The welding machine is popular among residents of private homes and specialized workers. The first one always needs to cook something, but there is no knowledge. This article is for them, because you don’t want to call the masters every time for a considerable amount. Therefore, below we will analyze how to use a welding inverter correctly, what a welding inverter is, how it works, how a seam is obtained during welding, how to weld metal with inverter welding.
Why inverter? This is the best welding for private traders. The inverters are high-power, light/space-saving, efficient, generate direct current, easy to transport, inexpensive. A good inverter will cost you 7-10 thousand rubles.

The content of the article
- Inverter - what is it. How an inverter welding machine works
- What is an inverter made of? What does an inverter welder look like.
- How to cook with an inverter. Tips for beginner welders. How welding takes place. What is an electrode made of?
Inverter - what is it. How an inverter welding machine works
An inverter is a type of welding machine used in everyday life and industry by professionals. Its task is to connect / weld metal surfaces / workpieces. This happens by heating them with a large current.
The inverter consists of a transformer, a rectifier, connecting cables, adjustment elements, a housing, and a working handle.
AC voltage from the network enters the inverter, from there it enters the transformer. There the voltage is reduced. With the help of the control panel, you can adjust the variable voltage. Next, the current enters the rectifier, where it passes through the transistors and becomes constant. Direct current is supplied through the cables to the working handle. An electrode is inserted into the pen. The mass is combined with the cleaned metal surface. This is how a circuit is created - from the mass through the inverter to the electrode of the working part. When the circuit is closed, an electric arc with a large current is formed. This arc heats up the air and metal next to it. This melts the workpiece and the electrode. The fused metals mix and cool, forming a seam - the surfaces of the metals are connected.
Inverter welders operate on a mains voltage of 220 volts. There is specialized equipment that operates on 380 volts.
In addition to the main advantages of inverters (size, dimensions, power), it can be noted that inverters do not drop voltage in the network. During operation of some welding machines, the voltage in the network may decrease - sufficient voltage will not reach electrical appliances. Because of this, they may not work correctly / not work. Inverter welding can also work at low voltage - household models turn on at 180 volts, professional ones - depending on the model. This is a plus for rural residents. Reduced mains voltage in the villages does not surprise anyone, for some this is the norm.
Welders say that inverters are popular because of their advantages, one of which is the arc. It is softer, easier to control, so welders learn to work on inverters first.
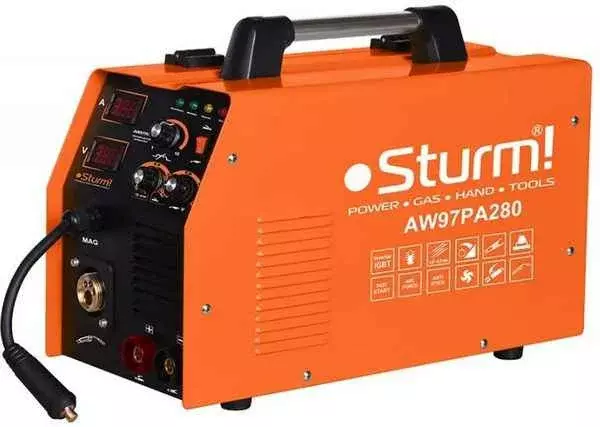
What is an inverter made of? What does an inverter welder look like.
Welding is a small box of sheet metal. It has ventilation holes, a control panel with overheating protection indicators, networks, regulators, two connectors for working welding cables, one connector for welding power.
Internally, the inverter consists of a rectifier, a DC bus, the inverter itself, and connecting cables.
This design weighs up to 7 kilograms (household models). Professional ones weigh more. To make it convenient to carry / use the tool, it always has a handle / carrying strap.
When choosing an inverter, consider the length and flexibility of the cables - the longer and more flexible they are, the more convenient it is to use the device. But flexible cables are not equipped with high-power inverters.
How to cook with an inverter. Tips for beginner welders. How welding takes place. What is an electrode made of?
The general concept of welding of all types is that they create a circuit that is completed by the metal being processed and the electrode / wire. The circuit is obtained from the electricity of the network, its voltage decreases, the current increases. When the circuit closes, an arc is formed. It melts the metal rod in the electrode and the metal of the part.
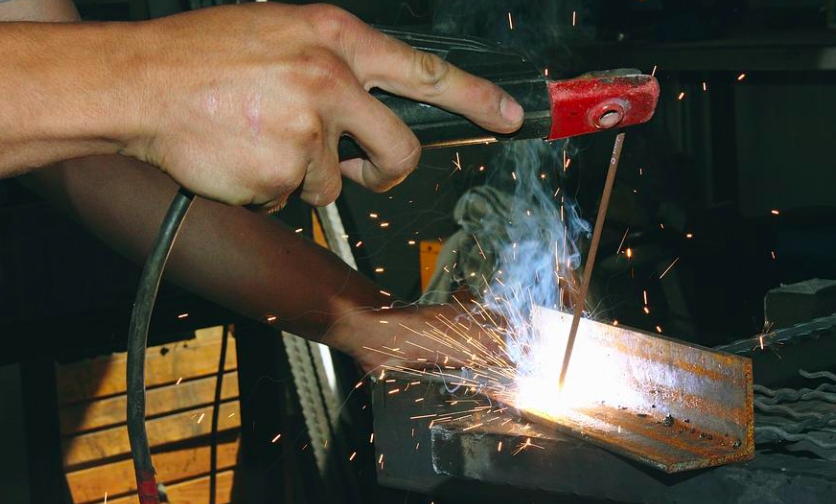

There are two welding methods:
- connect the mass to the plus, and the electrode to the minus;
- ground to minus, electrode to plus.
They are called, respectively, direct and reverse. What is the reason for this division? The thickness of the welded metal. The reverse method is used for welding thin sheets, the direct method is used for metals from 3 millimeters. Why? The object connected to the positive output heats up more. If you connect sheet metal to the plus, it will overheat, melt, melt, so an electrode is connected to the positive output. Thick metal tolerates high temperatures, so a mass is connected to it from the positive output.
The electrode consists of a coating and a metal rod. During welding, the surface of the part, the electrode rod and the coating melt. The coating passes into a liquid form, partially into a gaseous form and evaporates. The liquid coating covers the molten metal, creating a protective environment and a weld pool. A bath is a mixture of molten metals that cool down and form a seam. The protective environment does not allow the metal to come into contact with air, so it will not oxidize. As the joint cools, the protective fluid/molten wash cools down as well. This is the slag that remains after welding.
Before using the welding inverter, inspect, check it and the mains voltage. Connect the device to the mains. Let him warm up. Choose a welding method depending on the thickness of your metal. Connect appropriate cables to the outputs. Insert the electrode into the handle. Clean places on welded metal for mass and welding. Connect ground. Hard-to-reach places are cooked at a right angle. By tilting the handle with the electrode 30-60 degrees towards you and moving it forward (away from you), you can cook horizontal and vertical surfaces. Similarly, tilting the handle with the electrode, but leading it towards you (back), make connections in the corners / at the joints.
During welding, you need to write out figures with an electrode in order to expand the seam, to make it more reliable. The main figures written out by the electrode are circles, triangles, lightning, zigzags.
Depending on your welding duty cycle, take breaks to allow the inverter to cool down. PV - duration of inclusion. This is an indicator of how much welding can work. That is, if the PV is 50%, then in a conditional 10 minutes the device can work / cook for 5 minutes. The remaining 5 minutes it will cool. There are models of inverter welding that can work continuously - the duty cycle is 100%.