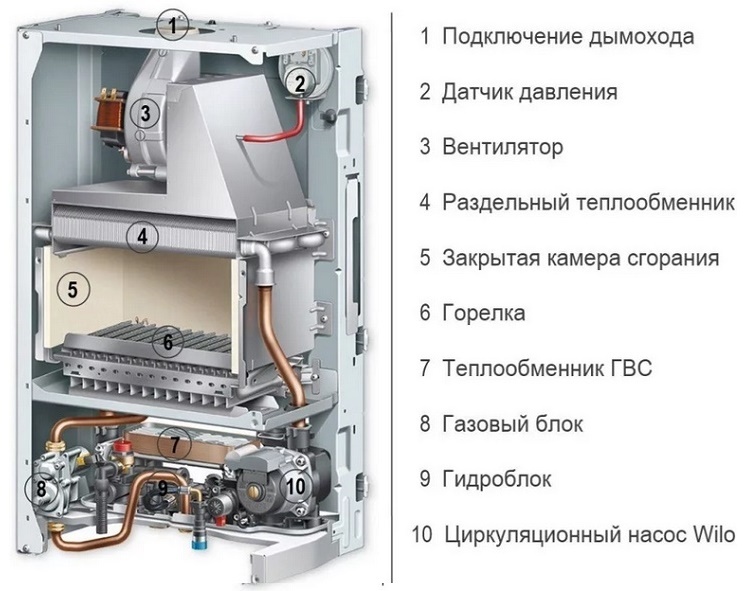
Seeing that water is flowing from a gas boiler, do not postpone the solution of this problem on the back burner. After all, you do not want to change the entire boiler because of a small crack in the heat exchanger, do you? Let's say right away that coolant leaks occur for other reasons and in other places. How to detect and eliminate them is the topic of our article.
We will tell you how you can quickly identify a leak. We will show you which structural components are most susceptible to loss of tightness. Our recommendations will help you quickly identify the cause in order to eliminate it without waiting for irreparable breakdowns.
The content of the article:
- Places of water leakage
- How can you tell if a boiler is leaking?
- What to do with condensation?
- Does it flow through threaded connections?
- Expansion tank problem
- Safety valve leaks
- Damage to the heat exchanger and pipes
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Places of water leakage
Leaks can occur along the entire water path. If a double-circuit gas boiler is flowing, the problem may be in the following nodes:
- heat exchanger;
- pipes;
- expansion tank;
- places of detachable connections.
The level of complexity of the upcoming repair largely depends on the location of the water leak.
The easiest way is to eliminate leaks at the points of detachable connections. It is more difficult to repair a leaking pipeline inside the equipment. The most time consuming process is the repair or replacement of the heat exchanger.
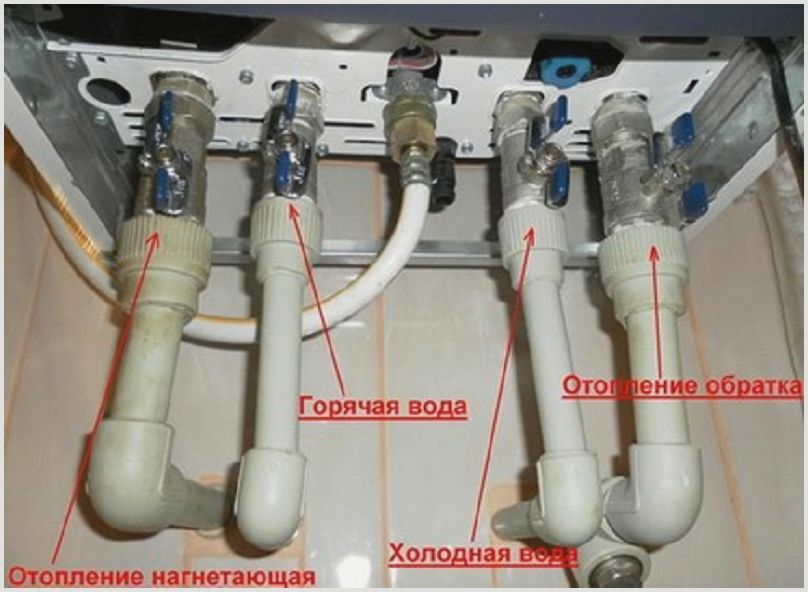
The double-circuit boiler is equipped with connections for connecting 4-pipes through which water is transported. In case of insufficient sealing of their joints, a leak of coolant, cold or hot water occurs
Leaks should be repaired as soon as possible after they occur. Loss of heating medium can lead to automatic shutdown of the boiler.
An attempt to compensate for the loss of the coolant by periodically adding a new portion is fraught with accelerated wear of the boiler. The water is saturated with oxygen, which accelerates the corrosion of metal components, which shortens the life of the heating equipment.
How can you tell if a boiler is leaking?
Leaking heating medium reduces the hydraulic pressure in the heating system. Let's say right away that pressure can also change for other reasons, for example, due to a change in the density of water. But if the arrow of the pressure gauge stubbornly falls down or the display shows a notification about the lack of water in the system, you must definitely check for leaks.
Inspection of problem areas is carried out: first of all, detachable connections, including taps. But it is not always possible to determine the place of the leak visually, because coolant will not necessarily flow in a continuous stream, flooding the floor. More often than not, it just drips. Drops evaporate on hot surfaces.
Therefore, you need to pay attention not only to damp places, but also to traces of drips, rust spots. It is better to look for leaks with a flashlight; inspect hard-to-reach areas with a mirror. Place napkins under the possible leaks. Their wetting will serve as confirmation that there is a coolant leak here.
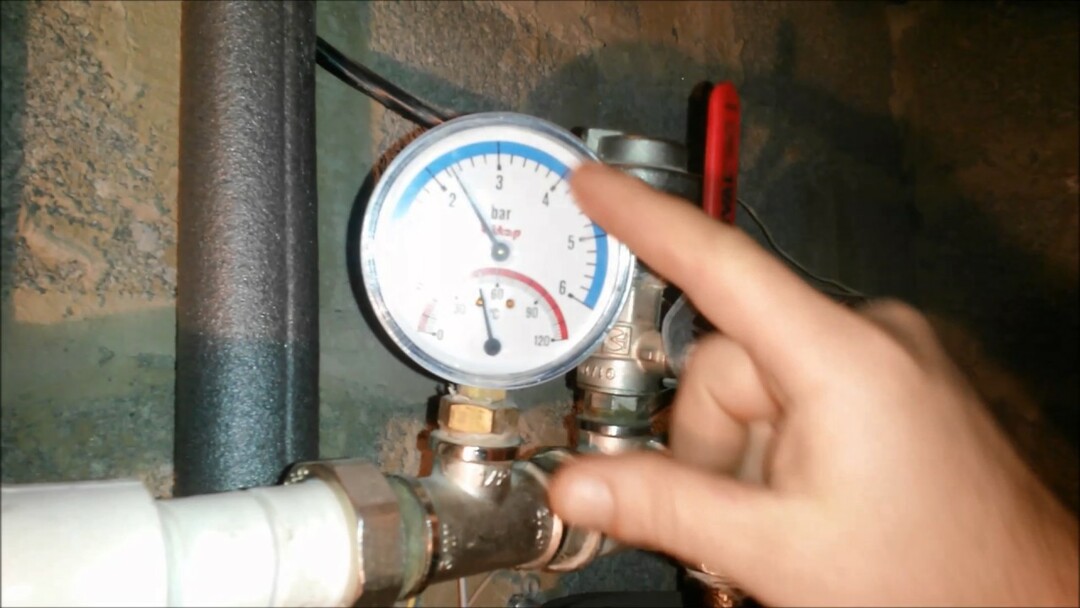

A mandatory element of the heating system is a pressure gauge that measures hydraulic pressure, a pressure drop may indicate a coolant leak
If only a pressure drop indicates a leak, it may not be in the boiler, but in other elements of the heating system, including radiators, which also need to be checked.
It can be done as follows: water is drained from the circuit and air is pumped in with the help of a compressor. It will come out of the leak with a characteristic noise. If pipes are laid under tiles or in concrete floors, you will need to use a phonendoscope to hear the sound of the air coming out. Also in this case, leak detection can be performed using a thermal imager.
What to do with condensation?
A puddle of water under a boiler is not necessarily a sign of a leak. Perhaps this is condensation, that is, water formed during the condensation of steam.
When the boiler is started, air containing moisture enters its combustion chamber. When a gas-air mixture is burned, this moisture turns into hot steam much faster than the heat carrier heats up. The vapors come into contact with the still cold surface of the heat exchanger and settle on it in the form of condensate.
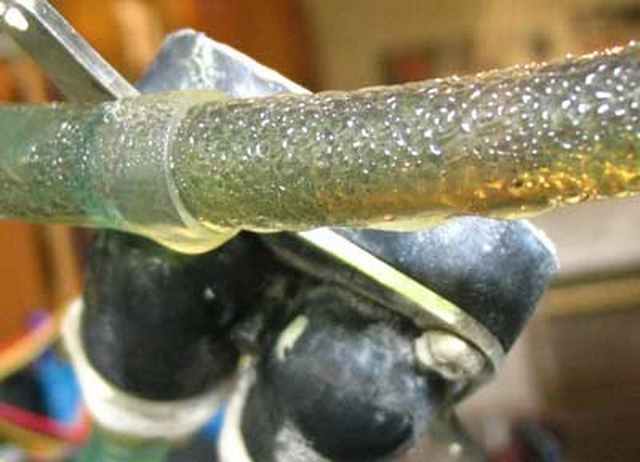

When condensation occurs, the vapor settles on cold surfaces in the form of water droplets, which contain a small percentage of acids that corrode metal surfaces
After heating the coolant to 60-70 degrees, the condensate evaporates. To speed up this process, when starting the boiler, you can set the adjustment knob to the appropriate division, and then, if necessary, reduce the heating to 40-50 degrees.
The formation of condensation with a long-running boiler with a coolant temperature above 60 degrees may indicate an improper organization of the heating system. It is worth checking again whether mistakes were made in the design and installation of the piping.
Don't underestimate the problem condensation, since prolonged exposure to an acidic environment on metal surfaces leads to their corrosion. Wet surfaces attract soot to them, which leads to a deterioration in the thermal conductivity and a decrease in the efficiency of the boiler.
Condensation also settles on the inner surfaces of non-insulated chimneys, which leads to accelerated pollution and wear. Chimney insulation helps to solve the problem.
Does it flow through threaded connections?
The boiler heating circuit is closed. The heated coolant flows from the heat exchanger tube to the supply line and then to the radiators. The coolant returns through the return pipeline, entering the heat exchanger again and then continuing to circulate in a circle.
The heating circuit pipes are connected to the flow and return pipe by means of threaded (detachable) connections using connecting parts - sleeves with union nuts, or otherwise American women.

With the help of American women with union nuts, expansion tanks, shut-off valves and other elements of the heating system are connected to the highways
Threaded connections are sealed with elastic heat-resistant seals in the form of rings. If they are worn out or if installed incorrectly, water leakage occurs. Poorly tightened nuts lead to the same consequences.
If you see water dripping at the threaded connection, you should first try to tighten the nut. Excessive zeal is useless here, since if the nut is tightened too tightly, it can break. If, after tightening the nut, water continues to leak, the seal must be replaced.
Turn off the gas and water supply in advance, drain the water from the heat exchanger. Unscrew the union nut, replace the seals and reinstall the nut.
Manufacturers of heating boilers seal detachable joints with gaskets made of rubber, silicone, paronite or other elastic materials. They are easy to use, durable and always commercially available. Often come complete with clamps. When choosing gaskets, take into account the size of the thread.
You can also use sanitary flax as a sealant. Regardless of the presence of leaks, the seals are changed every time the water lines are disassembled.
Expansion tank problem
The volume of water in the heating circuit varies depending on the heating level. As the temperature rises, the volume of water increases, which entails a change in the hydraulic pressure inside the closed heating system.
At this moment, the elements of the heating circuit would undergo an increased load, fraught with their breakdown. But this does not happen, since the design of the boiler is complemented by a safety system, which includes an expansion tank that receives the resulting excess water.
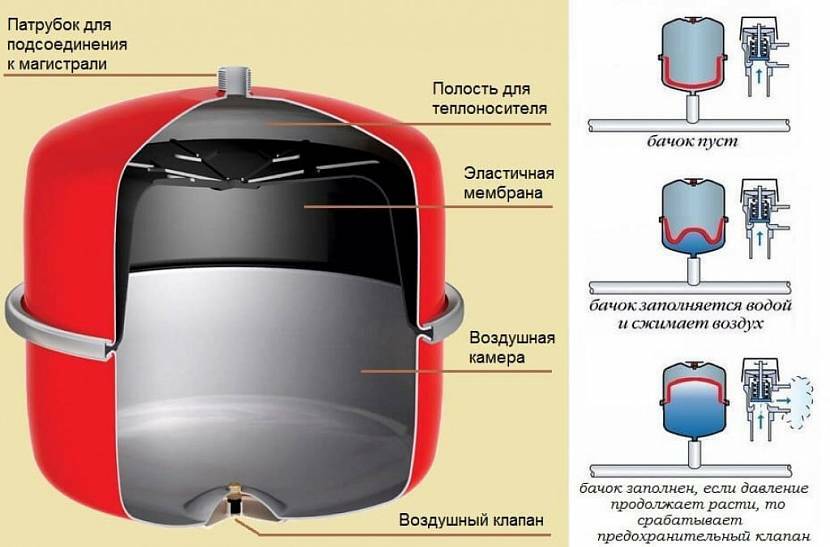
The device and principle of operation of the expansion tank, divided into two chambers by a membrane, the location of the air valve and the branch pipe for connection to the water main
For installation on heating pipelines, open and closed expansion tanks. Open tanks are installed outside boiler rooms, for example, in attics, and are supplied with a whole system of pipes for connecting expansion, circulation, signal, overflow pipes.
All models of wall-mounted, two- and single-circuit boilers are equipped with built-in expansion vessels. They are of a closed type, have only one branch pipe and two internal cavities, separated by a membrane. To ensure regulatory expansion tank pressure, in its upper cavity there is air or an inert gas, for example, argon, and there is an air valve with a nipple.
Excess coolant flows through the pipe into the lower cavity. The membrane bends, air is compressed in the upper cavity, and the coolant occupies part of the internal space of the expansion tank.
The excess coolant generated during heating is discharged safety valve the boiler itself or the heating system. If necessary, the liquid is replenished through the boiler make-up valve.
In open and closed expansion tanks, leaks occur at the threaded joints of the pipes with pipes. To eliminate them, tighten the union nuts or replace the gaskets, as mentioned above.
The metal bodies of the expansion tanks are subject to corrosion due to the presence of oxygen bubbles in the water mass. Corrosion leads to the formation of fistulas (holes), which become the place of leakage of the coolant.
The more often you have to pump a new portion of water into the system, the higher the risk of damage to the expansion tank housing and other metal components. If there are fistulas, the tank is changed to a new one.
Safety valve leaks
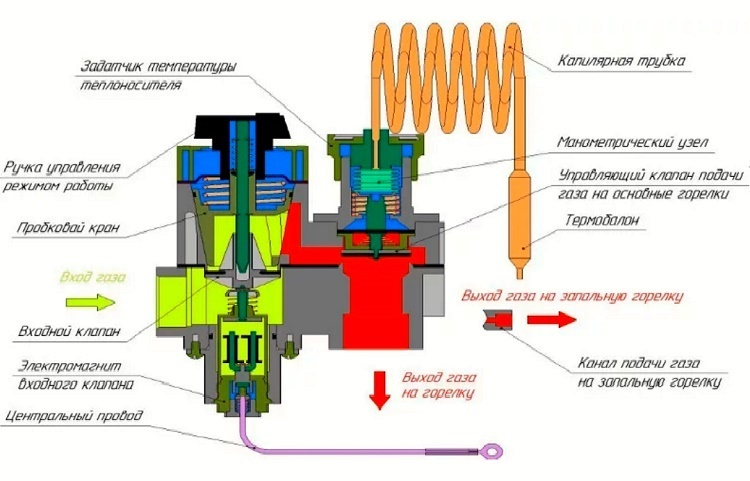
An important element of the safety system is a safety valve, which is necessary to "back up" a closed expansion tank. In boilers for individual heating systems, spring-loaded safety valves are usually installed.
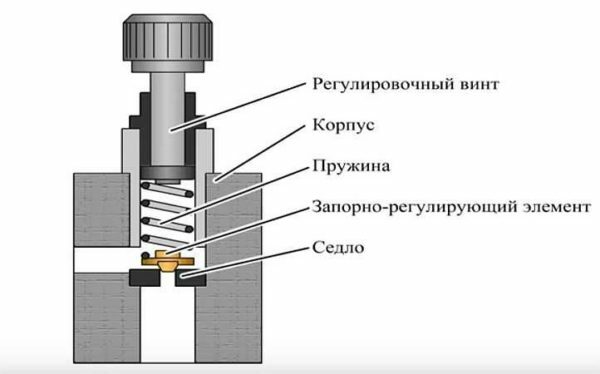
Spring Type Valve Diagram showing major functional parts including down spring, poppet, seat
There is a metal spring in the body of such a valve, which presses on the stem, and this, in turn, holds the support plate in a position when it is tightly pressed against the seat.
If, when the pressure in the heating system rises, the expansion tank for one reason or another does not cope with its functions, the coolant increases the pressure on the plate. The spring at this moment is compressed and lifts the plate over the seat. Through the hole formed, the excess coolant rushes into the drain pipe and further into the sewer.
If the expansion tank is selected incorrectly and its volume is insufficient to accommodate all the incoming water, the membrane may rupture and water will fill the entire upper cavity. With a further increase in pressure, the safety valvethrough which the formed excess coolant is removed.
The safety valve is also triggered if the diaphragm is torn due to wear, when air leaks through a faulty nipple, or if the control automation malfunctions
If the connection of the valve branch pipe to the drain pipe is not tight enough, the coolant will not be in the sewer, but on the floor. To prevent this from happening, during a technical inspection, they pay attention to this area and, in the presence of the slightest leaks, they are sealed.

The safety valve, installed outside the heating boiler, has a similar design and can also leak, requiring urgent repair
Be sure to determine the cause of the valve actuation. If necessary, install a new expansion tank, taking into account the volume of the coolant in the system, change a worn out diaphragm, a faulty nipple or a tank assembly, solve problems with settings and management.
An emergency situation for a heating boiler is standard for the safety valve itself, because it is needed precisely in order to reduce the damage from the consequences of an accident. But the valve can fail itself, causing the coolant to leak.
Most often, a breakdown is associated with a spring that is constantly under stress and eventually loses its elasticity, which leads to leaks even during normal operation of the system. The defective valve is replaced with a new one.
When choosing a valve, its technical parameters are taken into account:
- nominal diameter of the nozzle bore (DN);
- size of the threaded connection;
- response pressure.
Requirements for safety valves for heating systems are regulated by GOST 12.2.085-2002.
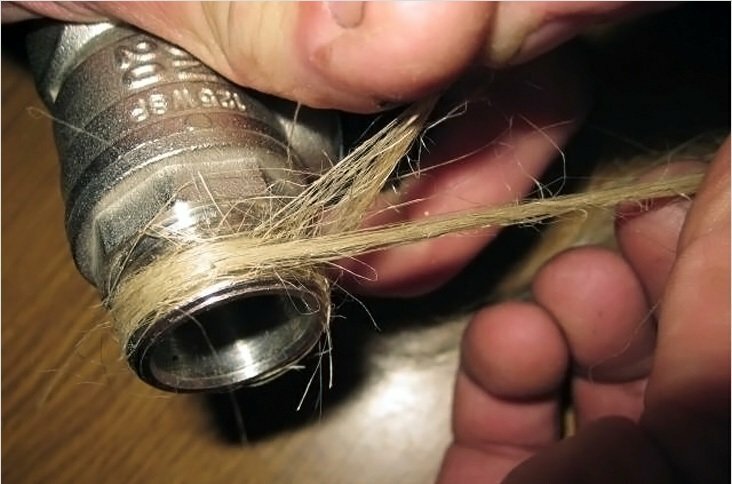

The traditional material for sealing threaded connections is sanitary flax (tow); to increase the reliability and durability of sealing, flax is impregnated with a special compound
But what if the gas boiler is leaking due to the breakage of a recently installed valve? This happens when a grain of debris, such as rust from an expansion tank, gets between the plate and the saddle. In this case, the valve is removed, rinsed under running water and installed in place.
The valve is installed so that the spring is vertical. An arrow is shown on the body indicating the direction of flow of the coolant. Heat-resistant elastic gaskets or sanitary flax are used to seal threaded connections.
Damage to the heat exchanger and pipes
If the heat exchanger of a gas boiler is leaking, the wall may have burnt out, a crack or fistula may have formed. According to the material of manufacture, heat exchangers are divided into copper, steel, cast iron.
Metal cracks are formed by thermal stress and hydraulic pressure. Corrosion processes lead to the formation of fistulas. Repair is carried out by soldering.
The main stages of the process:
- dismantling the heat exchanger;
- cleaning and degreasing the area around the leak;
- soldering using flux and solder;
- trial;
- mounting.
In case of leakage in an easily accessible place, complete dismantling heat exchanger for repair not required. It is enough to remove the casing, shut off the gas and water, turn off the electrical wires, drain the rest of the water.

For soldering, select a solder corresponding to the material of manufacture, for example, for copper heat exchangers copper-phosphorus solder containing silver is suitable; temperature must be observed at the soldering point mode
The soldering point is cleaned and degreased with a solvent. Soldering is carried out using a soldering iron or a gas torch. The heat exchanger is installed in place and communications are connected to it.
The tests are carried out by pressing. The circuit is filled with water, the pressure is increased to the test value and checked with two pressure gauges for at least 5 minutes. If no pressure drop is recorded, no leaks are noticed during visual inspection, the repair can be considered complete.
In case of severe damage, the repair of the heat exchanger is impractical. They just change it to a new one. It is also impossible to solder many Chinese-made heat exchangers, since they are made of thin sheet alloys that cannot withstand soldering.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Methods for sealing threaded connections in individual heating systems using various materials:
Eliminating a leak from an overpressure valve in a double-circuit gas boiler:
In heating boilers, a coolant leak can occur in different sections of the heating and DHW circuits. Replacing the seal on threaded connections is not difficult to do yourself. To eliminate a leak through a heat exchanger fistula, you will need the skills of a plumber and a welder, considerable experience, and tools.
Repair of damaged elements is not always possible, sometimes it is more expedient to replace them. With the prompt elimination of leaks, negative consequences do not occur and the boiler is operated in the same mode.
Please leave comments, ask questions, post photos on the topic of the article in the block below. Tell us if you have had to repair a heating unit, share the technological nuances you know. It is possible that your advice will be very useful to the readers of the site.