It is often necessary to measure the pressure generated by the gas. For example, in cylinders, in gas pipelines, in various containers and vessels. For control and monitoring of indicators, pressure gauges are used to measure gas pressure. These devices serve in various spheres of life, ranging from medicine to heavy industry.
In order for the purchase of the device to be not in vain, and the purchased pressure gauge to meet the requirements of production processes, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the classification. We will introduce you to the varieties of gas pressure meters. Let's talk about their design features and principles of operation.
The content of the article:
- Classification by type of measured pressure
-
Classification according to the principle of operation
- Deformation view of pressure gauges
- Deadweight type of pressure gauges
- Electric Gaseous Medium Meter
- Liquid Measuring Instruments
-
Division by functional purpose
- General purpose pressure gauges
- Group of special pressure gauges
- Reference devices for measuring pressure
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Classification by type of measured pressure
Devices used to obtain data on the parameters of gas pressure in gas tanks, transporting lines, in gas cylinders and other tanks are classified according to several criteria. They differ in their structure and principle of operation.
Devices with which pressure is measured are divided into classes according to:
- type of measured pressure;
- appointment;
- the principle of action;
- accuracy class.
By the type of pressure being measured, devices designed to determine accurate indicators are divided into manometers, vacuum gauges, traction gauges, pressure gauges, barometers and others.
Depending on the degree of protection from the influence of the external environment, the following devices are produced:
- standard;
- protected from dust;
- waterproof;
- protected from aggressive environments;
- explosion-proof.
One product can combine several types of protection.
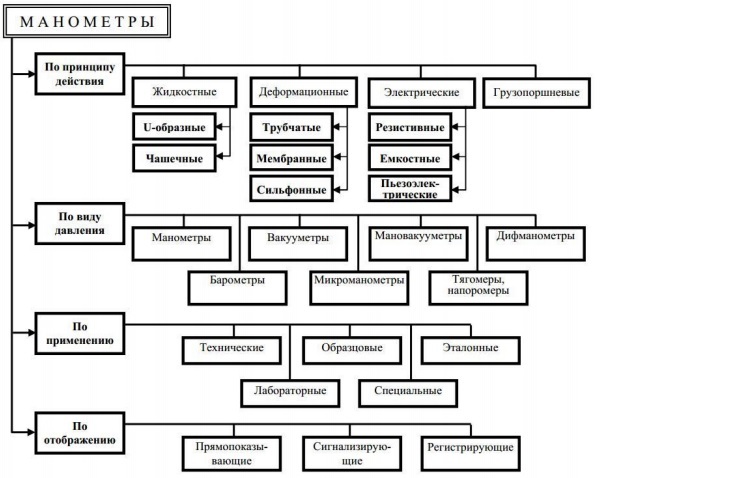
The diagram shows the division of measuring devices by principle of operation, by type of pressure, by application and by display. Liquid and deadweight instruments are rarely used to obtain data on gas pressure.
A pressure gauge is a small instrument used to measure pressure or differential pressure. The principle of operation of this test and measuring device depends on its internal structure. Within one class, they are further subdivided into groups depending on the accuracy class.
To measure the absolute pressure, the indicators of which are counted from absolute zero (vacuum), use absolute manometers. Overpressure is determined with an overpressure gauge. In general, all types of such devices are called with one word: "pressure gauge".
Most types of pressure gauges are designed to measure overpressure values. Their peculiarity is that they show pressure, which represents the difference between absolute and atmospheric.
Vacuum gauges are devices that indicate the pressure of a rarefied gas. Using manovacuum meters, they measure the excess pressure and the pressure of the rarefied gas. Information is displayed on a single scale.
With the help of pressure gauges, parameters of overpressure with values up to 40 kPa are determined. Traction meters, on the other hand, allow you to measure rarefaction up to - 40 kPa. Draft gauges measure rarefaction and excess pressure in the range from - 20 to + 20 kPa.

Pressure gauges are used in a wide variety of industries. Working with gas involves a high risk, therefore it is important to monitor all indicators of the system. Pressure information gives users information about the current state of the measured object
Differential pressure gauges can be used to determine the pressure difference at two arbitrary points to be examined. A micromanometer is a differential pressure gauge that allows you to measure pressure differences within 40 kPa.
Classification according to the principle of operation
Gas pressure gauges, depending on the reading mechanism, are divided into:
- Deformation;
- Electrical;
- Deadweight;
- Liquid.
Each type has its own characteristics.
Deformation view of pressure gauges
The principle and basis of the operation of deformation class devices is that the pressure acts on the sensitive element of the device, which is deformed. The pressure level is determined by the degree of deformation.
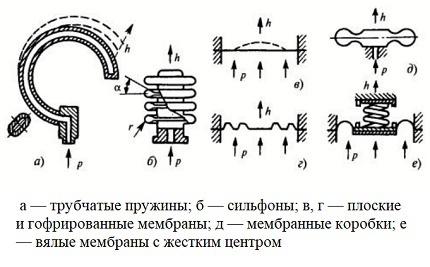
Deformation pressure gauges are produced with tubular-spring, bellows or diaphragm working components with high sensitivity.
The sensing elements in tubular spring devices are tubular springs. These products are tubes bent in a circle with a cross-section oval cross-section. The gas acts on the inner surface of the tube. In the course of this action, the tube is deformed and changes its shape, approaching a round one.
One end of the tube is sealed and movable. The second one is open and fixed by the holders. When the spring tube is bent, the rings are also affected, which then unbend the spring. The sealed end of the spring moves according to the force of the pressure. This movement is transmitted to the measuring scale.
Circular springs are used to measure pressures up to 40 bar. At higher pressures, helical or spiral springs are used that are in the same plane. The error of readings when measuring pressure by this method is from 1 to 4%.
Diaphragm and bellows-type sensing elements effectively measure small values of overpressure and vacuum gauge pressure.
The bellows is manufactured according to the principle of a sanitary bellows hose. It is a thin-walled metal tube made of movable transverse rings. Depending on the material and manufacturing parameters, the bellows can be more or less rigid.

Under the influence of high temperature, plastic deformations accumulate over time, which disturbs the correctness of the readings. In addition, at elevated temperatures and pressure pulsations, the change in the static characteristic is accelerated.
Sensitive membrane elements have the greatest variety. The accuracy class of such devices is never higher than 1.5. Such devices are provided with a protective system. In the event of an overload, the diaphragm rests against a special protective device.
Diaphragm boxes are often installed in devices that measure pressure and vacuum. Pressure gauges, traction gauges and draft gauges with membrane boxes are produced with accuracy classes 1.5; 2.5 and measuring limit up to 25 kPa.
Flat diaphragms have little displacement at the operating point, so they are most often used to convert pressure to force. They are unstable, but they calculate well.
Pleated diaphragms are used in conjunction with similar boxes to improve static performance. The former move better, but are difficult to calculate. The latter are used much more often due to their reduced rigidity.
To measure low pressure values, devices with flaccid membranes are used.
Devices need protection from exposure to high temperature, as it negatively affects the elasticity and sensitivity of the main working elements.
Mechanical indicating pressure gauges
Many tube spring gauges are actually direct conversion devices. This means that the pressure is converted into displacement of the sensing element and the mechanical device in contact with it.
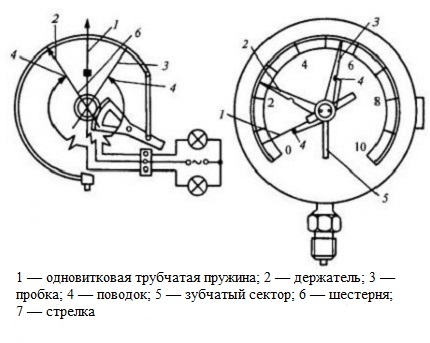
In the diagram, the nozzle is located radially, however, pressure gauges with an axial position of the nozzle are also produced.
Under the influence of pressure, the free end of the spring moves, the leash acts on the toothed sector, the gear and the indicating arrow rotate.
Spring-loaded indicating manometers are manufactured with a measuring range from 0.1 to 103 MPa and have various accuracy classes. Exemplary models are produced with accuracy classes 0.15; 0,25; 0,4. Meters of the working category of increased accuracy - 1 and 0.6. General technical workers - with accuracy classes 1.5; 2,5; 4.
Electrocontact pressure gauges
Structurally, it is a modification of the indicating manometer. The essence of the work is that when the arrow reaches the threshold pressure value, the network closes.
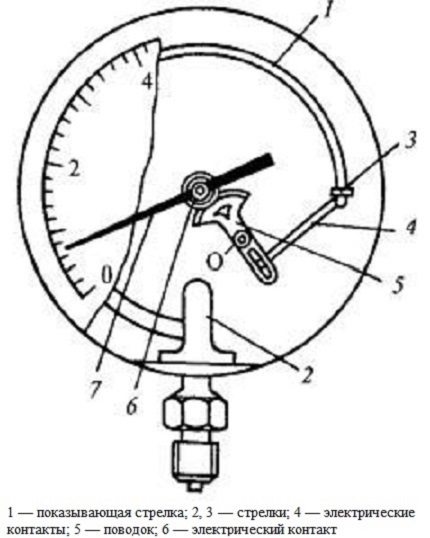
The design of the indicating manometer additionally has built-in arrows with pressed-in electrical contacts, which are located opposite the indicated values
The electrical circuit is closed and an alarm is triggered when the indicating arrow reaches one of the contact arrows. The accuracy class of such pressure gauges is 1.5. The measuring range corresponds to the standard values.
To provide signaling or for the purpose of positional control, a pressure switch with a taxiway marking is used. They measure pressures ranging from 12 to 1600 kPa. The relay is set to the upper and lower activation limits as indicated by the control device and has a breaking capacity of 10 W.
Self-recording models of pressure gauges
The industry produces pressure gauges with a built-in reading system that records the values on a disk chart so that you can then trace the dynamics of the indicators. One revolution can be completed in 8, 12, 24 hours. The movement is driven by an electric motor or clockwork.
The operation of the gauge recorder is based on the transmission of a signal by a large diameter tubular spring, which has a pulling force. It transfers movement from the sensing element to the display system. Devices with the MTS marking record the overpressure values.
Such devices assume control by the operator and have accuracy classes 1; 1,5; 2,5.
Bellows sensitive elements are used in self-recording differential pressure gauges, which can be additionally equipped with an alarm device and a pneumatic transducer. Such devices measure pressure in the range from 6.3 kPa to 0.16 MPa and have accuracy classes 1; 1,5.
Deadweight type of pressure gauges
Such pressure gauges are often used as a standard when verifying other measuring instruments. Their measurement range is very wide. Depending on the design of the device, it can start with serious values of vacuum, and end with redundancy up to 2500 MPa. The accuracy class reaches maximum values up to 0.0015.
Each time the measuring device is exposed to a load in excess of the prescribed norm, it loses in the duration of its service life and in the accuracy of measurements
The principle of operation is to keep the cylinder in the piston in a specific state while the calibration weights act on one side and the measured pressure on the other. Depending on the weight of the loads, the value of the created pressure is judged.
The main working element of the device is the measuring column. Depending on the quality of its production, the accuracy and purity of the compounds, the magnitude of the error also changes.

The smallest measurement error has PMM operating on gas. However, such devices cost many times more due to the peculiarities of their design and the need to filter gas from foreign particles.
Functionally, the deadweight tester consists of a pressure generating device, a measuring system and weights. The device is equipped with a rotary mechanism for increasing and decreasing pressure, as well as a pressure relief valve.
Unsealed piston gauges are widely used. They have a gap between the piston and the cylinder. The reservoir under the piston is filled with oil, which is poured into the gap under pressure and lubricates the rubbing surfaces.
Electric Gaseous Medium Meter
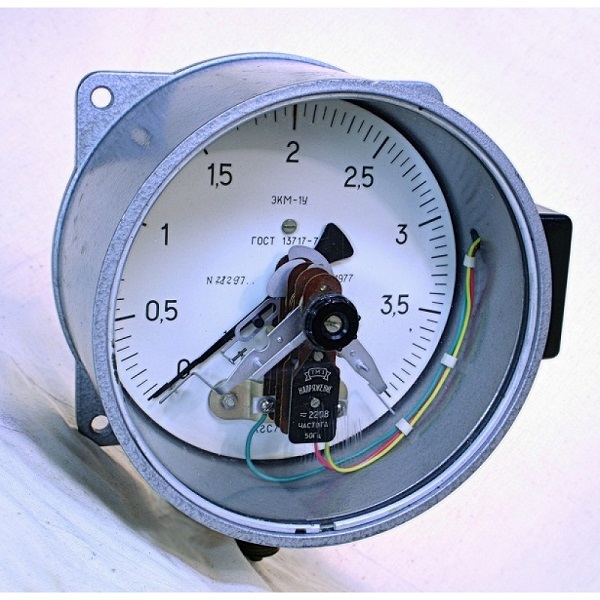
Such pressure gauges are used to convert direct or indirect gas pressure into an electrical parameter. The most common pressure gauges of this type are: strain gages, capacitive and resistance devices. The pressure is measured in the range from 100 Pa to 1000 MPa. The devices are manufactured with accuracy classes from 0.1 to 2.5.
The work of pressure gauges operating on the basis of the tensoresistive effect is to change the value of the resistance of the conductor due to deformation. Measure pressure in the range from 60 to 108 Pa with a minimum error.
The flange mounting of the sensor and the special design of the device allow reading pressure data in especially aggressive media with temperatures up to 300 ° C. They are used to measure pressure in systems with fast processes.
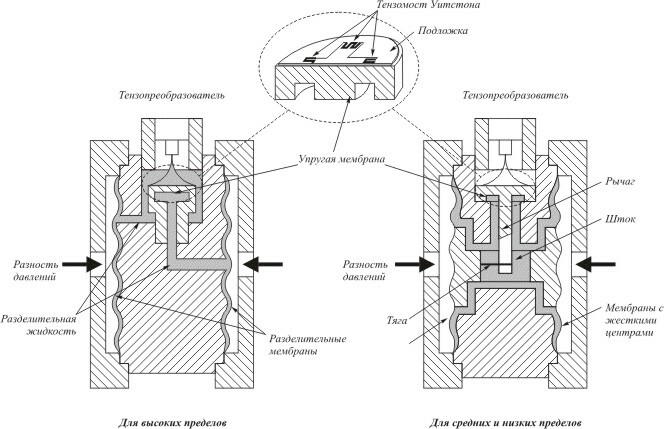
The scheme of operation of resistance manometers is based on the dependence of the resistance of the conductor on pressure. Typically, this type of device is used to measure pressure at an especially high level over 100 MPa.
The sensitive element in such a device is a manganin wire, the resistance of which is easily measured by a balanced bridge.
Capacitive pressure gauges work by applying pressure to a diaphragm, which is a movable electrode. When the diaphragm moves, the transducer capacitance changes. They are characterized by significant temperature errors.
In capacitive pressure gauges, the deflection of the diaphragm is determined by the electrical circuit. Such devices are used in systems with rapid pressure drops.
Liquid Measuring Instruments
Determination of pressure by these devices occurs by balancing the detected pressure with the pressure generated by the liquid column. In this way, you can measure small overpressure, atmospheric pressure, vacuum level, pressure difference.
This group is represented by U-shaped manometers, which consist of communicating vessels, and the pressure is determined by the liquid levels; compensation micromanometers; cup manometers, in which a reservoir is used instead of the second tube; float, bell and ring differential pressure gauges.
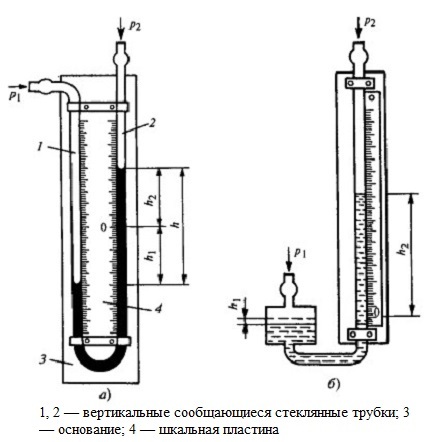
Two-pipe manometers allow the measurement of pressure differences. In this case, pressures are applied to each of the tubes, which must be measured.
In liquid measuring instruments, the working fluid is analogous to the sensing element.
Differential pressure gauges are usually equipped with signaling devices, flow meters, regulators and recording devices. Measurement range from 10 to 105 Pa. The measurement limit changes depending on the liquids filling the device.
Division by functional purpose
By appointment, the following types of pressure gauges are distinguished, used to measure gas pressure:
- general technical;
- reference;
- special.
Consider the features of each type.
General purpose pressure gauges
This type of pressure gauge is produced to measure the values of vacuum and gauge pressure for general technical purposes. Various device modifications allow them to be used in a wide variety of environments. They are used to measure pressure in production directly during technological processes.

The pressure in such devices acts on the inside of the tube and causes the unsecured end to move. It interacts with a mechanism that moves the arrow
These pressure gauges can measure the pressure of gaseous media that are non-aggressive towards copper alloys at operating temperatures up to 150 ° C. Usually, the body of the product is made of steel, and the parts of the movement are made of brass alloy.
General technical pressure gauges for low or high pressure gas are manufactured to withstand vibrations with a frequency in the range of 10 to 55 Hz and a displacement amplitude of a maximum of 0.15 millimeters. They have several accuracy classes from 1 to 2.5.
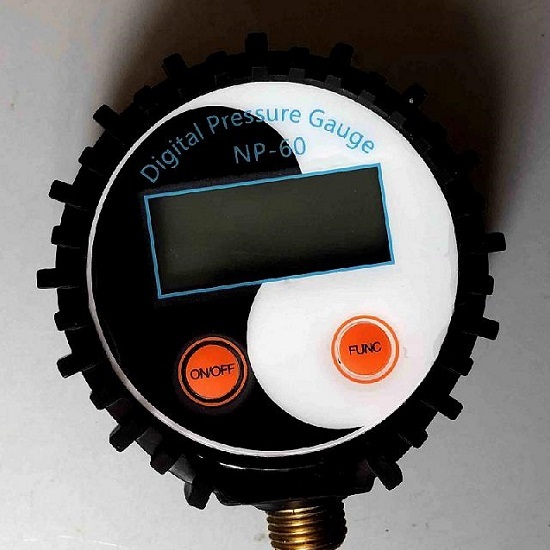

Digital pressure gauges are small in size, characterized by high measurement accuracy and long service life. Moreover, such devices can be calibrated
Gas pressure gauges for general technical purposes with an electronic board, which display the data of the measurements, are gaining popularity. They are often equipped with converters that automate technological processes. The pressure values are displayed on an electronic dial.
Group of special pressure gauges
Such devices are made for a specific type of gas and the environment it creates. For systems with increased pressure, manometers are made for high pressure gas. Some gases are corrosive to certain alloys and therefore require the use of stable materials.
Special pressure gauges are painted in different colors depending on the type of gas.
Propane pressure gauges are painted red, have a steel body, and have the characteristics of general technical pressure gauges. The working pressure of such devices is from 0 to 0.6 MPa. This is the standard propane pressure. Operation in the temperature range from - 50 to + 60 ° С is possible. Working environment temperature up to + 150 ° С. Often included in the package with balloon reducers.
Ammonia pressure gauges in cylinders and other tanks are colored yellow. Multi-stage compression units are equipped with a temperature scale. The gauge components are made of materials that are resistant to ammonia vapors.

In the presence of serious dynamic loads, manometers are filled with glycerin or silicone
The acetylene gauge turns white. Manufactured as a safety system pressure gauge from fat-free materials. Used to measure gauge pressure in various distribution and generation of acetylene systems. The body is made of steel, the internal components are made of brass alloy. The range of permissible temperatures is from - 40 to + 70 ° С.
The hydrogen pressure gauge turns dark green. The pressure gauge for other combustible gases is colored red. The measuring device for non-combustible mixtures is painted black. The oxygen gauge is colored blue.
Reference devices for measuring pressure
This type of pressure gauge is intended for checking, calibrating and adjusting other instruments in order to ensure the highest possible measurement accuracy. Such devices are distinguished by a higher accuracy class in comparison with general technical ones. Working standards are divided into three categories.
Test gauges used to check the accuracy of meter readings at the installation site are also called high precision gauges. Working range of measurement from 0-0.6 to 0-1600 bar for gaseous media.
Pressure gauges for conventional and composite gas cylinders must go through the verification procedure at least once a year, unless other terms are indicated in the documents for the device. Verification is carried out by accredited metrological organizations with the status of legal entities. After verification, a certificate is issued and a stamp is put.

The device must be removed from the cylinder and taken to the metrological service. There, verifiers and calibrators, using a set of standards and auxiliary instruments, will carry out verification for about 10 days.
The gears in the reference gauges are processed with an increased gearing frequency. They are characterized by minimal friction in the switch mechanism, as well as high sensitivity of the internal elements.
Exemplary pressure gauges, with an accuracy class of 0.4 have a scale of 250 units, with an accuracy class of 0.15 or 0.25 have a scale of 400 units with a graduation of 1 unit. Operation of the device is possible at different temperatures, depending on the filler of the case. The ideal operating temperature is 20 ° C.
He will acquaint you with the specifics of refueling gas cylinders next article. It is worth reading it to all owners of suburban property that are not connected to a centralized gas supply.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The principle of operation of the spring pressure gauge:
Characteristics and scope of application of the pressure gauge:
Pressure gauges are produced for various tasks. The most popular are general technical types used in small industries, by various firms when working with gas equipment and systems. Electrical contact pressure gauges are devices that signal when a critical value is reached.
For checking and adjusting the manometers, reference manometers are used. Special manometers are made to measure the pressure of a specific gaseous medium. Among them, propane pressure gauges are very popular, which are often installed complete with a reducer on gas cylinders.
Do you want to share useful information on the topic of the article, ask a question or post a photo? Please leave your comments in the form below. Share useful information and recommendations that may be useful to site visitors.


