures in the region, a cable is selected that is sufficiently resistant to extreme ambient temperatures. It may be that the indicator at which occurs freezingturns out to be too low for the heater itself.
There are also more unambiguous situations. Pipelines with an underground location are covered only with self-regulating wire, because this is more profitable and more convenient. Thin gas pipes should not be protected with a resistive wire - sometimes it happens that the communication melts, and a hole forms at the point of contact.
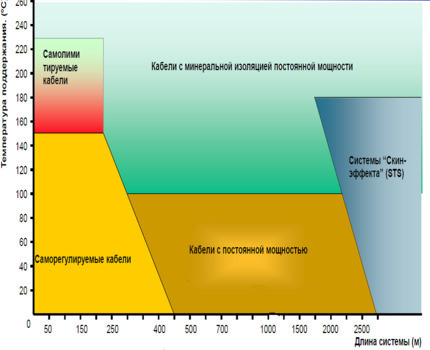
Thanks to this diagram, it becomes clear how much advantage self-regulating cables have: the parameters of the length of the cable line and the temperature of the heated object are indicated
It will be nice if you have a table at hand heat loss. In it, the heat loss is determined by the difference in temperature between the pipe and the environment in combination with the ratio of the pipe diameter and the thickness of the heat-insulating layer.
The information is available in a convenient format - watts per meter.
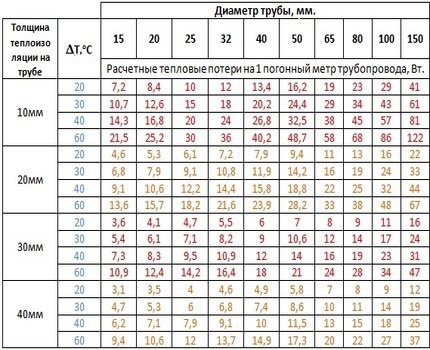
For an illustrative example of energy efficiency, you need to look at the table of heat losses of pipelines - it will help in determining the required cable power for the planned thickness of insulation on the pipe
Installation rules and guidelines
Operational problems will not appear if the general standards are observed. In accordance with the rules for the installation of electrical appliances (PUE), the frost protection system must be equipped with a residual current device (RCD). Mount on non-conductive surfaces and units are made only with a protective sheath. Cables finished with this coating are also installed on synthetic pipes.
During installation, the air temperature matters: work is carried out if it is not colder than -15 ° C. After installation, they arrange mandatory thermal insulation. To reduce heat loss, the thickness of this layer is adjusted exactly to the pipe diameter. Moreover, exceeding this indicator will not lead to anything bad, but it will only get better.
The heating wire is considered functional if the bending radius reaches at least 3 product diameters. T. e. if the radius of an imaginary circle, the center of which is located directly at the edge of the cable bend zone, is at least three times the diameter and 6 times the radius of the wire itself.
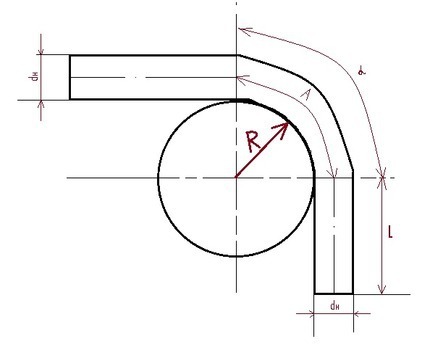
In the figure, R is the bending radius, dh is the cable diameter, A is the length of the bent part, L is the length of the straight parts, α is the plane angle between two imaginary straight lines that intersect at the center of the conditional circle
After work, the thermal insulation and the cable itself are checked for resistance. Then marks are made on the trench and the pipeline with a warning about the presence of a heating element. Additionally, a plate is installed.
Cable installation allows designers to place the pipe in a convenient location. In this case, there is no need for laying, taking into account the level of soil freezing.
Installation methods for heating cables
There are four main options for placing a heating cable, but the first two are most often used:
- longitudinal laying of one cable;
- fastening the cable with a spiral around the gas pipeline;
- placing several heating wires along the pipe;
- installation with a wavy outline.
The cable is usually passed along the bottom of the pipe at the 4th or 8th hour, if we imagine that its cross section is the round dial of a mechanical watch. At the junction - they are raised by 60 °. This is, in a sense, a precautionary measure: place the heating cable away from the mounting bracket.
There are separate ways of laying in different nodes of the system. Next to the valve, the core is bent, laid below the moving part and fixed fiberglass tape. With a wavy or spiral mount, the pitch of the turn is made larger where there is a turn in either direction. For example, knee joints.

When installing a heating cable near nodes and connections, the most important thing is to leave easy access to all controls.
The essence of the installation is extremely simple. It is only required to choose a trajectory for the cable and secure it from above with aluminum tape. First of all, the wire is fixed in fragments. After - pressed against the pipe until tight contact. You should not put much effort, the minimum tension is enough, especially since the cable has the ability to stretch unnecessarily.
In the future, you will need to fix it with tape along the entire length of the cable:
- to improve heat dissipation;
- for strength;
- to avoid contact with thermal insulation.
Aluminum tape or foil is used to process plastic pipes. In this way, excessive heating of the plastic is avoided and a more even distribution of heat is achieved over the entire area and length of the gas pipeline. Whatever material the pipe is made of, a sleeve is installed on it and the cold lead and the heating wire are fastened together.
In the same place, on the gas pipeline, the thermostat sensor is also placed - ideally exactly in the middle between the laid lines. In the future, the site will need to be insulated, after which the work can be considered finished.
Longitudinal heating cable installation
Technically, this is the easier way. At the same time, one should not expect the same effect as with spiral installation, when the gas pipeline is covered with a "net" of a twisted cable. Fixation is performed parallel to the pipe closer to the bottom. Safety regulations do not prohibit taller shims, but the likelihood of damage from above will by definition be higher.

Straight-line installation of the heating cable is often used for gas, as well as - water pipelines, sewer and drainage pipes
The distribution diagram of heating cables on a gas pipe directly depends on their number. One line is laid at the bottom, corresponding to 4 o'clock, if, again, you imagine a dial instead of a cut. Adding a second would mean placing it on the same level, but on a different side.
In the variant with three branches, they are placed in an imaginary triangle on the lower half of the pipe, and it should look slightly to the right or left. A regular square pattern is already made of four cables, and then two wires will be on top.
Spiral fixation around the pipe
The method is preferred in the northern regions. The probability of moisture freezing in gas pipes there is much higher, so the contact area is increased. The contact zone in the spiral method covers the pipe at different angles, in a principle similar to a corrugated gasket, but even more effective.
Long cables are produced for spiral installation. So manufacturers provide an option for selecting the pitch between turns. In practice, the interval is sometimes adjusted to 5 cm or less. The cable will then exceed the length of the pipeline itself by about 2 times.
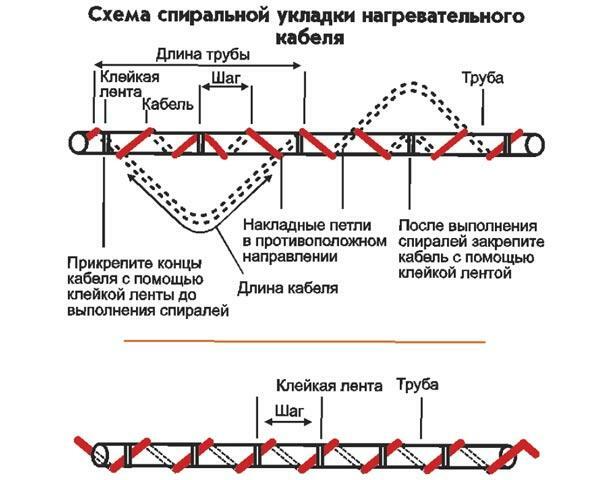
The spiral mounting method has more advantages: in difficult situations and at extreme temperatures, preference is given to it
In some places, cable routing is difficult. The way out of the situation will be precisely the screw-like installation, but using a different technology. The vein is first wound with a margin, and then tightened with a change in the direction of the loops.
Important installation nuances
A successful installation involves several things. The first violin is played by the algorithm of actions. The pipeline must first be tested and painted, and a suitable day should be selected for installation when there will be no precipitation. Moreover, the laying of some cables is possible only on one side. It is enough to miss this one nuance - and all the work will have to start anew.
Practical points about using heating cables:
- the lower the wire is, the better the heat exchange processes are;
- the adhesive layer accelerates heating;
- thin metal pipes must be additionally insulated with foil or tape, as well as plastic ones.
Do not rush the process of attaching to valves and threaded parts. The wire should be laid in such a way that then it is easy to maintain, repair and replace the pipe elements without dismantling the heating system.
The cable must be shaped into a loop near the connection, and then rolled up to a state of slight tension and secured with tape.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Self-regulating heating cable overview including operating principle, applications and tests:
An illustrative example of a longitudinal installation on a thin pipe, also with a gasket near the valve:
There are 2 types of cables for installation on a gas pipeline: self-regulating and resistive. It is unlikely that you will have to puzzle over the choice, because the first option is clearly better in terms of the sum of its characteristics. The heating system is installed longitudinally, in a spiral or wavy line.
Before that, the length and power of the heater are selected, calculations are made with a large number of physical indicators. After all, you need to understand what happens when a gas pipe is heated with specific types of heating cable, and what should be abandoned. Once installed, gas discomfort and problems are a thing of the past.
Do you have any questions or can you add valuable information to our material? Please leave your comments - the contact block is located below.