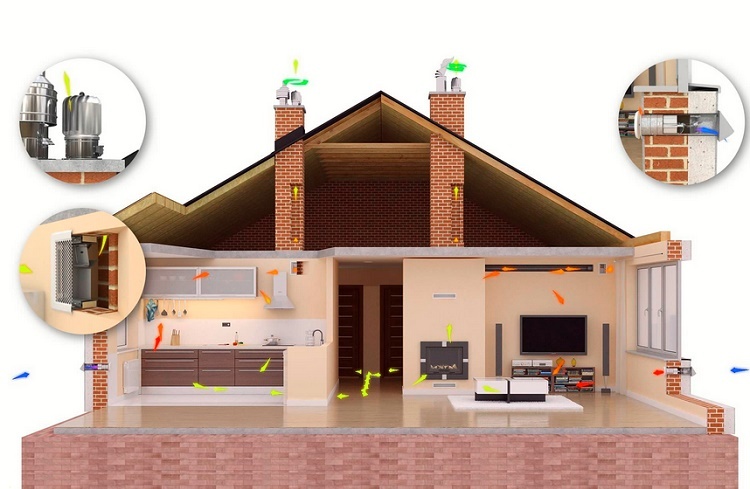
In the arrangement of country houses, gravitational ventilation is often chosen more often than the more efficient and independent mechanical one. Time-tested natural ventilation in a private house is easier to implement and much more practical. It does not require special care, maintenance and power supply.
We will tell you how to organize air exchange that occurs naturally. The article presented by us describes in detail the principle of operation of gravitational ventilation. Let's get acquainted with the devices that are used in the construction of systems that operate without third-party coercion.
The content of the article:
- How does the air exchange process work?
-
Components of gravitational air exchange
- Window inlet valve
- Wall exhaust or supply device
- Internal transfer grilles
-
Specificity of duct exhaust
- Types of ventilation ducts
- What is a deflector?
- Basic rules and recommendations
- Advantages and disadvantages of natural air exchange
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
How does the air exchange process work?
The main purpose of the gravitational version of the air exchange device is to maintain the required microclimate. In addition to saturating the space with fresh air, it also removes exhaust air, gas combustion products, and various odors.
The efficiency of the natural ventilation system, arranged in a country house or in the country, is due to the difference in atmospheric pressure inside and outside the house, which also depends on temperature, humidity and the strength of the wind.

Natural ventilation should ensure uniform supply, movement inside and removal of air flows, regardless of the number of storeys of the house
Natural air exchange works as follows:
- Air from the street enters the house through open transoms, elements of window and door structures that are loosely adjacent to each other. Air currents rush inward during ventilation through slightly opened plastic windows or through ventilation inlet valves.
- The movement of air from one room to another and inside it occurs spontaneously. So that the flow does not have obstacles between the floor and the doors, gaps are left. Their function is successfully performed overflow gratings installed in the walls.
- The exhaust air leaves the house through the exhaust ventilation ducts. They are located in rooms with unstable humidity / temperature - in kitchens, separate and combined bathrooms.
All city dwellers are well acquainted with exhaust components. These are ducts connected to a public ventilation shaft. They are covered with grates that need to be cleaned periodically.
In the arrangement of a private house organization of natural extraction may vary significantly. For example, it can be an outlet in the upper part of the wall, an exhaust pipe or a hole in the ceiling with an exit to the ventilation duct to the attic, and from there to the street.
Components of gravitational air exchange
One of the most common problems with natural ventilation in a private house is the lack of fresh air in the room. Gravitational ventilation works flawlessly only when the density of the air mass outside the window is much higher than inside the premises. In summer, when their density is equal, the air from the street itself does not flow.
In addition, serious obstacles are now being placed in the path of naturally moving air currents. Seals for windows and doors, offered to the consumer today, perfectly resist heat leaks, but they also do not let air in from the outside.
In order to ensure a natural inflow in houses with sealed windows, it is worth installing supply valves in the wall, and supplying exhaust ventilation pipes with deflectors
The issue of fresh air supply to rooms with practically sealed windows and doors is solved by installing ventilation supply valves. If you do not want to install valves, you will have to purchase air inlets for plastic windows or buy window bags with air inlets initially mounted in them.
Window inlet valve
This device is also called a window ventilator. Refers to the most common options for solving the problem of air exchange. The design of such a valve is mounted directly into the window profile.

The flow of incoming air through the window ventilator is directed upwards so that the cold supply air is more efficiently mixed with the already heated one inside the room and does not cause discomfort to residents
Some valves are equipped with an automatic air flow control. It is worth noting that manufacturers do not equip all models with mechanical adjustment. ventilators. This can create certain problems with sudden changes in temperature.
The main disadvantage window supply valve is a relatively low performance. Its throughput is limited by the size of the profile.
Wall exhaust or supply device
For wall installation ventilator you need to make a through hole in the wall. The performance of such a valve is usually higher than that of a window valve. As in the case of the window inflow, the incoming volume of fresh air is controlled both manually and automatically.
Wall exhaust valves usually located at the top of the wall, where the exhaust air naturally rises. Supply valves in the wall, they are most often mounted between the window and the radiator. This is done so that the incoming cold air is also heated at the same time.

If the wall vent valve is installed directly above the radiator, the fresh air flow will spontaneously heat up before it is delivered to the room.
Advantages of installing a supply valve over conventional ventilation:
- The ability to regulate the flow of fresh air;
- The ability to transmit significantly less street noise;
- The presence of filters of varying degrees of air purification.
The design of the wall supply and exhaust valve does not allow moisture to penetrate into the room. Many models of these local ventilation devices often include filters to clean the air.
Interroom overflow lattices
In order for fresh air to freely penetrate into all parts of the house, overflow components are needed. They allow air currents to flow freely from the supply to the exhaust, taking with them the weighed air mass dust, animal hair, carbon dioxide, unpleasant odors, household vapors and the like inclusion.
The flow is carried out through open doorways. However, it should not stop even if the interior doors are closed. For this, a gap of 1.5-2.0 cm is left between the floor and the leaf of the interior doors.

In order for fresh air to move freely to the hood and wash all rooms, transfer grilles are installed in the door leaves. If they are not there, then a gap of up to 2 cm is left between the floor plane and the canvas.
Also for these purposes are used overflow grilles mounted on a door or wall. The design of such grilles consists of two frames with louvers. They are made of plastic, metal or wood.
Specificity of duct exhaust
The exhaust air leaves the house through vents, ventilation shafts or air ducts. The ventilation ducts are usually led out into the attic or connected to a ventilation shaft located in the center of the house.
Ventilation ducts in the device and organization of natural ventilation of a private house are used mainly when arranging the exhaust part of the system. Natural inflow through air ducts is most often impossible or ineffective. In order for it to somehow work, a duct fan would have to be mounted.
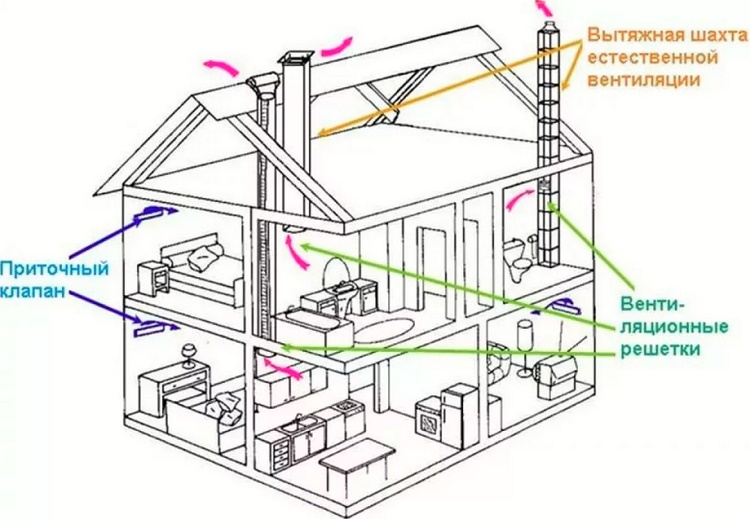
In natural ventilation schemes, ducts provide the exhaust part of the system. Exhaust air ducts in private houses are often combined into mines
The air masses are pushed to the gravity ventilation hood by fresh portions of air drawn in through a window, a PVC window inlet or an open front door. The cross-section of the air ducts is selected taking into account the air exchange standards for certain types of premises, which are given in the collection SNiP 41-01-2003.
In addition to residential and utility rooms in a private house, ventilation systems are required to provide a basement and a storage facility built in it, a foundation without a basement, a cold attic or an equipped attic. In natural schemes, they are provided with air vents, gable and dormer windows.
Types of ventilation ducts
By location they are distinguished:
- Built-in. They are built from hollow concrete or ceramic blocks, bricks. Such exhaust ducts are usually erected during the construction phase.
- Suspended. Made of galvanized steel or reinforced plastic. It is quite easy to equip overhead canals, even after the house has already been built.
Air ducts are divided into round and rectangular sections. Each type has its own advantages:
- Round duct. Easy installation, better air exchange, less weight;
- Rectangular duct. Takes up less space, easier to mask with boxes, false ceilings and walls.
In turn, pipes for a round duct are rigid and flexible, i.e. corrugated.

Corrugated ventilation pipes are easier to install, but their installation is possible only on horizontal surfaces and on small sections of vertical walls
Rigid pipes carry air without obstruction, so they provide the least resistance and the least noise. However with the help corrugated pipes faster and easier installation.
What is a deflector?
The deflector is a special hood that is installed at the mouth of the exhaust pipe of the ventilation system. It cuts the wind flow, due to which a low pressure zone is formed, while the thrust force can increase up to 20%.
Also ventilation deflector excludes the ingress of atmospheric water into the ventilation system and prevents wind from blowing into the ventilation duct.
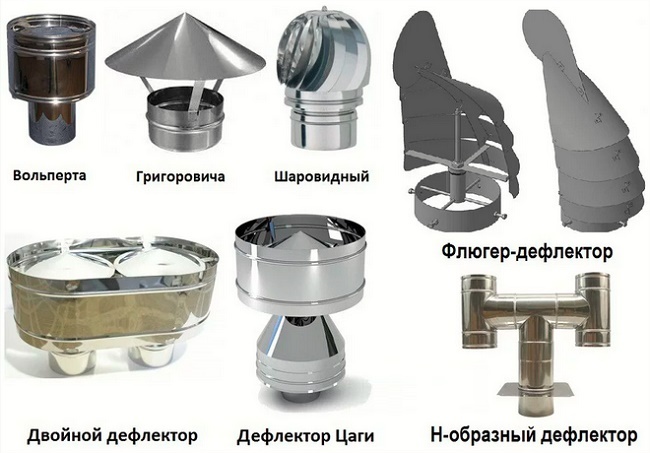

The deflector is installed at the mouth of the chimney. This device has two important functions: increases traction + protects against precipitation
There are the following types of deflectors:
- Cylindrical or umbrella Volper. It is a curved cylinder covered with a plate. Possesses average efficiency, well protects ventilation ducts from wind blowing;
- H-shaped deflector. The body is made of H-shaped pipes. Differs in increased protection against wind blowing, ingress of moisture and reverse thrust into the channel, but due to the design features it has a low performance;
- Deflector type TsAGI. The design includes a beaker with an extension at the end, an umbrella cover and a cylindrical shell. Recognized as one of the most effective. It protects well from wind, snowfalls, rains, has the lowest drag coefficient;
- Turbo deflector. It is a rotating ball with blades, it is characterized by increased efficiency, but it usually costs a little more;
- Vane. It resembles a wing. The principle of operation is similar to turbo deflector.
Deflector model selection depends on local conditions. In regions with high wind loads, common fungi are preferred. In areas with low wind activity, it is better to install a deflector with a turbine, it will provide traction even with a light breath.
Basic rules and recommendations
Regulatory data on the volume of air exchange are given in SP 44.13330.2011, SP 66.13330.2012 and the already mentioned SNiP 41-01-2003.
The natural ventilation system should provide:
- In the main premises, such as living rooms, bedrooms, children's rooms, the amount of air exchange for each person should be at least 30 m3/ч;
- For the kitchen, the constant air exchange according to the rules is 100 m3/ч. Of these, for maintenance of the electric stove - 60 m3/ h, for 1 burner of a gas hob - 80 m3/ч;
- In the shower and bath, the constant air exchange should be less than 75 m3/ч;
- In toilets with one toilet 50 m3/ h, if a bidet is installed, then it must be increased by 25 m3/ч. In the combined bathrooms, the norms for each plumbing fixture are summed up;
- In the pantry and dressing room, constant air exchange is 10 m3/ h, the same figure and in service mode.
If the natural system cannot cope with the standard air exchange, fans are installed on the supply or exhaust air.
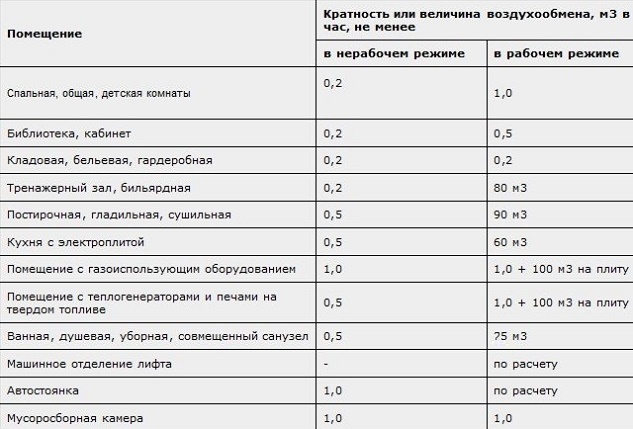
Regulatory data on air exchange are needed to calculate the performance of the inlets and the diameter of the exhaust ducts.
It is advisable to select pipes for the installation of ventilation ducts of the same diameter. All elements of the duct must be fixed evenly and securely. The fewer the turns of the ventilation ducts, the higher the efficiency of the ventilation system.
Intake openings of the natural system should be located no higher than 1.5 m from ground level so that they can be cleaned and maintained.
The longer and wider the duct, the stronger the draft. You can calculate the required duct dimensions using one of the online calculators.
Advantages and disadvantages of natural air exchange
Like any engineering system, the natural variety is not without its drawbacks, but it also has significant advantages. To be sure whether to arrange it or not, it is worth comparing the list of pluses with the list of minuses.
Positive sides:
- Easy and inexpensive installation. This is the cheapest option for organizing stable air exchange.
- Low maintenance costs. If the system does not have mechanical devices, then it only needs periodic cleaning.
- Energy independence. Does not consume electricity, except for the installation of additional electrical appliances.
- Extremely quiet operation. Differs in low noise.
- Engineering flexibility. Ventilation can be upgraded, supplemented with various devices. It is possible to adjust the performance of the system.
Negative sides:
- Traction instability. Its dependence on atmospheric pressure and specific weather conditions. Natural ventilation may not work well in summer.
- Formation of drafts. In winter, strong traction can not only bring discomfort to residents of the house with drafts, but also significantly increase heat loss. This leads to increased costs for heating the room. It is worth noting that there are various ways to solve this problem.
Everyone can organize a natural ventilation system in a private house. Its imperfection is compensated for by its simplicity of design and minimal maintenance costs.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The following video will acquaint you with the specifics of the device of the air exchange system according to the natural scheme:
Normal air exchange has a beneficial effect on human health, increases the performance of the brain, counteracts the onset of symptoms of lethargy, weakness and sleepiness, and also prevents dampness, fungus and mold.
Do you want to talk about how you arranged the ventilation system of your own house or summer cottage? Do you want to share useful information on the topic of the article? Please leave comments in the block form below, post photos and ask questions.