Lighting sources, called luminescent, in contrast to analogs equipped with a filament, need launchers called ballast for operation.
Content
- What is ballast?
- Types of Ballast
- Electromagnetic implementation
- Electronic implementation
- Benefits
What is ballast?
Ballast for LDS (fluorescent lamps) belongs to the category of ballasts that are used as a current limiter. The need for them arises if the electric load is not enough to effectively limit the current consumption.
An example is a conventional light source, which belongs to the category of gas discharge. It is a device that has negative resistance.
Depending on the implementation, the ballast may be:
- ordinary resistance;
- capacity (with reactance), as well as a choke;
- analog and digital circuits.
Consider the most common implementation options.
Types of Ballast
The most common electromagnetic and electronic implementation of ballast. We will tell you in detail about each of them.
Electromagnetic implementation
In this embodiment, the operation is based on the inductance of the inductor (it is connected in series with the lamp). The second necessary element is the starter, which regulates the process necessary for “ignition”. This element is a compact sized lamp that belongs to the category of gas discharge. Inside her bulb there are electrodes made of bimetal (it is allowed to make one of them bimetal). Connect the starter in parallel to the lamp. The two ballasts are shown below.

The work is carried out according to the following principle:
- when voltage is received inside the starter lamp, a discharge is produced, which leads to heating of the bimetallic electrodes, as a result of which they close;
- shorting the starter electrodes leads to an increase in the operating current by several times, since it is limited only by the internal resistance of the inductor coil;
- as a result of increasing the operating current level of the lamp, its electrodes are heated;
- the starter cools and its bimetal electrodes open;
- opening the circuit with a starter leads to the appearance of a high voltage pulse in the inductance coil, due to which a discharge occurs inside the source flask, which leads to its "ignition".
After the lighting device goes into normal operation, the voltage on it and the starter will be less than the mains voltage by about half, which is not enough to trigger the latter. That is, it will be in the open state and not affect the further operation of the lighting device.
This type of ballast is easy to implement and low cost. But we should not forget that this version of ballasts has a number of disadvantages, such as:
- it takes one to three seconds to “ignite”, moreover, during operation this time will grow steadily;
- sources with electromagnetic ballast flicker during operation, which causes eye fatigue and can cause headaches;
- the power consumption of electromagnetic devices is much higher than that of electronic counterparts;
- during operation, a characteristic noise is emitted by the throttle.
These and other shortcomings of electromagnetic starting devices for LDS have led to the fact that at present such ballasts are practically not used. They were replaced by "digital" and analog electronic ballasts.
Electronic implementation
Ballast of the electronic type, in essence, is a voltage converter with which power is supplied to the LDS. The image of such a device is shown in the picture.

There are many options for implementing electronic ballasts. One can imagine a common block diagram characteristic of many devices of this type, which, with few exceptions, is used in all electronic ballasts. Her image is shown in the figure.

Many manufacturers add a power factor correction block to the device, as well as a brightness control circuit.
There are two most common ways to launch LDS sources using electronic ballast implementation:
- Before applying the ignition potential to the LDS cathodes, they are preliminarily heated. Due to the high frequency of the incoming voltage, two tasks are achieved: a significant increase in efficiency and flicker is eliminated. Note that, depending on the design of the ballast, the ignition can be instantaneous or gradual (that is, the brightness of the source will gradually increase);
- a combined method, it is characterized by the fact that an oscillatory circuit takes part in the “ignition” process, which must enter into resonance before a discharge occurs in the LDS flask. During resonance, an increase in the voltage supplied to the cathodes occurs, and an increase in current ensures their heating.
In most cases, with a combined start method, the circuit is implemented in such a way that the thread the filament of the LDS cathode (after series connection through the capacitance) is part contour. When a discharge occurs in a gaseous medium of a luminescent source, this leads to a change in the parameters of the oscillatory circuit. As a result, he leaves the state of resonance. Accordingly, there is a voltage drop to normal mode. An example of the circuit of such a device is shown in the figure.

In this scheme, the oscillator is built on two transistors. The LDS receives power from the winding 1-1 (which is step-up at the transformer Tr). Moreover, elements such as capacitance C4 and inductor L1 are a series oscillatory circuit with a resonant frequency different from that generated by the oscillator. Similar electronic ballast circuits are common in many budget table lights.
Video: how to make ballast for lamps
Speaking of electronic ballast, one can not help but mention compact LDS, which are designed for standard cartridges E27 and E14. In such devices, ballast is integrated into the overall design.

As an example of implementation, the ballast diagram of the 21W Osram energy-saving LDS is shown below.
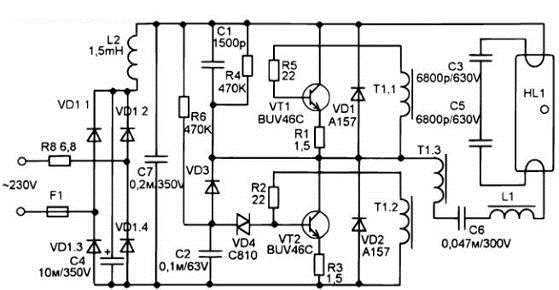
It should be noted that due to the design features, serious requirements are imposed on the electronic elements of such devices. In the products of unknown manufacturers, a simpler element base can be used, which becomes a frequent cause of the failure of compact LDSs.
Benefits
Electronic devices have many advantages over electromagnetic ballasts, we list the main ones:
- electronic ballasts do not cause flicker of the LDS during its operation and do not create extraneous noise;
- the circuit on electronic elements consumes less energy, weighs lighter and more compact;
- the possibility of implementing a hot start circuit, in which case the LDS cathodes are preheated. Thanks to this inclusion mode, the service life of the source is significantly extended;
- The electronic ballast does not need a starter, because it is responsible for the formation of the voltage levels necessary for the start and operation.
- Electronic and electromagnetic chokes for ...
- Emergency lighting - types, requirements, schemes ...
- How to choose LED lamps for home and apartment?
- Features of using and connecting LED ...


