In case of any breakdown, most owners of a gas water heater call a specialist service technician. However, services usually come with financial costs, right?
Why not solve a seemingly insignificant problem on your own, having the skills of a mechanic? With a situation where the gas valve on the gas column does not work, you can try to cope on your own. But what is needed for this and where to start?
In this article we will talk about the design features of the gas valve. Let's analyze the main breakdowns leading to the inoperability of the column. For a better understanding of the process of diagnostics and disassembly, we will provide the presented material with visual photographs and a video.
The content of the article:
- Gas column valve device
-
Valve troubleshooting and elimination
- Stage # 1 - simple inspection of electrical components
- Stage # 2 - valve disassembly and testing
- Stage # 3 - checking the electromagnet coil and repairing it
- Stage # 4 - search and elimination of mechanical defects
- Stage # 5 - valve assembly and leak test
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Gas column valve device
In order to make it easier for home craftsmen to restore the operation of a gas boiler, in particular when a malfunction of the gas valve is noted, we will consider the device of the unit and the technical nuances of diagnostics and repair.
But, if you do not have experience in disassembling gas water heaters and the relevant knowledge on the topic, then for repair and maintenance it is preferable to invite a master.
A device called a gas solenoid valve performs an important function of a gas water heater - controlling the flow of the fuel component (natural gas). The picture below shows a common design of the regulation unit, which includes the valve.
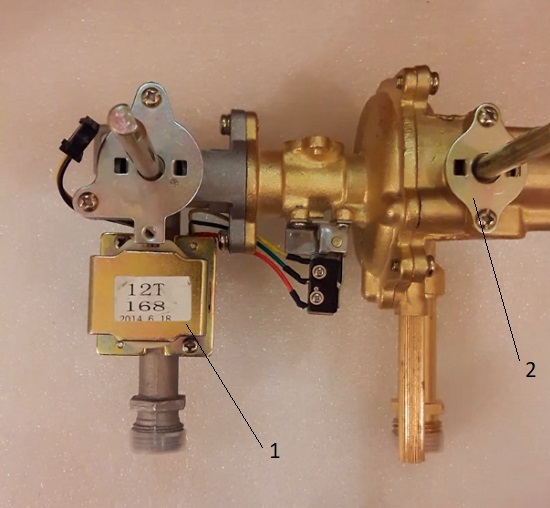
External view of the unit that performs the functions of regulating the gas supply to the gas burner system of the boiler (column). The device includes a solenoid gas valve (1), a manual rod (2)
In fact, the regulation unit is a two-stage mechanism, the first stage of which is the gas solenoid valve (1). The second stage is a mechanical device that provides adjustment by means of a manual control rod (2).
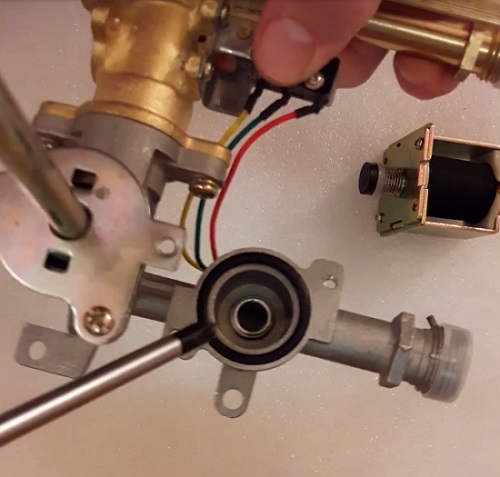
The design of the gas valve is quite simple - it is made on the principle of an electromagnetic traction device, which are used in a wide variety of devices and devices. If you dismantle this component from the circuit of the regulation unit, for which it is enough to unscrew a couple of screws, before the eyes of the master, the valve part will appear, which is fixed on a spring-loaded metal stock.
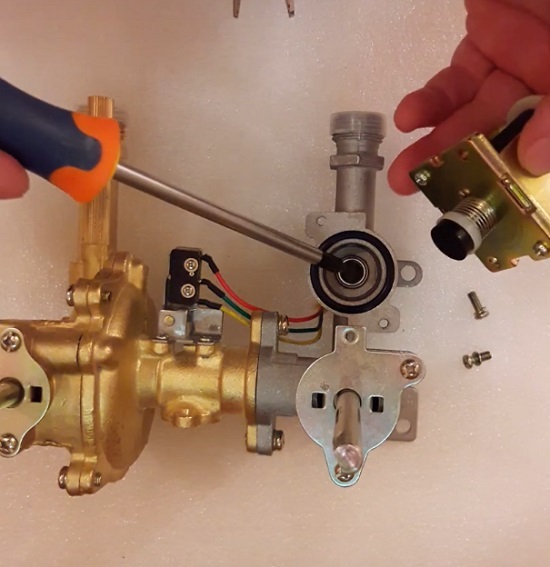
This is how the inside of the device looks like (in fact, the valve itself), after dismantling the gas valve from the composition of the column (boiler) regulation device
As you can see from the picture, the structure consists of body-skirtswhere the valve part is included - membrane and electromagnetic module. The valve part is fixed on a metal stockspring-loaded for return travel to closed position.
When voltage is applied to the coil of the electromagnet, the metal rod magnetically moves upward and pushes the membrane away from the bore of the skirt. This opens the gas passage towards the manual valve and further to the burner.
Valve troubleshooting and elimination
Loss of functionality of the gas valve leads to the complete impossibility of operating the heating equipment, or to a situation where the required heating level is not provided due to incomplete opening the membrane.
On the other hand, there may be reasons that, on the contrary, lead to a constant flow of gas to the boiler burner (column). That is, a situation arises when the gas valve is constantly open.
Stage # 1 - simple inspection of electrical components
It is permissible to test the operability of the gas solenoid valve on the dispenser (boiler) without dismantling the regulation device. However, to perform the test directly on the equipment, it is necessary to ensure that the gas supply is turned off by closing the valve on the line. In this case, the gas water heater (boiler) remains connected to the electrical network.
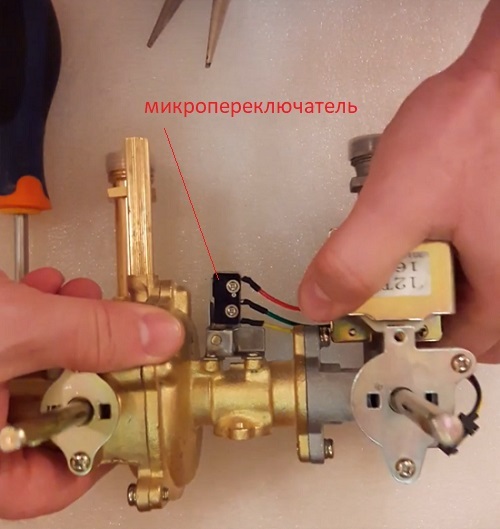
Microswitch installed on the gas flow control device. This circuit component switches the supply voltage to the base elements, including the gas solenoid valve.
The burner gas regulator usually contains an electronic component - a microswitch (see. picture above), through which, when the gas column is turned on, power is supplied to the main technological parts.
In particular, the supply voltage is applied via a micro-switch:
- to the ignition module;
- on the traction turbine fan;
- onto the solenoid valve coil.
So, if forcibly, for example, with a screwdriver blade, act on the pusher plate of the microswitch, these systems of the gas column (boiler) will receive power.
As a result, the following components are activated:
- fan;
- electric lighter;
- solenoid valve.
That is, the inspector will hear the sound of a working fan, the characteristic clicking sounds of a gas lighter, and, of course, the characteristic click of the solenoid valve stem. This state of the equipment demonstrates the health of the components, at least electrical.
Stage # 2 - valve disassembly and testing
Various defects can be the reason for the inoperability of the unit.
Among them:
- violation of the shape of the membrane seal;
- ingress of a foreign object into the skirt body;
- break (wedge) of the return spring;
- breakage of the conductor of the coil of the electromagnet.
The first three defects in the list are found after disassembling the device with a careful examination of the structure and checking the stem for free axial movement.
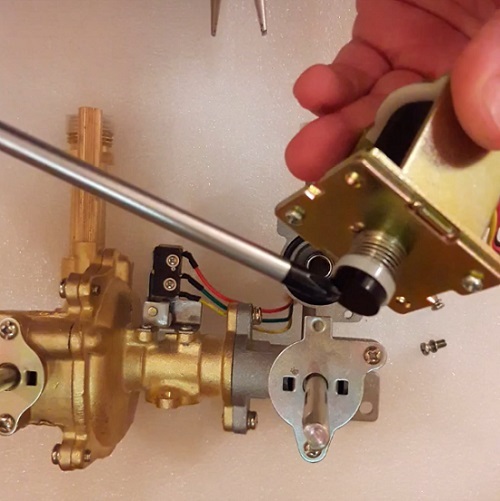
A loose diaphragm seal on the skirt plate and easy stroke are the primary test steps after disassembling the mechanism.
The last item of the list requires a separate approach to testing - break in coil conductor electromagnet. We will talk about the types of breakdowns and methods of their elimination further.
Stage # 3 - checking the electromagnet coil and repairing it
The practice of operating gas water heaters and boilers shows that a defect in an electromagnet coil is not only a break in the winding conductor.
There are frequent cases turn-to-turn closure, which also leads to the loss of the node's performance. How to check the solenoid valve of a household gas water heater at home?
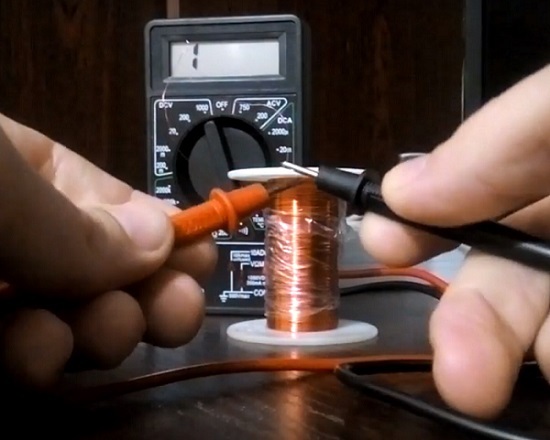

Testing any inductor with a tester is common in repair practice. Accordingly, the coil of the gas solenoid valve is also checked for open or interturn short circuit using this device.
Of course, each individual manufacturer of gas water heaters (boilers) original valve designs are used. Therefore, the resistances of the inductors included in the electromagnet are significantly different.
In general, a certain range of resistances can be noted, typical for such inductors: 1.3 - 7.5 kOhm. Basically, the specific parameter should indicated in the equipment documentation.
Measurement of the inductor is performed traditionally in the resistance measurement mode - by connecting the tester probes to the contacts of the inductor. If the device does not respond to the connection, it is obvious that there is an open circuit.
If the measured resistance parameter differs from that specified in the documentation, most likely there is an interturn short circuit. In either case, the coil should be replaced.
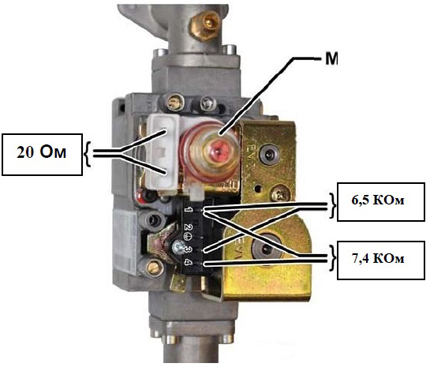
The picture shows the resistance of the working (serviceable) coils of gas valves of Baxi boilers, in particular, devices of the SIT series SIGMA 845078
In practice, replacing the coil, as a separate element of the gas boiler valve, is rare. As a rule, if it is the inductance winding that is faulty, the craftsmen change the complete solenoid valve assembly.
This replacement is due to the complexity of finding a specific component. And the procedure for replacing an individual element itself is more complicated compared to replacing a gas solenoid valve assembly.
Stage # 4 - search and elimination of mechanical defects
As noted above, a solenoid valve for a household gas water heater may become unusable for purely mechanical reasons. For example, the accidental appearance of a foreign element inside the valve threatens to lose the tightness of the diaphragm seal.
To find the cause of the breakdown, the master has to perform a number of steps:
- removal of the gas valve;
- its subsequent disassembly;
- careful check.
These manipulations allow you to detect and eliminate a malfunction associated with the ingress of foreign objects into the working chamber.
Visual inspection of the seat plate surfaces of the valve skirt allows you to find the reasons for insufficient sealing of the seal in the mode of closing the gas flow on the column
Among mechanical defects, a rather frequent moment is elastic membrane defectwhen a violation of the shape or partial destruction of the landing site is noted. Here, in principle, you can get by with the installation of a new membrane on the stem, but traditionally the craftsmen in such cases resort to a complete replacement of the solenoid valve.
A similar situation with the repair of the device when it comes to breakage of the return spring or loss of necessary pressure this element. To replace the spring, you have to completely disassemble the structure.
At the same time, some valve models are assembled using a joint without screws - by riveting or metal clips. Therefore, it is much easier to replace the structure completely than to restore it.
Stage # 5 - valve assembly and leak test
If the repair of the gas solenoid valve was accompanied by disassembly of the mechanical structure, reassembly must be carried out carefully. leak test. You should definitely check gasket integrityinstalled on the upper rim of the skirt, if necessary, replace the gasket.
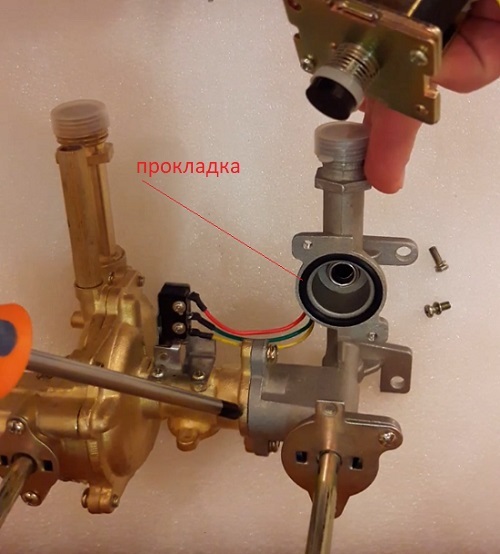

Gasket on the side of the body skirt. Special attention should be paid to this element during the assembly of the structure, since the gasket is often damaged during disassembly.
The assembled unit is checked in a standard (traditional) way with the gas supply turned on. A suitable container is taken, where a little water is poured and soap powder is added. Created thick lather, which is applied to the body of the skirt in the place where the gasket is installed. If the formation of bubbles is not visually observed, then the tightness is within normal limits.
Have you figured out the valve, but are faced with attenuation of the gas column or other problems? We recommend that you familiarize yourself with our other articles, in which we examined the most common breakdowns and how to fix them:
- Why the gas water heater goes out: typical causes and a guide to their elimination
- Gas boiler draft sensor: how it works and how it works + subtleties of checking functionality
- How to replace the gas column membrane: reasons + instructions on how to carry out repairs
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Testing the device in a simple way, filmed on video, demonstrates clearly how this process is carried out. Of course, not for all gas water heaters, without exception, this technique is suitable, but for most of the models the material is quite relevant:
The performance and serviceability test of the solenoid gas valve can be performed by hand or by contacting a specialist. However, it is worth remembering that gas equipment belongs to equipment of an increased level of danger and when handling it, you should adhere to certain rules and regulations. The slightest shortcomings, omissions, ignorance when performing installation (repair) work can lead to serious consequences.
At the same time, contacting specialists negates the risk component. Therefore, without experience in performing repairs and relevant knowledge, it is not recommended to compare monetary costs and personal safety in such matters. Easier and safer is to call the specialized service wizard with which you have contract signed.
Would you like to supplement the above material with useful tips for troubleshooting solenoid valve breakdowns in gas equipment? Or are you engaged in self-diagnosis and disassembly of the unit and want to clarify a couple of nuances? Ask your questions, add unique photos containing an illustrative example, write recommendations in the feedback box below the article.


