The refrigerator does not turn on, and you need to find out the cause of the breakdown? Are you choosing a new unit and want to understand the difference in the principle of operation of different models? The electrical circuit of the refrigerator, which reflects the interaction of its main components, will help in this.
Understanding the principle of operation, you can avoid cheating the craftsmen or repair the refrigerator yourself, as well as reduce the risk of breakdowns and increase the working life of the device. In this article, we will consider diagrams of devices of various types: single-chamber and 2-3-chamber, with and without the NoFrost system, two-compressor, with mechanical and electronic control.
The content of the article:
- Schematic diagram of the refrigerator device
- Two-chamber and two-compressor models
- Three-chamber refrigerators and zero temperature zone
- No Frost system and self-defrosting
- Smart refrigerators with electronic control
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Schematic diagram of the refrigerator device
Even 30 - 40 years ago, household refrigerators had a rather simple structure: the motor-compressor was started and turned off by 2 - 4 devices, there was no question of using electronic control boards.
Modern models have many additional options, but the principle of operation as a whole remains unchanged.
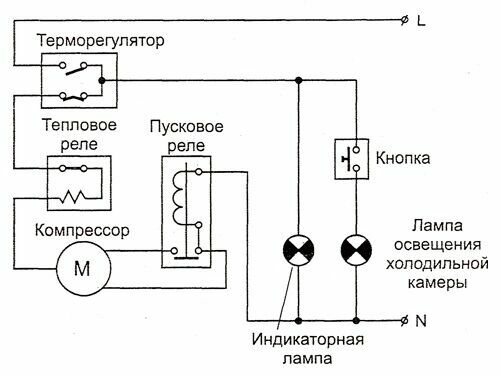
In older refrigerators, all additional equipment comes down to a power indicator and a light bulb in the refrigerator compartment, which is turned off by a button when the door is closed
thermostat - the main and only control with which the user can adjust the operation of the old refrigerator is usually located inside the refrigerator compartment. The bellows spring is hidden under the power lever - a rotating handle. It contracts when the chamber is cold, thereby opening the electrical circuit and turning off the compressor.
As soon as the temperature rises, the spring straightens and closes the circuit again. The handle with indicators of the freezing force of the refrigerator regulates the allowable temperature range: the maximum at which the compressor starts and the minimum at which cooling is suspended.
Thermal relay performs a protective function: it controls the temperature of the engine, therefore it is located directly next to it, often combined with a starting relay. If the permissible values \u200b\u200bare exceeded, and this can be 80 degrees or more, the bimetallic plate in the relay bends and breaks the contact.
The motor will not receive power until it cools down. This protects against both compressor failure due to overheating and a fire in the house.
motor-compressor has 2 windings: working and starting. The voltage to the working winding is supplied directly after all previous relays, but this is not enough to start. When the voltage on the working winding rises, the starting relay is activated. It gives an impulse to the starting winding, and the rotor begins to rotate. As a result, the piston compresses and pushes through the system freon.

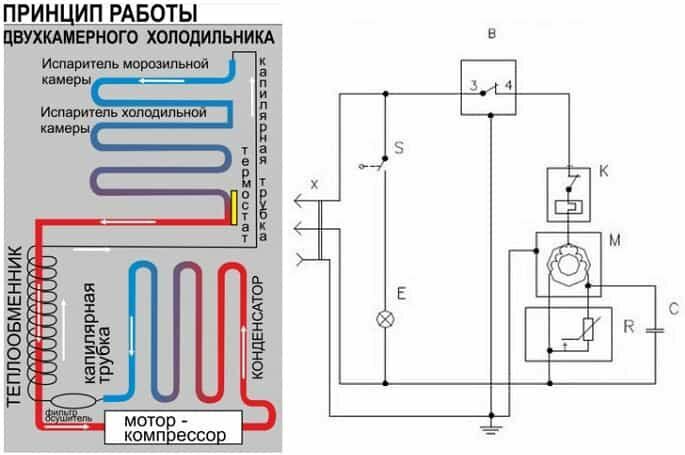
The motor-compressor compresses and pumps freon through the tubes of the system, which ensures the transfer of heat from the refrigerator chambers to the outside, cooling the products
Generally refrigerator cycle can be described as follows:
- Connecting to the network. The temperature in the chamber is high, the thermostat contacts are closed, the motor starts.
- Freon in the compressor is compressed, its temperature rises.
- The refrigerant is pushed into the condenser coil located behind the back or in the refrigerator tray. There it cools, gives off heat to the air and turns into a liquid state.
- Through the dryer, freon enters a thin capillary tube.
- Getting into the evaporator located inside the refrigerator chamber, the refrigerant expands dramatically due to an increase in the diameter of the tubes and the transition to a gaseous state. The resulting gas has a temperature below -15 degrees, absorbs heat from the refrigerator chambers.
- Slightly heated freon enters the compressor, and everything starts anew.
- After some time, the temperature inside the refrigerator reaches the set values, the thermostat contacts open, the motor and freon movement stop.
- Under the influence of the temperature in the room, from new warm products in the chamber and opening the door, the temperature in the chamber rises, the thermostat closes the contacts and a new cooling cycle begins.
This diagram exactly describes the operation of old single-chamber refrigerators, in which there is one evaporator.
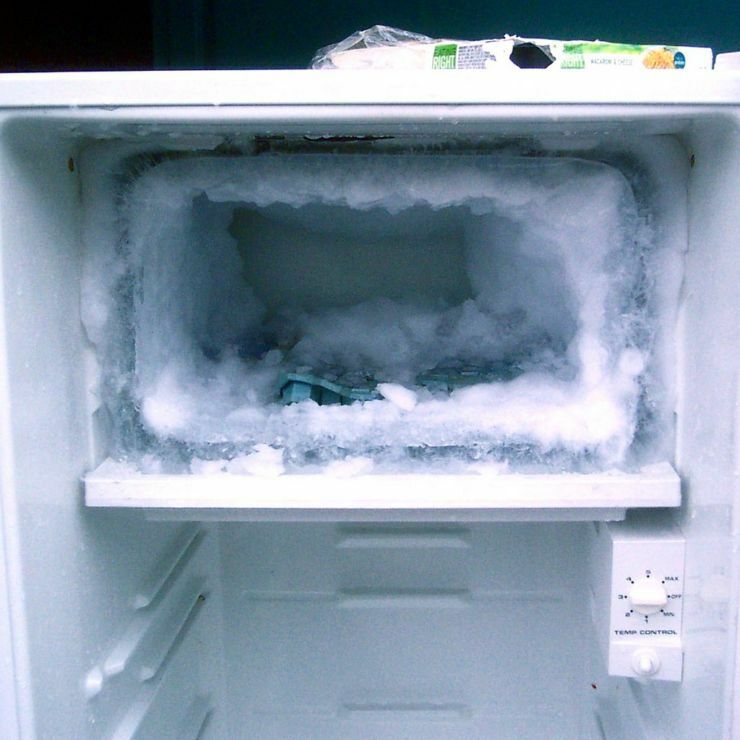

Single-chamber refrigerators have a small freezer, not separated by thermal insulation from the main one, with one door. Food in the front of the freezer may thaw
As a rule, the evaporator is the freezer housing at the top of the unit, not isolated from the refrigerator compartment. We will consider the differences in the device of other models below.
Two-chamber and two-compressor models
In most of the available two-chamber models, there is a common freon circuit: after passing through the evaporator of the freezer, the refrigerant is sent to the main chamber, and only from there to compressor.
The temperature difference is achieved by a significant difference in the length of the coil, which could not be reflected in the diagram: in in the freezer, it completely covers 4 faces, and in the positive temperature compartment, it covers only a small part of the back walls
The motor is turned off by a signal from a thermal relay located in the main chamber; the general electrical circuit does not differ from single-chamber models.
IN Refrigerators No Frost this system is often implemented by one common evaporator located in the partition wall between the chambers. The temperature difference is regulated by turbines and the number of air ducts, we will talk more about such models and their electrics later.
Two-compressor models allow you to independently control the temperature in each chamber. In fact, these are two separate, independent devices in one housing - accordingly, the electrical circuit is completely duplicated: a separate thermostat for each chamber, a separate start protection relay for each compressor.
Independent temperature control in each chamber is also possible with one compressor, with a two-circuit system. It can be implemented in various ways: with the advantage of freezing or completely independent circuits.
In the first case, the thermostat of the refrigerating chamber, when the set temperature is reached, closes the valve, and freon begins to circulate in a small circle - only through the freezer. The compressor stops when the freezer thermostat contacts open.
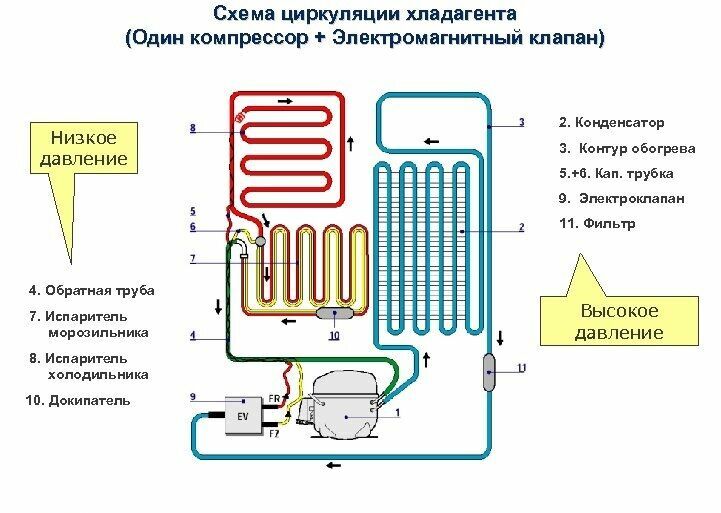
The two-circuit system allows for independent regulation of the temperature of the chambers without increasing energy consumption and noise level, other things being equal, it is cheaper than two-compressor models
In the second version, freon has the ability to circulate through any one of the circuits or both at once, and this process is regulated by the opening and closing of certain valves at the signal of the electronic board management.
Three-chamber refrigerators and zero temperature zone
Fresh meat, poultry and fish are not stored for long in the main compartment of the refrigerator, and when frozen, they lose some of their useful properties, taste and aroma. They often have a separate box with a temperature close to zero, or even a separate chamber.
The temperature in the freshness zone is most accurately maintained under the following conditions:
- a separate chamber with its own evaporator and thermistor, a two- or three-circuit freon circulation system. The option is quite expensive and bulky, but the volume of the chamber is significant;
- an insulated compartment in the main chamber of the refrigerator with a No Frost system, equipped with additional manually adjustable air ducts from the evaporator and a thermometer. Temperature accuracy depends on the timeliness of manual adjustment;
- similar to the previous version, in which the air dampers are controlled by an electronic unit.
An alternative option is cooling from the “weeping” evaporator of the main chamber.

The freshness zone is most often located between the freezer and refrigerator compartments, it is cooled by an additional air flow from the first
As you can see, the zero zone can be implemented in refrigerators with different electrical circuits to ensure it work, a thermostat or thermistor can be additionally included, as well as an expanded electronic circuit board. management.
No Frost system and self-defrosting
The refrigerators described above have a drip defrost system. This means that the “weeping” evaporator is installed in the refrigerating chamber: during the idle period of the compressor, frost melts on it naturally, because the temperature in the chamber is positive.
The resulting water flows down special gutters through a tube into a container located above or near the motor. Later, the running motor becomes very hot, and the water evaporates. A freezer with such a system never thaws on its own, moreover, frost forms not only on the walls of the chamber, but also on the products.
Refrigerators No Frost do not need to be defrosted, you will not see frost in their chambers, even in the freezer. A characteristic feature of such models is the presence of a fan that distributes cold air from the evaporator to the chambers.

No Frost refrigerators have standard start and protection relays, an advanced thermal relay, as well as a fan and heating elements for automatic defrost
The cooling coil itself in such models does not look like the usual solid metal plate, but like a car radiator or condenser coil at the back of old refrigerators.
In the general scheme of operation of the refrigerator, the new elements behave as follows:
- the fan or turbine starts together with the compressor and evenly distributes cold air throughout the chambers;
- when the thermal relay opens the contacts that feed the engine due to reaching the set temperature, the fan is also turned off at the same time;
- every 8 - 16 hours the thermostat turns on the heating element. This is an electrical mat or wire that heats the evaporator coil to defrost it. Warm air does not enter the refrigerator chambers, since the evaporator is hidden and the fan is turned off;
- when all the frost has thawed, the temperature compensation switch turns off the heating;
- in addition, the thermostat can control a damper that regulates the supply of cold air to the main chamber through the channels.
The defrosting of such refrigerators is similar to a “weeping” evaporator in only one way: the resulting water also flows through the channels into a container near the motor.
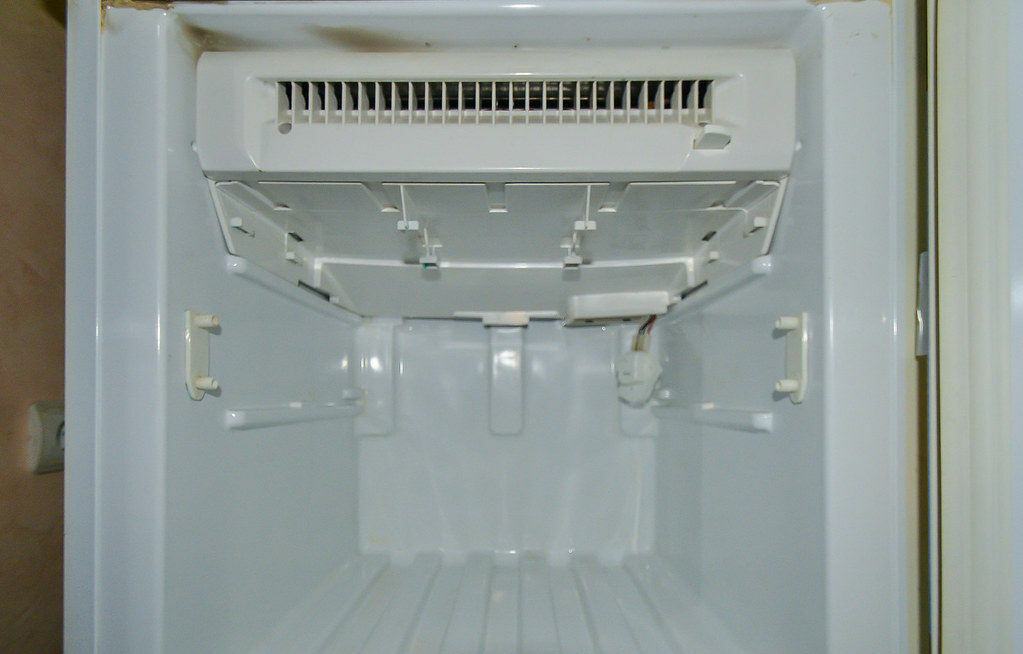

The evaporator and fan can be hidden in the partition between the chambers, and a different number of air ducts and movable dampers in them are used to control the temperature.
The scheme described above is the most primitive. Most modern models are controlled centrally, from an electronic board.
The main disadvantage of No Frost refrigerators is the drying out of products due to constant air circulation. Everything has to be stored in containers with tight lids or wrapped in foil.
The original solution to the problem offers Electrolux V Frost Free system. In these units, the freezer works according to the No Frost system, and a classic, “weeping” evaporator is installed in the positive temperature chamber. The electrical circuit is generally identical to the standard "frost-free" systems.
Smart refrigerators with electronic control
Classic thermostats, with a mechanical rotary knob and a bellows inside, are becoming increasingly rare in modern refrigerators. They are giving way to electronic boards capable of managing an ever-increasing variety of operating modes and additional options for the refrigerator.
The function of determining the temperature instead of the bellows is performed by sensors - thermistors. They are much more accurate and compact, often installed not only in each compartment of the refrigerator, but also on the evaporator body, in the ice maker and outside the refrigerator.
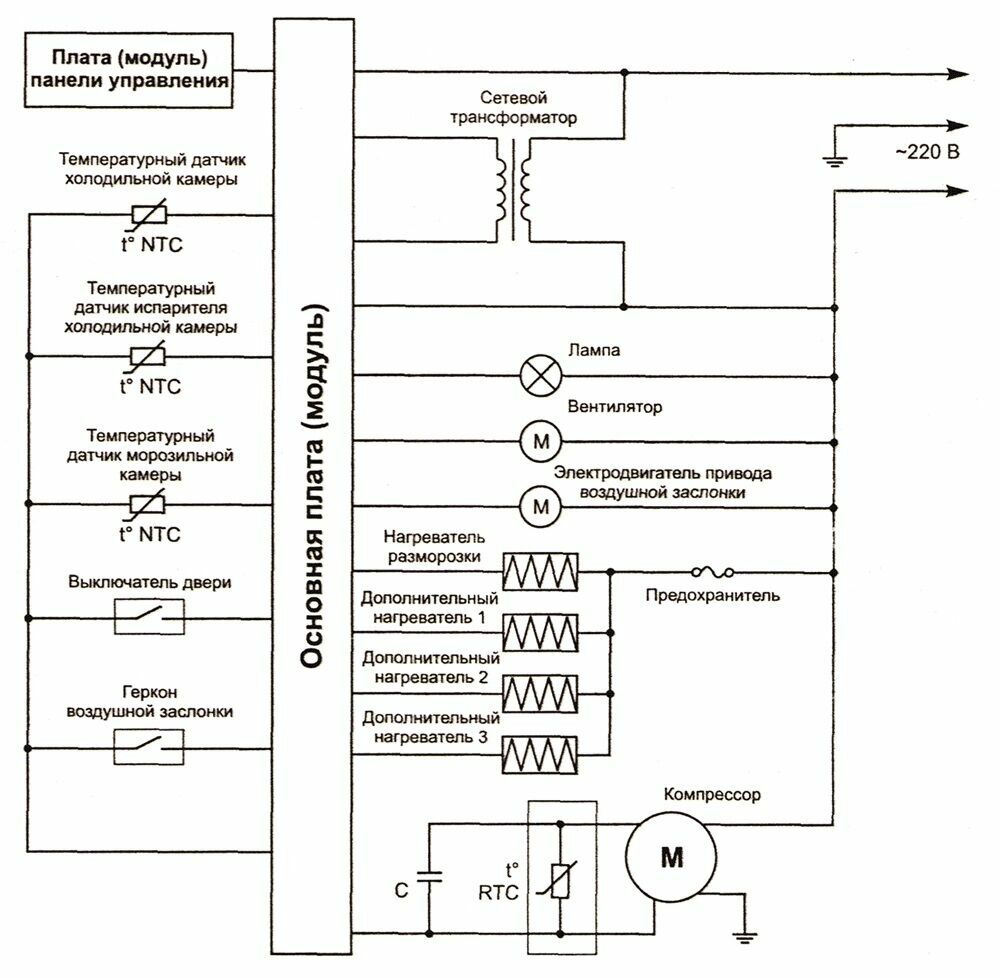
Many modern refrigerators have an electric air damper, which makes the No Frost system as efficient, convenient and accurate as possible.
Control electronics of many refrigerators performed on two boards. One can be called user: it is used to enter settings and display the current state. The second one is system, through the microprocessor it controls all the devices of the refrigerator to implement the given program.
A separate electronic module allows the use in refrigerators inverter motor.
Such motors do not alternate cycles of operation at maximum power and idle time, as usual, but only change the number of revolutions per minute, depending on the required power. As a result, the temperature in the refrigerator chambers is constant, energy consumption is reduced, and the compressor life is increased.
The use of electronic control boards incredibly expands the functionality of refrigerators.
Modern models can be equipped with:
- control panel with or without a display, with the ability to select and set the operating mode;
- many NTC temperature sensors;
- FAN fans;
- additional electric motors M - for example, for crushing ice in an ice generator;
- heaters HEATER for defrost systems, home bar, etc.;
- solenoid valves VALVE - for example, in the cooler;
- S/W switches to control the closing of the door, the inclusion of additional devices;
- Wi-Fi adapter and remote control.
The electrical circuits of such devices are also repairable: even in the most complex system, a failed temperature sensor or similar trifle often becomes the cause of a malfunction.
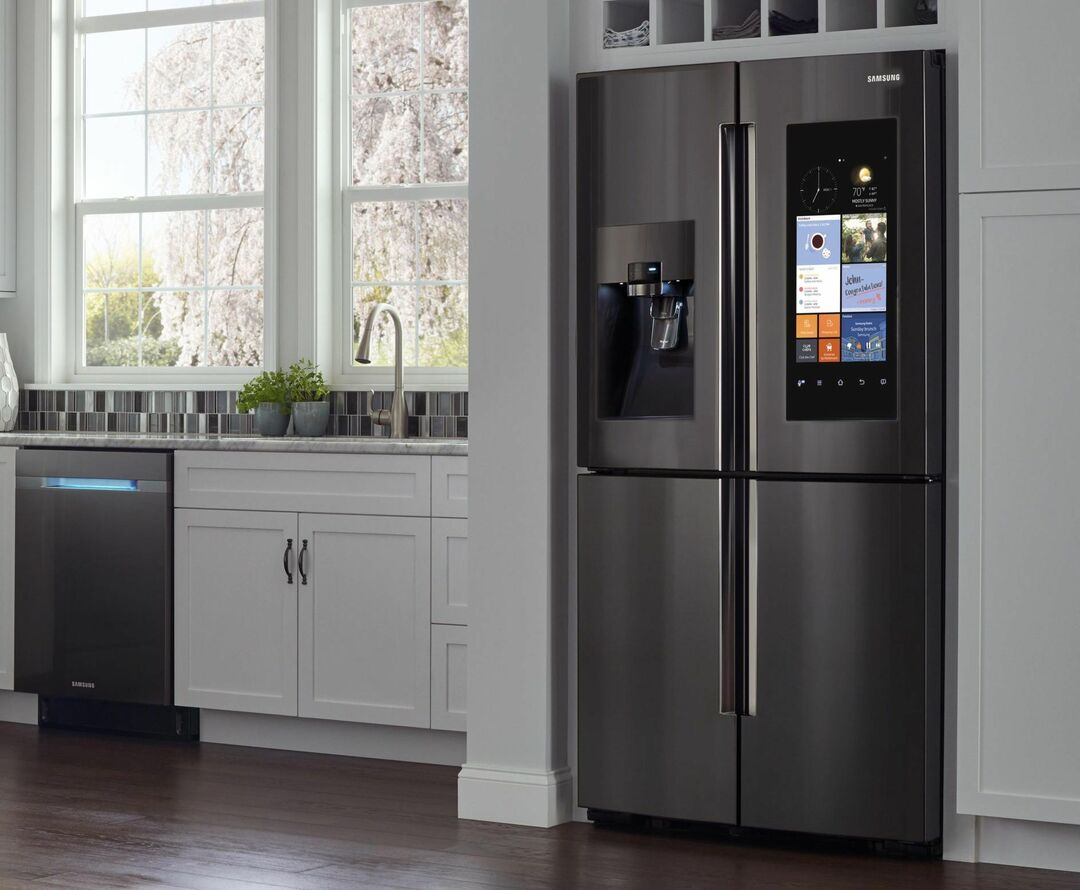

Side-by-side refrigerators with touch screen controls, ice maker, built-in cooler and many customization options are controlled by a rather extensive and complex electronic board
If the refrigerator is “buggy” and refuses to correctly execute the specified program, or not at all turns on, most likely the problem concerns the board or the compressor, it is better to entrust the repair specialist.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
How the compressor of a domestic refrigerator is arranged and works is clearly and in detail described in this video:
And here at the stand they assemble and connect all the elements of the electrical circuit of the No Frost refrigerator:
The whole variety of modern household refrigerators comes down to one circuit diagram, improved and supplemented by various components. No matter how different the latest Indesit model is from the old Minsk, they produce cold according to the same principle.
The electrical circuits of budget and old refrigerators are quite amenable to home repairs according to a typical scheme, while electronic control boards differ for each series. But even they have a similar general structure.
Which refrigerator do you prefer? Were you able to learn something new, interesting and useful from this article? Share your opinion, experience and knowledge in the comments below.


