Hot water at the tap and stable +23 ° C in the house, when there is a hard frost outside the window - isn't it, these benefits of civilization have already become familiar? Now answer a simple question: Was the gas boiler heat exchanger flushed after the previous heating season? If your answer is “no”, you risk being left without heat in winter.
To prevent this from happening, read our article on the fight against scale and the prevention of the accumulation of mineral deposits. We have detailed proven methods of combating calcium deposits in practice, due to which the efficiency of the unit decreases and fuel consumption increases. Our advice will help to increase heat transfer and extend the boiler life.
The content of the article:
- How is scale formed and why is it dangerous?
- Soot on external surfaces
- How often should the heat exchanger be flushed
- Methods for removing contamination
- Chemicals for cleaning and prevention
- Design features of heat exchangers
- How to descale a plate heat exchanger
- Flushing the shell and tube heat exchanger
- Features of flushing coaxial heat exchangers
- Cleaning and flushing floor standing boilers
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
How is scale formed and why is it dangerous?
No liquid can compare with ordinary water in terms of specific heat. Depending on temperature and pressure, this indicator varies in the range from 4174 to 4220 Joules / (kg · deg). Water is non-toxic, readily available and cheap, making it an almost ideal thermal fluid.
And yet, N2But there is a significant drawback - in its natural state, it contains salts of alkaline earth metals Ca and Mg. When heated, they form insoluble carbonate, or, in other words, lime deposits on the inner surfaces of the heat exchange equipment - scale.
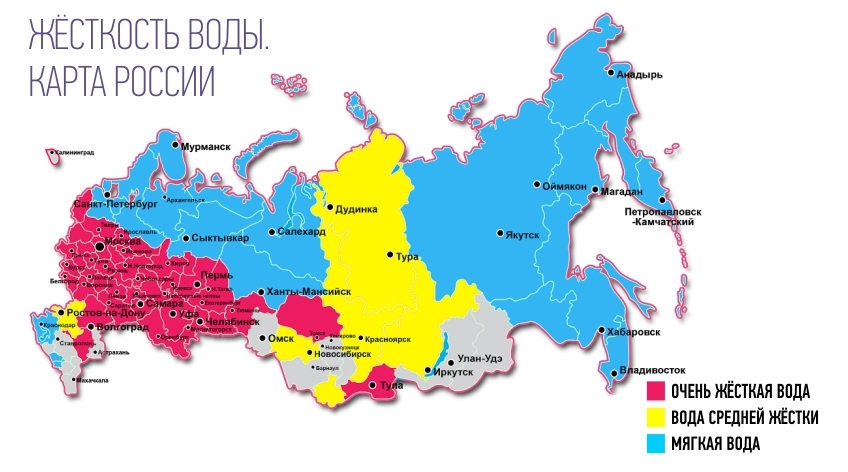
Hard water is typical for a large part of Russia and especially for the middle zone, where the degree of mineralization reaches a maximum
The negative consequences of scale formation are as follows:
- efficiency decreases;
- the water pressure decreases;
- boiler wear is accelerated;
- costs increase.
Domestic heating boilers and hot water heaters are mainly equipped with surface heat exchangers, in which heat is transferred through the surfaces of the metal walls. But scale has high thermal resistance, that is, low thermal conductivity.
For this reason, in dirty heat exchangers, the heat transfer coefficient decreases, which leads to a decrease in temperature. coolant in the heating circuit and insufficient water heating at the outlet of the hot water circuit.
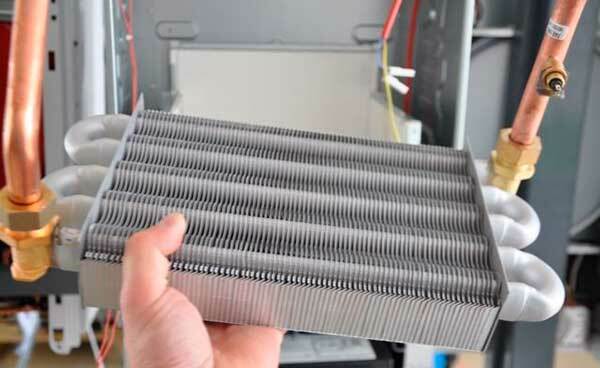
If your boiler does not heat water well, check the condition of the heat exchanger, perhaps it's all about scale, which caused a decrease in efficiency
Hard deposits with a thickness of only 0.2 mm increase fuel consumption by 3%. If the scale is 1 mm thick, the excess gas consumption will reach 7%.
With a decrease in heat transfer, more gas is required to maintain the set water temperature, which indicates a decrease in efficiency. At the same time, with an increase in fuel consumption, the volume of flue gases increases, the emission of harmful substances that pollute the air around the household and the atmosphere in general increases.
Deposits completely or partially overlap the flow area of the pipe, which leads to an increase in hydraulic resistance in the system, violation of the circulation of the coolant, a decrease in the supply of hot water in points of water intake.
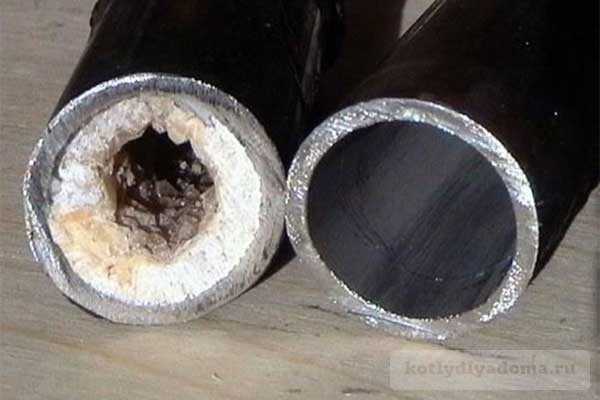

When using water of normal hardness, a layer of scale 2-3 mm thick is formed in a year. With higher salinity, the rate of carbonate sedimentation increases.
Disruption of heat transfer leads to overheating of the pipes, which causes the formation of microcracks - future foci of corrosion. Due to operation at limit modes, the unit breaks down prematurely.
To prevent equipment damage, descale must be periodically removed. Routine cleaning of heat exchangers gas wall boilers and floor units are performed within the timeframes set by the manufacturer. A simple procedure helps to maintain the energy efficiency of the equipment at the original level, extends the turnaround time, and reduces the total cost of operation.
Soot on external surfaces
In case of incomplete combustion of gas, soot - an amorphous allotrope of carbon - settles on the outer surfaces of the heat exchanger. Heat exchangers of boilers with an open combustion chamber and natural draft suffer more from soot.
One of the reasons for its increased formation is the dustiness of the air in the room, from where the combustion air comes from. A lot of dust is emitted during construction work. If the construction site is near the entrance coaxial chimney, the heat exchanger of the boiler with a closed chamber may also become dirty.
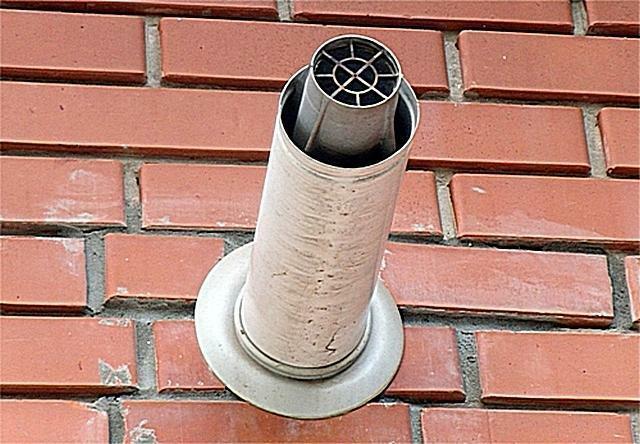

The coaxial chimney consists of an inner and an outer pipe. One of them serves to remove combustion products, the other - to supply air to a closed combustion chamber
Insufficient diameter, incorrect configuration, chimney blockages lead to a deterioration in draft. With poor draft, the removal of combustion products becomes difficult, and they settle in the form of soot on the lower outer part of the heat exchanger.
Like scale, soot has a low thermal conductivity and reduces the efficiency of heat exchange equipment, leads to its accelerated wear, and reduces the overhaul period. The efficiency of a heat exchanger contaminated with soot and scale can decrease by 25% or more.
How often should the heat exchanger be flushed
The frequency of cleaning is specified by the equipment manufacturer in the operating instructions. For example, heat exchangers in Neva boilers must be descaled every 12 months.
The concentration of alkaline earth salts in water can vary. If the concentration is high, the water is called hard. Scale builds up more quickly when used and may require unscheduled cleaning. Also, the rate of formation of deposits depends on the thermal regime and the intensity of the boiler.
The presence of scale in the pipes of the heat exchanger and soot on its fins is indicated by a decrease in the heat output of the equipment. To determine whether the actual heat output corresponds to the one declared in the documentation, the temperature and composition of the flue gases are measured using a gas analyzer.
In the absence of a device, the presence of scale can be judged by indirect signs: a decrease in temperature and water pressure at the outlet of the boiler. If the water heater piping is normal water pressure, and a thin stream is running from the tap, check for deposits on the inner surfaces of the heat exchanger tubes.
Insufficient water heating at standard gas flow and normal head also indicates a clogged heat exchanger.
Note that malfunctions in the operation of complex equipment can be caused by various reasons and the presence of scale is only one of the options.
Methods for removing contamination
To remove scale and soot, mechanical, hydraulic, chemical and other methods or their combinations are used.
Mechanical cleaning heat exchange equipment is performed using a cleaning rod, wire brush, scraper. Both hand tools and electric or pneumatic drives are used.
Application hydraulic method it is possible only with a high-pressure apparatus, which will provide a powerful flow of liquid that can knock down deposits and bring them out.
Chemical method provides for the use of special products that loosen and dissolve dirt.

When flushing heat exchangers by a chemical method, pumping units can be used to supply the reagent to the water circuit, this is more effective than simple soaking
Magnetic, electromagnetic, ultrasonic methods are relatively new and provide for the use of filter-converters and other technical means.
To clean the heat exchangers of domestic water heaters and heating boilers, a combination of mechanical and chemical methods is most often used. After soaking (etching) in the detergent, the remaining scale is mechanically cleaned. Also, modern techniques are gaining popularity, which were mentioned above.
Chemicals for cleaning and prevention
Descaling agents contain organic or inorganic acids. In the production of household products, adipic and orthophosphoric acids are most often used. At home, prepare aqueous solutions of citric or acetic acid.
Acids are reagents - they can react with alkaline earth salts and form other, water-soluble salts, which are then removed from the heat exchange equipment.
Alkalis are also used, such as soda ash or caustic soda, to loosen carbonate deposits and soot, facilitating subsequent mechanical and chemical cleaning. Alkaline solutions are also used to neutralize acid traces left in the heat exchanger after descaling.
Most reagents are supplied to customers in the form of highly concentrated aqueous solutions and require additional dilution with water in certain proportions specified in the instructions for application.
It is necessary to follow the manufacturer's instructions for preparing the working solution and do not exceed the concentration of the agent. Otherwise, the contact of the materials of the heat exchange equipment with an aggressive substance will lead to accelerated corrosion.
When choosing the means, the material for the manufacture of the heat exchanger is taken into account. Usually it is copper, stainless steel or cast iron. For example, Aminat D designed for heat exchangers made of stainless and carbon steels. Another reagent from the same series Aminat D (K) used for cleaning copper surfaces.
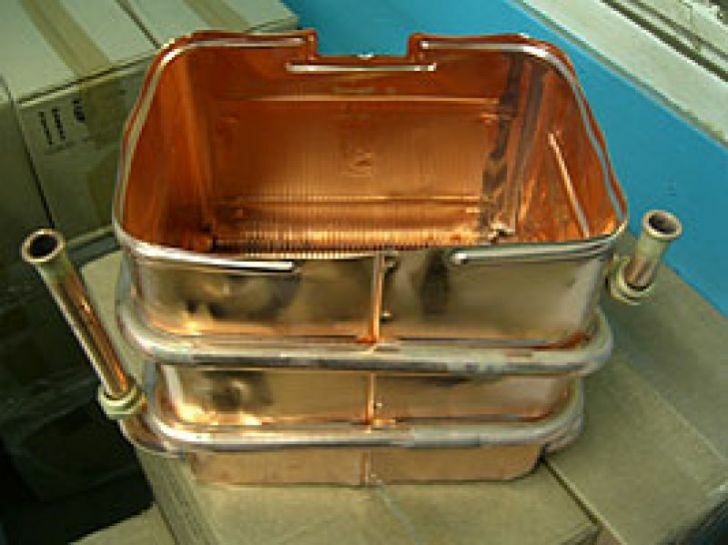

Copper heat exchangers are installed in many domestic boilers. When choosing a descaler, make sure that it is approved for use on non-ferrous metals
Versatile remedies include citric acid, vinegar, Medesk-Plus, Trilon B. They are used to flush non-ferrous metal and stainless steel heat exchangers.
Trilon B Is the disodium salt of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. Appears in the form of a white crystalline powder. When Trilon B interacts with alkaline earth salts (scale), calcium and magnesium ions are replaced by sodium ions. As a result, sodium salts are formed, which dissolve well in water.
Products with a complex composite composition are produced. They simultaneously contain components that cleanse scale and prevent its formation.
Composite KKF differs from other chemicals in the principle of action. It is not a solvent, like acids, but in its presence self-cleaning of carbonate deposits (scale) occurs.
Under normal conditions, calcium carbonate crystals form in the form of mineralized fossilized deposits. This is scale. In the presence of CCF, instead of a mineral deposit, another modification of calcium carbonate, aragonite, is formed.
Needle crystals of aragonite destroy calcium deposits during their growth. In contrast, aragonite has poor adhesion to the surface of the heat exchanger and therefore can be easily removed by rinsing with ordinary water.
The active ingredients of CCF already at the initial stage prevent the formation of calcite crystals. As a result, scale formation is significantly slowed down or completely suppressed. This process is called inhibition (translated from Latin: "to delay").
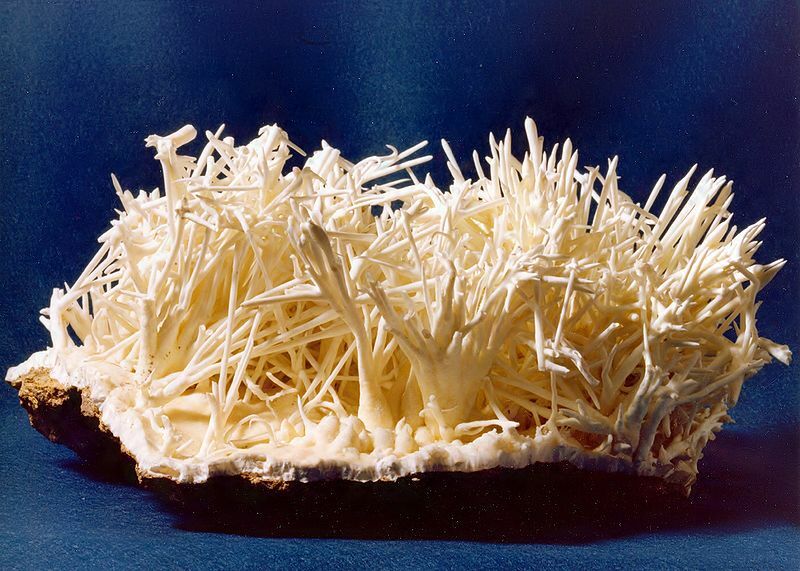
Aragonite is a polymorphic modification of calcium carbonate. Its crystals have a needle-like pointed shape and easily destroy scale, and they themselves are washed out with plain water.
CCF inhibits not only scale, but also corrosion due to the formation of a protective film on the metal surface. When buying anti-scale products, do not forget to clarify whether they have Rospotrebnadzor certificates.
Design features of heat exchangers
To properly flush a heat exchanger, you need to know its design. You will find all the information on your boiler in the operating manual.
Just in case, we recall that for the organization of autonomous heating and hot water supply in apartments and private houses, gas boilers and water heaters with heat exchangers of the following types:
- shell-and-tube;
- coaxial;
- lamellar.
In widespread shell-and-tube heat exchangers, water circulates through a pipe that coils around the side walls of the shell. In terms of design, such a unit is brazed or welded, that is, non-separable.
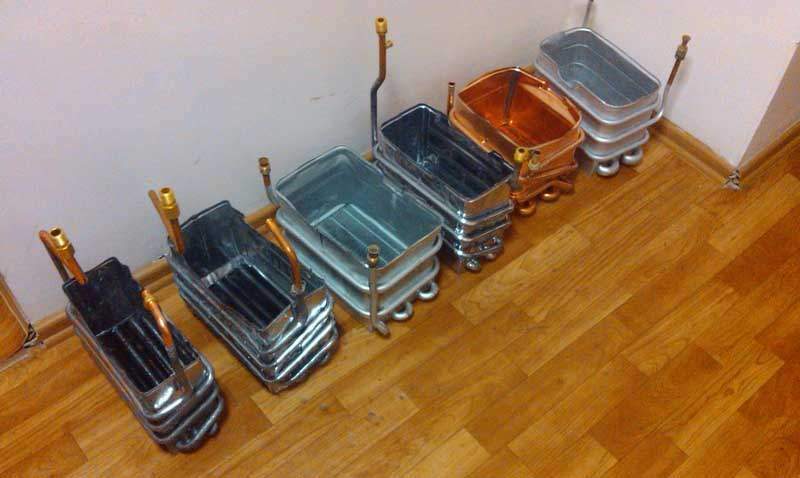

The shell-and-tube heat exchanger is one of the most effective and simple in design, it is easy to descale it with your own hands.
Plate heat exchangers are less common. Their main structural part is a metal package in which several plates are assembled.
For example, heat exchangers of Italian boilers Westen zilmet and Baxi include from 10 to 16 plates. They give their heat to the water moving between them through the channels. Such a device must be disassembled before cleaning.
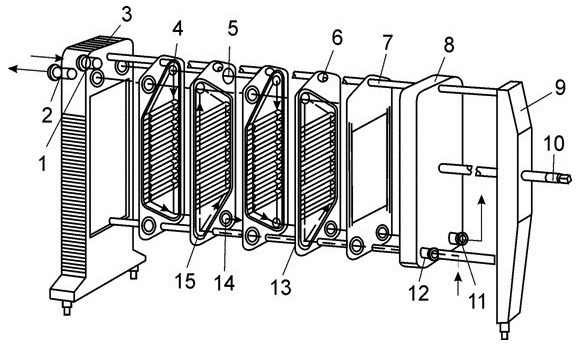
Diagram of a plate heat exchanger, where the following are indicated: pipes for supplying the coolant and the heated medium (1, 2, 11, 12); fixed and movable plates (3, 8); channels along which the coolant moves (4, 14); small and large spacers (5, 13); heat exchange plate (6), upper and lower guides (7, 15); rear support and hairpin (9, 10)
The main element of a coaxial (bithermal) heat exchanger is two coaxial pipes. In its simplest form, it looks like a spiral with tightly fitting turns.
For double-circuit boilers, the presence of 2-3 heat exchangers is characteristic. For example, the "NEVALUX-8023" boiler is equipped with three heat exchangers, one of which is coaxial, but not spiral type, but with series-connected links.
How to descale a plate heat exchanger
Turn off the boiler, shut off the gas and water supply, drain the water from the heat exchanger and wait until it cools down. Disconnect the piping, unscrew the tie rods, move the pressure plate under which the plates are located.
Separate them carefully from each other. Remove each plate separately so as not to cut yourself on sharp edges, work with heavy protective gloves. When working with acid, change them to rubber ones.
Prepare a container in which you will soak the plates, taking into account that they must be completely immersed in the liquid.
Use the cleaning agent according to the instructions supplied. Table vinegar is diluted with water in a ratio of 1 to 3. Powdered citric acid - in a ratio of 1 to 10. The water for the solution is preheated to 40 ° C. The plates are immersed in the solution for 1 hour, after which the remaining deposits are removed with a brush under running water.
After dismantling and cleaning, place the plates in a horizontal position so that they lie on a table or other work surface.

To flush the heat exchanger from scale, it is not necessary to buy a booster, it is enough to have a pump, and everything else is easy to do with your own hands
When disassembling the heat exchanger, at the same time inspect the gaskets and sealing elements and, if damaged, replace them with new ones. It is recommended to replace all gaskets at once, even if only one of them is worn out. Assemble all elements in the reverse order of dismantling. Reinstall the heat exchanger.
Flushing the shell and tube heat exchanger
Turn off the boiler, turn off the taps on the inlet pipes to keep the water in the heating system. Drain the water from the heat exchanger. Disconnect the wires from the thermostat and disconnect the hot water pipes. Unscrew the nuts and self-tapping screws securing the heat exchanger, remove it.

With regular maintenance of the boiler and its correct operation, soot is formed in moderate quantities and can be removed with a regular toothbrush.
To flush the shell and tube heat exchanger from the thick layer of carbonate deposits, it must be removed from the housing. The dismantling process does not require special skills
Visually inspect surfaces. If there is soot on the fins or other areas, immerse the heat exchanger in a detergent containing alkali. It can also be a solution of ordinary laundry soap.
Unless otherwise stated in the instructions, soaking should continue for about 15 minutes. Then use a brush to remove the soot. Rinse the heat exchanger under good running water.
Place the heat exchanger in a basin or other container for descaling. Pour citric acid solution (10% concentration) into the pipe. After 12-15 hours, flush the pipes with clean water. Also rinse or replace the hot water filters.
Reinstall the heat exchanger. After cleaning, it is also advisable to replace all gaskets. If the gaskets are rubber, use silicone to lubricate them.
Next, the heat exchanger must be checked for leaks. A saturated soap solution is applied to the detachable connections of the gas circuit. If there are leaks, bubbles will form in the washed areas.

After completing the flushing of the floor boiler, they check its tightness, electrical connections and performance in different modes, restore the settings and put it into operation
When checking the water circuit in double-circuit gas boiler separately turn on the heating and hot water supply system and inspect each detachable connection. If a leak is found, tighten the nut or install a new seal.
Features of flushing coaxial heat exchangers
Bithermic heat exchanger tubes are often made of different metals. The outer pipe can be made of steel and the inner pipe can be made of copper. Therefore, for flushing, you need to use a universal agent that is poured into the pipes, kept for the required time and drained. The heat exchanger is rinsed and returned to its place.
Cleaning and flushing floor standing boilers
Descaling and soot removal is carried out without dismantling the heat exchanger. A flush pump (booster) is used. An aqueous solution of citric acid is poured into its container. 2 liters of warm water requires 200 grams of powdered citric acid.
Before cleaning floor standing gas boiler, turn off the gas and water supply taps, drain the water from the heating and DHW circuits. Next, you need to get to the heat exchanger. Remove the door, disconnect the wires connected to the piezoelectric element, remove the thermocouple and the nozzle, dismantle the ignition system and the burner.
Unscrew the nuts securing the top cover and remove it. You have gained access to the heat exchanger and can clean it of soot with a brush and a brush.
Connect the outputs of the booster to the pipes of the heat exchanger, which will pump citric acid solution into the pipe under pressure. Circulating around the circuit for 4-6 hours, it will dissolve the scale. The flushing time depends on the level of contamination.
Use a pH meter to keep the process under control. This device will show the change in the concentration of acid in the solution, which occurs due to the ongoing chemical reaction of dissolution of carbonate deposits.
If the acid has neutralized and the meter shows a pH value of 1, you may have to repeat the process from the beginning. A stable pH level of 2 to 4 indicates descaling.
At the end, the pipes are washed with a baking soda solution to neutralize the residual traces of the reagent. Next, it remains to install the parts in their places, check the unit for leaks by soaping and visual inspection of the detachable connections, or by pressing. In the absence of gas and water leaks, the boiler is operated normally.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The heat exchanger of a gas boiler can be easily washed at home without the use of professional equipment:
How to descale the secondary heat exchanger of a double-circuit boiler and what is needed for this:
Modern methods and tools help to effectively fight scale and prevent its formation. The main thing is not to forget to periodically flush the heat exchanger so that the real characteristics of the gas boiler correspond to the passport indicators throughout the entire period of operation.
Tell us about how you flushed the heat exchanger of your own gas boiler. Share an effective method for removing mineral plaque that you are familiar with. Please leave comments in the form below, ask questions and post photos on the topic of the article.


