Repairing the floor in a house or apartment is not only the selection of flooring, glue baseboards, calculation of consumption and budgeting. This is also the flour of choosing the lining material. The modern floor is so arranged that the basis for it is usually plywood or OSB. Without lining material in any way, today it is the best solution for any type of housing.

The content of the article:
-
General characteristics of OSB
- Characteristics of OSB
- General characteristics of plywood
-
Parameters for comparing materials
- Environmental friendliness
- terms of Use
- Care
- Durability
- Mounting method
General characteristics of OSB
Often on the plates or on the price tags you can find another name for the material - OSB. It is the phonetic twin of the English abbreviation OSB. In the documents you can find the full name - "oriented strand board". In everyday life, both options are used, and OSB, and OSB - “oriented strand board”.
Structurally, OSB is a thin slab or panel (up to 20 mm), consisting mainly of wide and long chips. It is generally accepted that this is the main difference between OSB and its closest competitor, chipboard (chipboard).
OSB production technology was developed in Canada and the USA to replace toxic chipboard, so the way the board is made is different:
- Large shavings of coniferous trees are soaked in an aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide, heated to 150℃ at a pressure of up to 40 bar.
- The raw material is held for some time, after which the pressure is abruptly released. The water on the surface of the chips boils with an explosion and at the same time destroys certain fiber structures. Hemicelluloses are released from the cells, which serve as a binder.
- The material is dried at 100-120℃, treated with a preservative, wax, paraffin are added and pressed into large sheets.
- A mixture of hemicelluloses, wax and paraffin melts under pressure, filling the pores and air gaps between the wood fibers. It turns out a rigid and solid structure.
So dense that if you knock on the OSB, the sound will be sonorous, like that of bog oak or bakelite plastic, which indicates the rigid structure of the plate. If you knock on chipboard, you will hear that the material is porous, soft.

The main advantage of OSB is that the original material contains practically no toxic formaldehydes, like chipboard or plywood sheets. Sometimes this argument becomes the main one in cases where you need to make a decision - which is better for the floor - plywood or OSB.
You can compare chips from sawing OSB, plywood and chipboard. In OSB, it is small, like powdered gypsum, and the smell is more like spruce. In plywood and chipboard, the chips strongly give off phenol-formaldehyde resin.
The material was in demand, but expensive to manufacture. Until Chinese enterprises took up the production of OSB. Instead of special preparation, the same phenol-formaldehyde or even isocyanate resin was added to the raw material (so that there was no smell) and pressed like ordinary chipboard. This is how new OSB brands appeared, some of which are not recommended for indoor use.
Characteristics of OSB
In addition to the classic OSB-1, plates of the OSB-2, OSB-3, OSB-4 brands are produced. Between themselves, the material differ in water absorption, strength and resistance to bending load.
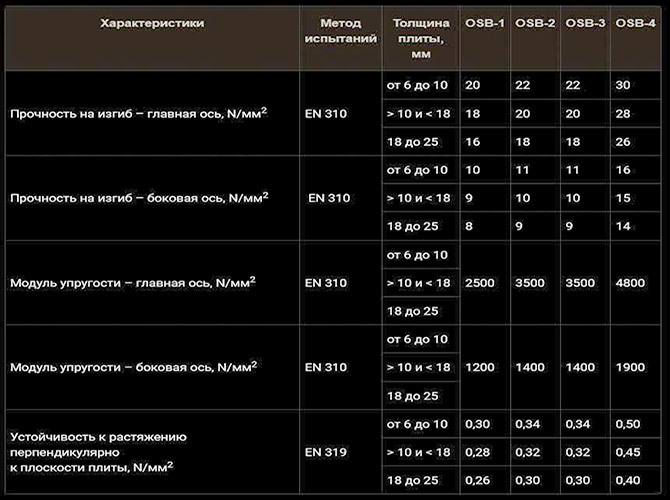
If you are looking for material for a subfloor, the vapor permeability and moisture resistance of the base will be more important characteristics. Worst of all, contact with moisture withstands OSB-1; in a day, the material can absorb up to 25% moisture. Even when dry, OSB swells and deforms upon contact with water vapor. Therefore, it is recommended to store the material in a dry and heated room. Laying OSB-1 in a base under linoleum is like leaving an old wooden floor, the problems will be the same.
OSB 2,3,4 also absorb water from 20% to 12%, respectively. The higher the resistance of OSB to water, the more phenol-formaldehyde resin and paraffin in its composition. OSB-2 can still be used for floors, OSB-3 and OSB-4 are building materials for use outside residential premises. From it you can make a good formwork, filing the roof or lay the floor on the balcony.
General characteristics of plywood
The demand for plywood sheets made from spruce or birch veneer is higher than for OSB. Plywood is actively used in low-rise home construction and even in the manufacture of furniture. Not because she, as a material, is better than OSB, but rather out of habit. It has been produced for decades in huge volumes, using a simple technology of gluing veneer into a multilayer bag using phenol-formaldehyde resin.
Therefore, plywood is a 20-25% polymer of phenol and formaldehyde, which, on the one hand, gives material high strength, but at the same time it becomes a source of a specific odor and toxic evaporation. On the other hand, if you choose what to lay on a plank floor - plywood or OSB - then the plywood sheet can be a better solution, since formaldehyde vapor often serves as a kind of preservative for floorboards.
The following brands of plywood are available for sale:
- PSF - increased moisture resistance. Can be laid as a subfloor in unheated or irregularly heated rooms. Upon contact with water, it swells and exfoliates.
- FOF - plywood for industrial construction. Withstands contact with aqueous emulsions, coolants and greases. For the floor in rooms where there are people, it is better not to use it. In extreme cases, you can hem the floor on the terrace, close the thermal insulation on the roof.
- FC is a material in which the veneer is glued together with a urea binder. It is classified as conditionally environmentally friendly.
- FKM - modification of FK with additional sizing of the surface with melamine compositions. The surface of plywood becomes more wear-resistant. Can be used as a temporary substitute for a full-fledged wooden floor.
- FBA - for gluing plywood, an albumin-casein composition (a variant of synthetic casein glue) was used.
- FB - bakelite plywood, waterproof. It can be used as a floor on an unglazed balcony, on an open veranda, for any construction, but not inside residential premises.
FB brand material can be used to level the base for a cement-sand screed, for tiles or self-leveling floors. Such plywood has a small coefficient of expansion, high rigidity and strength, making it indispensable in building structures.
For living rooms, it is best to choose FK or FKM - it is relatively safe in terms of the release of free phenol. But for floors of different designs, it is better to use material of different brands. Moreover, safety among the selection criteria is considered not the most important. Plywood is almost always covered with an additional coating, so the amount of phenol formaldehyde emission goes by the wayside.
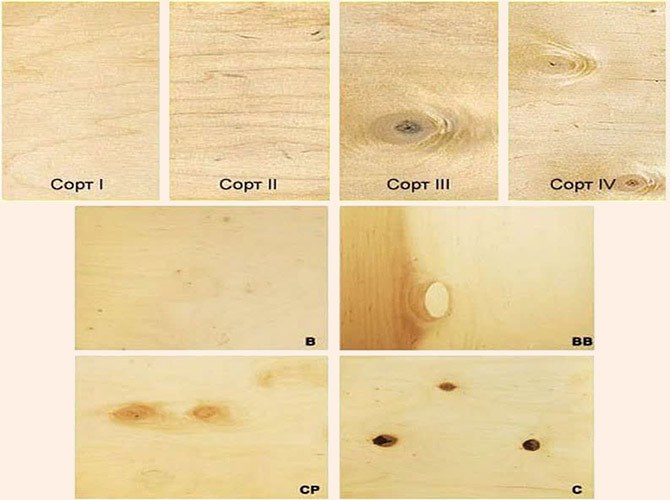

In addition to the brand, you will need to take into account the grade of the material. The best quality is "E" or the highest grade. It has no defects on the surface and the highest price. The rest of the plywood is divided into 4 grades depending on the number and size of defective spots.
Use plywood sheet the highest grade for laying on the floor does not make sense for economic reasons. Such material is expensive and is used mainly for the manufacture of furniture, parts for industrial installations and transport.
Grades 1-2 are inferior in appearance to the same OSB, so the slab is used only as a rough base. The rest is better not even plan for interior decoration. Their toxicity is approximately three times higher than that of the first grade.
Parameters for comparing materials
Sheets of plywood and OSB can differ greatly in strength, durability, resistance to alternating loads. In order for the comparison to be correct, it is necessary to take into account the amount of damage, the effective thickness, the level of surface protection. OSB is a defect-free material with a homogeneous structure. Plywood sheet almost always has defects in the inner layers, but its effective thickness and strength are higher than those of OSB.
For the subfloor, OSB sheets and plywood 12-16 mm thick are used.
Environmental friendliness
Comparison of 2 types of bases, plywood or OSB, according to safety conditions, makes sense for materials that are close in class.
The best brands of OSB without phenol of the classical scheme are produced mainly in Norway, the USA and Canada. The environmental certificate indicates E0, the output of phenol and formaldehyde from the material is zero.

The CIS countries, part of Eastern Europe, Turkey and China produce environmentally friendly OSB boards with a phenol and formaldehyde output of 2-3 mg per 100 g of material. In the so-called waterproof OSB, the formaldehyde yield per 100 g of the pressed mass reaches 10 mg and even 30 mg. These are OSB building brands and it is forbidden to use them inside residential premises.
Plywood loses to OSB in terms of environmental safety. Again, there are grades of E0 class plywood of the highest grade. The material is produced without the use of phenol-formaldehyde resins, so the yield of formaldehyde and phenol is zero. The cost of such plywood is approximately 3.5 times higher than that of class E1 material.
The most common material used for lining walls and floors indoors is plywood sheets of class E1 and E2. The content of formaldehyde, respectively, up to 10 mg and up to 30 mg per 100 g of pressed veneer. E1 plywood can be laid on the floor as a rough base. Even without coverage. E2 plywood is used for utility or residential premises; it can be used in tandem with subsequent additional finishing with gas-tight materials, such as linoleum.
Plywood E3 and E4 cannot be used in private households. It can be used as a formwork for concreting sites and structures of small volumes.
terms of Use
OSB is inferior to plywood in terms of strength, resistance to moisture, and the ability to withstand abrasion loads. If we compare 2 materials of the same class, then in terms of mechanical characteristics, sheet plywood with a thickness of 10 mm corresponds to the capabilities of OSB with a thickness of 16-18 mm. And in some cases - all 20 mm.

If you want to sew a rough base on the log beams, then it is better to use plywood sheets. OSB under such conditions (even twice the thickness) will not withstand bending loads. The material is hard but brittle. First of all, the screwing points of the fasteners will be destroyed.
Plywood floors, as well as any plywood-based reinforcing or leveling coatings, are more durable. They easily tolerate difficult operating conditions.
A plywood sheet with a sanded surface made of birch veneer of any brand (for example, FK) can withstand medium-intensity abrasion from people's shoes for 3 years. We are talking about a dry and ventilated room. A floor covered with OSB-2 sheets will last 1.5-2 years at best. OSB coating - 3 years. In terms of wear resistance, formaldehyde and phenol content, oriented strand board will be approximately on the same level as plywood.
For a dry, heated and well-ventilated area, OSB will be more preferable option than plywood due to lower phenol and formaldehyde content and low cost material. OSB is cheaper than plywood.
The only exception is underfloor heating. It would seem that OSBs have a more porous structure, good vapor permeability, and low thermal conductivity. Such a coating should be more comfortable than a plywood floor. In fact, under conditions of constant heating, OSB degrades rapidly. The plate loses moisture remnants, changes its structure, due to which the material crumbles into pieces and chips over time.
For underfloor heating, birch plywood (not pine) of class E1 is used.
Care
Plywood and OSB are capricious in operation. OSB, even when laminated with melamine film, absorbs moisture well, collects fine dust, water condensate and even sand. Therefore, if the sub-floor of oriented strand boards is not immediately covered with a floor coating, linoleum or laminate, then after a few months it will begin to show wear tracks from shoes.
And after another six months, the wear of the “bare” floor will become so strong that it will no longer be possible to lay linoleum. It is necessary to additionally sew on a fiberboard coating to hide and even out worn areas. Any attempt to clean the OSB floor ends in nothing.
Birch and pine veneer are more resistant to dirt, contact with moisture, and if you do not leave puddles of water on the floor, then plywood can stand for up to a year without flooring.
The only disadvantage of a rough base made of safe plywood can be considered a large coefficient of thermal expansion. Therefore, the floor itself is usually recruited from small square blanks, between which a gap is left to compensate for the expansion of the material.
Durability
The OSB surface is always rough and porous. Moreover, the chips from which the board is pressed have low mechanical strength when compared with veneer. With careless handling, OSB can be easily damaged if you try to drag heavy objects across the subfloor - a sofa, a washing machine or a refrigerator.
On the plywood floor, even without protective impregnation, you can move any home appliances. If scratches or dirty spots appear on plywood, they can be easily removed with a fine-grained grinder.
On the one hand, the high porosity of the OSB surface is a plus, especially if you need to stick it on mastic or paint. On the other hand, the absorbency of OSB is so great that any attempts to apply varnish, drying oil, and even PVA on OSB do not give the desired result. Moreover, if there is too much water in the composition of the impregnating mixture, then it will all remain inside the OSB.
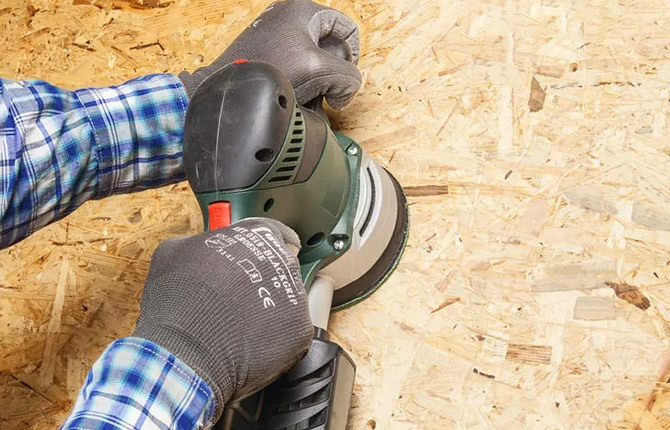

Therefore, the protective coating is applied to the OSB in 2 stages. First, a thin layer of acrylic varnish or any deep penetration primer is applied with a roller. In the next step, the subfloor can be painted over with oil paint or treated with an emulsion of a PVA mixture with water. After drying, a smooth film is formed, which well protects the material from moisture and dirt.
The advantage of plywood is that it will withstand any treatment - from drying oil to polyurethane varnish. In this case, the wear resistance of the surface is increased. Any floor covering can be laid on a plywood floor, even parquet.
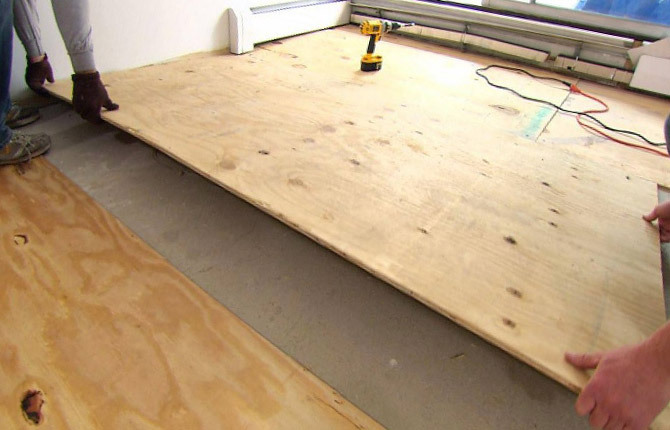

Mounting method
There is one fundamental difference between plywood sheet and OSB. Plywood of any quality, thanks to its layered structure, has the ability to deform (adapt) under load without breaking. OSB is more like a monolithic polycarbonate. With a small load, the plate allows deflection, but it is worth slightly exceeding the deflection value, as cracks appear and the material begins to delaminate.
Therefore, OSB is fixed in 2 ways:
- Stick on paint or elastic mastic.
- Self-tapping screws with rubber bushings are used.
In the first case, OSB can be laid directly on a pre-milled floor. The surface is initially primed, dried, a layer of oil paint is applied and the plates are laid.
Next, you need to lay out a dozen heavy objects on the floor surface. They are placed on the plates so that all the sheets lie approximately in the same plane. After the paint has dried, the load is removed, the joints and seams are cleaned with a grinder.
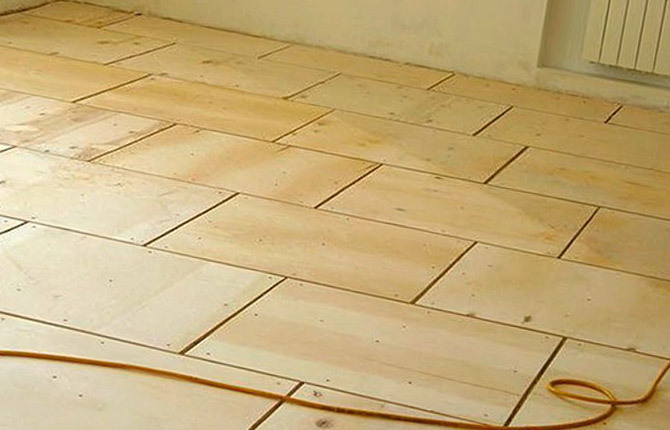

Plywood sheets are laid in a similar way, but instead of paint, mastic or glue is used. To fix the plywood blank on the plank floor, ordinary self-tapping screws are taken. Wrap several pieces along the joints. Before you wrap the fasteners in plywood, you need to drill a hole in diameter slightly smaller than the screw itself. Otherwise, you can split the material.
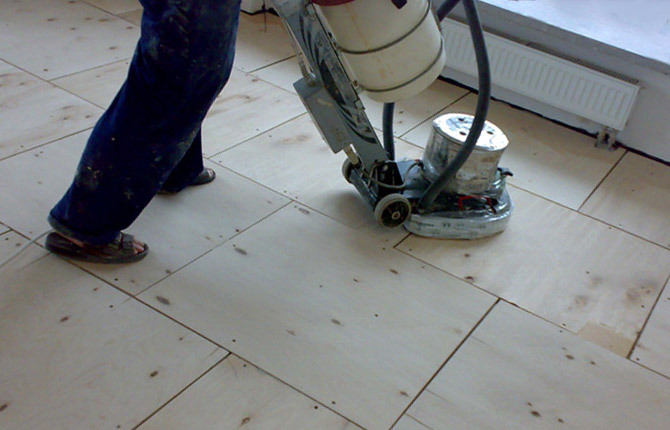

Dowels can be used to attach OSB or plywood to a concrete surface if the floor thickness allows. Holes are pre-drilled in concrete and plugs made of pine or oak are hammered. If a fresh screed is made for laying OSB or plywood, then instead of corks, a couple of wooden bars are placed in concrete.
As a subfloor material, plywood or OSB can be considered the best solution. All that is required is to correctly cut the sheets and lay them, taking into account the characteristics of plywood sheets or particle boards.
Tell us about your experience with plywood or OSB for flooring in your home. How successful was the choice and what disadvantages can be noted for each material? Bookmark this article so you don't lose any useful information.


